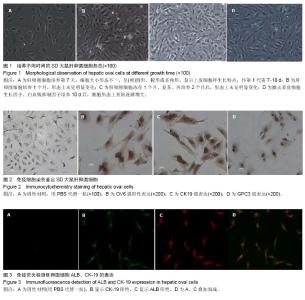
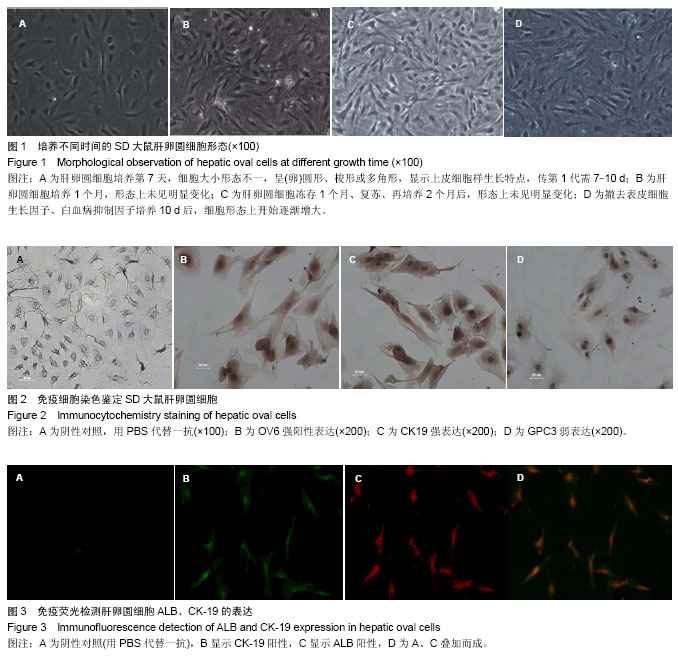
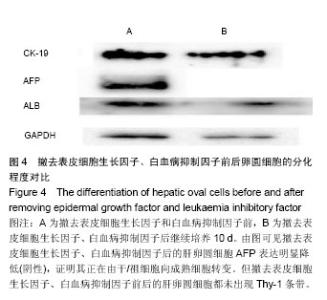
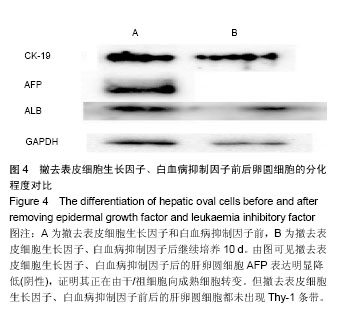
| [1] Poon D, Anderson BO, Chen LT,et al. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia: consensus statement from the Asian Oncology Summit 2009. Lancet Oncol.2009;10(11): 1111-1118.
[2] Sell S. Cellular origin of hepatocellular carcinomas. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002;13(6):419-424.
[3] Oertel M, Shafritz DA.Stem cells, cell transplantation and liver repopulation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1782(2):61-74.
[4] Fujio K, Evarts RP, Hu Z,et al. Expression of stem cell factor and its receptor, c-kit, during liver regeneration from putative stem cells in adult rat.Lab Invest. 1994;70(4):511-516.
[5] Petersen BE, Goff JP, Greenberger JS,et al. Hepatic oval cells express the hematopoietic stem cell marker Thy-1 in the rat.Hepatology. 1998;27(2):433-445.
[6] Shupe TD, Piscaglia AC, Oh SH,et al. Isolation and characterization of hepatic stem cells, or "oval cells," from rat livers. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;482:387-405.
[7] Koike H, Taniguchi H.Characteristics of hepatic stem/progenitor cells in the fetal and adult liver.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2012;19(6):587-593.
[8] Tong CM, Ma S, Guan XY.Biology of hepatic cancer stem cells.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26(8):1229-1237.
[9] Nakatsura T, Yoshitake Y, Senju S,et al.Glypican-3, overexpressed specifically in human hepatocellular carcinoma, is a novel tumor marker.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;306(1):16-25.
[10] He ZP, Tan WQ, Tang YF,et al. Activation, isolation, identification and in vitro proliferation of oval cells from adult rat livers.Cell Prolif. 2004;37(2):177-187.
[11] Hu Z, Evarts RP, Fujio K,et al.Expression of hepatocyte growth factor and c-met genes during hepatic differentiation and liver development in the rat.Am J Pathol. 1993;142(6): 1823-1830.
