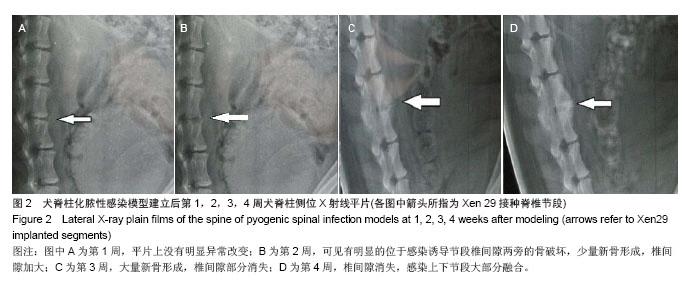
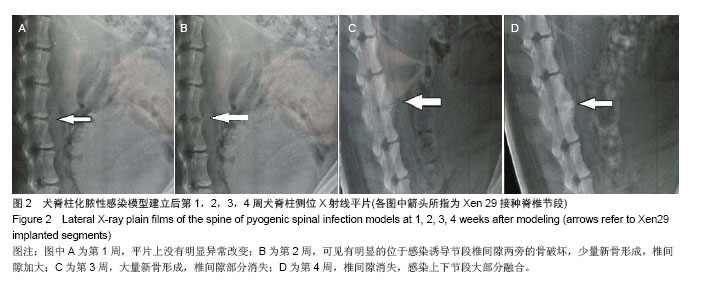
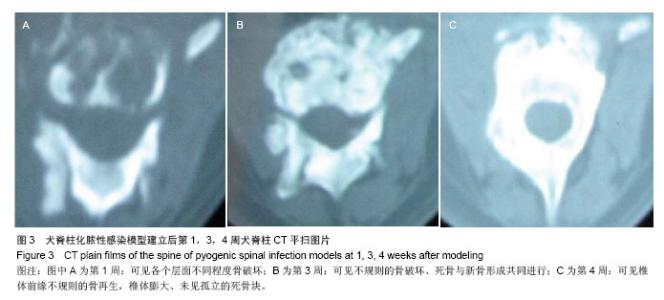
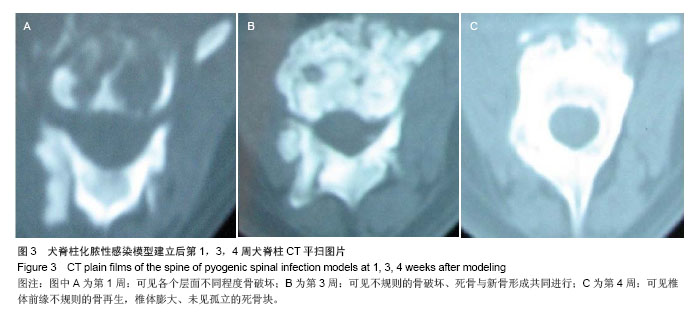
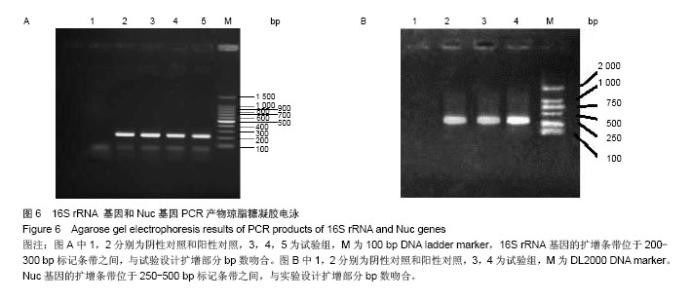
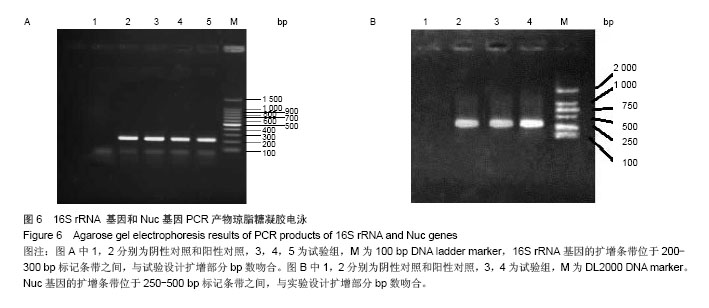
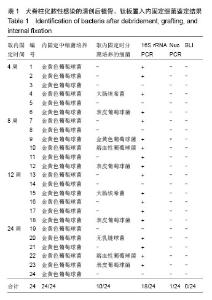
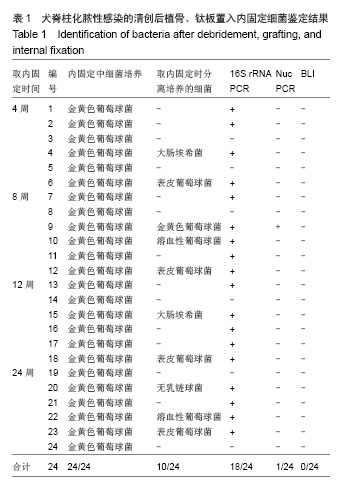
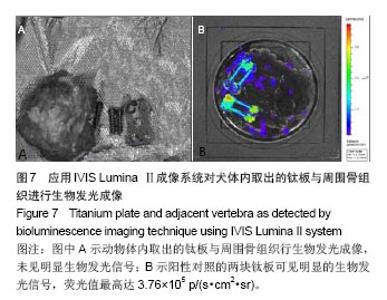
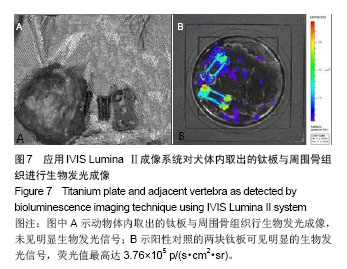
| [1]Dimar JR,Carreon LY,Glassman SD,et al.Treatment of pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis with anterior debridement and fusion followed by delayed posterior spinal fusion. Spine. 2009; 29:326-332; discussion 332.