[12] Dezso K, Jelnes P, László V,et al.Thy-1 is expressed in hepatic myofibroblasts and not oval cells in stem cell-mediated liver regeneration.Am J Pathol. 2007;171(5): 1529-1537.
[13] Apte U, Thompson MD, Cui S,et al.Wnt/beta-catenin signaling mediates oval cell response in rodents.Hepatology. 2008;47(1):288-295.
[14] Majumdar A, Curley SA, Wu X, et al.Hepatic stem cells and transforming growth factor β in hepatocellular carcinoma.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;9(9):530-538.
[15] Tsuchiya A, Heike T, Fujino H, et al.Long-term extensive expansion of mouse hepatic stem/progenitor cells in a novel serum-free culture system.Gastroenterology. 2005;128(7): 2089-2104.
[16] Sirica AE, Mathis GA, Sano N,et al. Isolation, culture, and transplantation of intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells and oval cells.Pathobiology. 1990;58(1):44-64. .
[17] Monga SP, Tang Y, Candotti F,et al.Expansion of hepatic and hematopoietic stem cells utilizing mouse embryonic liver explants.Cell Transplant. 2001;10(1):81-89.
[18] Kamiya A, Kinoshita T, Miyajima A.Oncostatin M and hepatocyte growth factor induce hepatic maturation via distinct signaling pathways.FEBS Lett. 2001;492(1-2):90-94.
[19] Riehle KJ, Dan YY, Campbell JS,et al.New concepts in liver regeneration.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26 Suppl 1: 203-212.
[20] Theise ND, Saxena R, Portmann BC,et al.The canals of Hering and hepatic stem cells in humans.Hepatology. 1999; 30(6):1425-1433.
[21] Steinberg P, Steinbrecher R, Schrenk D,et al. Drug-metabolizing enzyme activities in freshly isolated oval cells and in an established oval cell line from carcinogen-fed rats.Cell Biol Toxicol. 1994;10(1):59-65.
[22] Steinberg P, Weisse G, Eigenbrodt E,et al.Expression of L- and M2-pyruvate kinases in proliferating oval cells and cholangiocellular lesions developing in the livers of rats fed a methyl-deficient diet.Carcinogenesis. 1994;15(1):125-127.
[23] Lowes KN, Brennan BA, Yeoh GC,et al.Oval cell numbers in human chronic liver diseases are directly related to disease severity.Am J Pathol. 1999;154(2):537-541.
[24] Fotiadu A, Tzioufa V, Vrettou E,et al. Progenitor cell activation in chronic viralhepatitis.Liver Int. 2004;24(3):268-274.
[25] Huang T, Chesnokov V, Yokoyama KK, et al.Expression of the Hoxa-13 gene correlates to hepatitis B and C virus associated HCC.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;281(4):1041- 1044.
[26] Steinberg P, Steinbrecher R, Radaeva S,et al. Oval cell lines OC/CDE 6 and OC/CDE 22 give rise to cholangio-cellular and undifferentiated carcinomas after transformation.Lab Invest. 1994;71(5):700-709.
[27] Zhang F, Chen XP, Zhang W,et al.Combined hepatocellular cholangiocarcinoma originating from hepatic progenitor cells: immunohistochemical and double-fluorescence immunostaining evidence.Histopathology. 2008;52(2): 224-232.
[28] Hooth MJ, Coleman WB, Presnell SC,et al. Spontaneous neoplastic transformation of WB-F344 rat liver epithelial cells.Am J Pathol. 1998;153(6):1913-1921.
[29] 刘君,薛玲,张萌,等.肝细胞生长因子和表皮生长因子联合体外诱导大鼠肝卵圆细胞分化的研究[J].中华病理学杂志,2007,36(11): 756-759.
[30] Amit M, Carpenter MK, Inokuma MS,et al.Clonally derived human embryonic stem cell lines maintain pluripotency and proliferative potential for prolonged periods of culture.Dev Biol. 2000;227(2):271-278.
[31] Suzuki A, Iwama A, Miyashita H,et al.Role for growth factors and extracellular matrix in controlling differentiation of prospectively isolated hepatic stem cells.Development. 2003; 130(11):2513-2524.
[32] Masson NM, Currie IS, Terrace JD, et al. Hepatic progenitor cells in human fetal liver express the oval cell marker Thy-1.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;291(1): G45-54. |