[2]Belzunegui J, Intxausti JJ, De Dios JR,et al.Haematogenous vertebral osteomyelitis in the elderly.Clin Rheumatol. 2000;19: 344-347.
[3]Shad A, Shariff S, Fairbank J,et al. Internal fixation for osteomyelitis of cervical spine: the issue of persistence of culture positive infection around the implants. Acta Neurochir (Wien).2003;145:957-960,discussion 960.
[4]Chen WH, Jiang LS, Dai LY. A novel canine model of acute pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Neurosurg Rev.2009;32:485-490.
[5]Sigmon J, LarcomLL.Theeffect of ethidiumbromideonmobility of DNA fragments in agarose gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis.1996;17(10): 1524-1527.
[6]Vantarakis A, Komninou G,Venieri D,et al.Development of amultiplex PCRdetection of Salmonella spp. and Shigella spp. inmussels.Lett ApplMicrobiol.2000;31(2): 105-109.
[7]Marculescu CE,Osmon DR. Antibiotic prophylaxis in orthopedic prosthetic surgery. Infect Dis Clin North Am.2005; 19:931-946.
[8]Burke JF. The effective period of preventive antibiotic action in experimental incisions and dermal lesions.Surgery.1961; 50: 161-168.
[9]Classen DC,Evans RS,Pestotnik SL,et al.The timing of prophylactic administration of antibiotics and the risk of surgical-wound infection.N Engl J Med.1992;326:281-286.
[10]Carragee EJ. Instrumentation of the infected and unstable spine: a review of 17 cases from the thoracic and lumbar spine with pyogenic infections.J Spinal Disord.1999;10: 317-324.
[11]Asamoto S, Doi H, Kobayashi N, et al. Spondylodiscitis: diagnosis and treatment. Surg Neurol.2005;64:103-108.
[12]Madism BM,Baselski VS.Rapid idetification of Staphylococcus aureus inbloodculture by thermornuclease testing. J ClinMicrobiol.1983;18(3): 722-724.
[13]Tani H, Maehana K, Kamidate T.On-chip genotoxicbioassay based on bioluminescence reporter systemusing three-dimensional microfluidicnetwork.AnalChimActa.2006; 560(1):24-29.
[14]Hutchens M, Luker GD.Applications of bioluminescence imaging to the study of infectious diseases. Cell Microbiol. 2007; 9:2315-2322.
[15]Edinger M, Cao YA, Verneris MR, et al.Revealing lymphoma growth and the efficacy of immune cell therapies using in vivo bioluminescence imaging. BLOOD. 2003; 101: 640-648.
[16]Ahlberg A, Carlsson AS, Lindberg L.Hematogenous infection in total joint replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1978;4: 69-75.
[17]O'Boyle CJ, MacFie J, Mitchell CJ,et al.Microbiology of bacterial translocation in humans.1998;42:29-35.
[18]Trotha R, Hanck T, Konig W, et al.Rapid ribosequencing--an effective diagnostic tool for detecting microbial infection. Infection .2010;29:12-16.
[19]Southwood RT,Rice JL,McDonald PJ,et al.Infection in experimental hip arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1999; 67:229-231.
[20]Bornside GH, Cohn I Jr. The normal microbial flora: comparative bacterial flora of animals and man. Am J Dig Dis.1965; 10:844-852.
[21]Shittu AO, Lin J, Morrison D, et al.The discovery of a multi-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus clone in the hospital and community environment in south western Nigeria. Ostomy Wound Manage.2005;51:67-70.
[22]Ahn CY, Ko CY, Wagar EA, et al.Microbial evaluation: 139 implants removed from symptomatic patients. Plast Reconstr Surg.1996;98:1225-1229.
[23]Kuo CH, Wang ST, Yu WK,et al.Postoperative spinal deep wound infection: a six-year review of 3230 selective procedures. J Chin Med Assoc.2004; 67:398-402. |