Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (22): 3567-3573.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.22.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Implant fixation versus conservative treatment for clavicle fractures: a meta-analysis
Yang Fan, Wang Dong, Sun Hai-yu, Xu Kun, Ning Si-min, Li Yang, Zhao Chen
- Second Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Revised:2014-04-25Online:2014-05-28Published:2014-05-28 -
Contact:Wang Dong, Doctoral supervisor, Professor, Chief physician, Second Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Yang Fan, Studying for master’s degree, Second Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Fan, Wang Dong, Sun Hai-yu, Xu Kun, Ning Si-min, Li Yang, Zhao Chen. Implant fixation versus conservative treatment for clavicle fractures: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(22): 3567-3573.
share this article
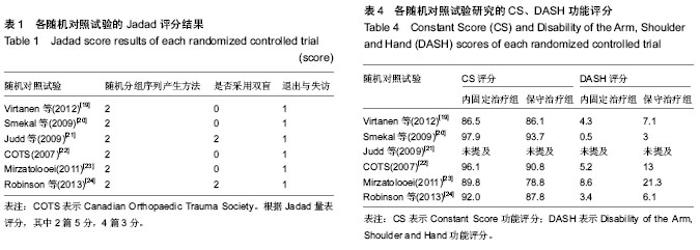
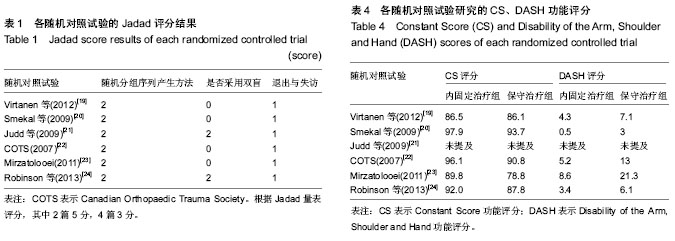
2.1 纳入研究的基本特征和相关指标 经过系统检索并利用EndNote软件剔重后,共搜索出1 825篇相关文献,其中中文文献1 237篇,英文文献588篇。通过阅读文章题目及摘要,初步筛查出69篇文献,进一步阅读全文,严格按照纳入和排除标准进行筛选,有9个随机对照试验可能研究符合入选标准[16-24]。其中排除了3篇文献,原因如下:有2篇是同一作者对同一研究的不同报道[16,22],其中1篇为多中心的随机对照试验[22],另一篇则详细介绍了该研究的手术方法[16],故排除了该文献;有2篇文献未正式发表[17-18],仅含有研究方法,无任何原始数据。根据Jadad量表评分,其中2篇5分[21,24],4篇3分[19-23](表1),可认为其质量较高。其中内固定治疗组(接骨板或髓内钉)纳入279例和保守治疗组(三角巾悬吊或锁骨带固定)291例。各随机对照试验研究的基本特征、内固定植入物选择、保守治疗方法、平均骨折愈合时间及治疗后1年功能评分见表2-4。"
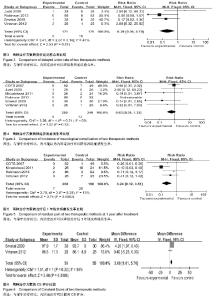
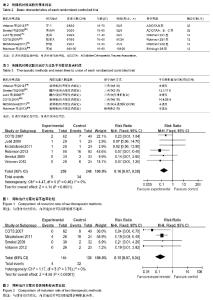
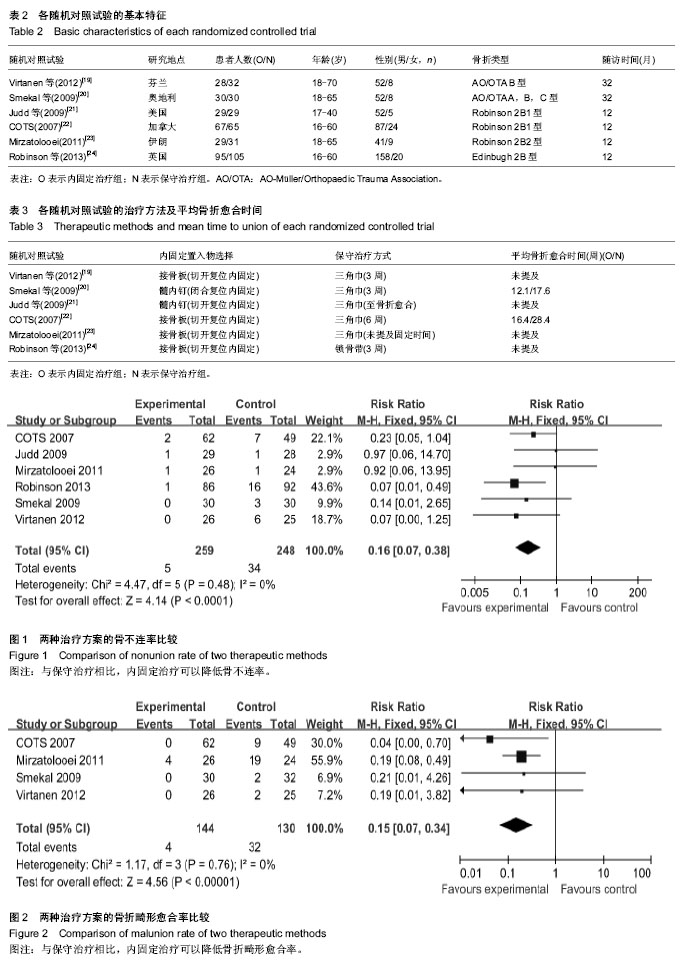
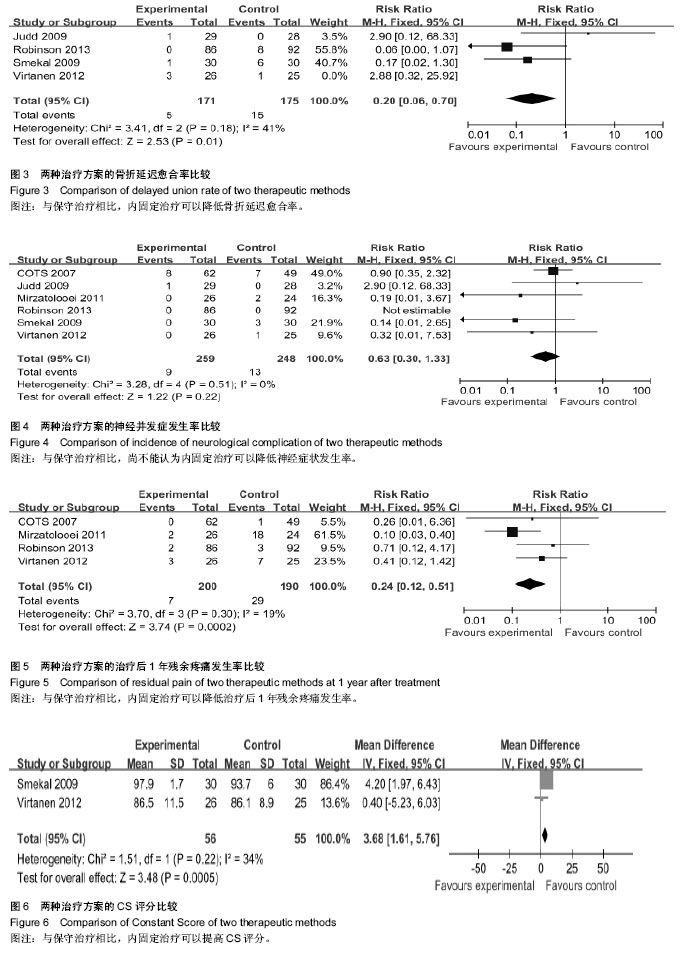
2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 骨不愈合率 共6篇随机对照试验报道了骨不愈合率[19-24]。Meta分析结果表明,研究效应量同质(I2=0%,P=0.48),采用M-H固定效应模型。两组相比差异有显著性意义[RR=0.16,95%CI(0.07,0.38),P < 0.000 1],认为与保守治疗相比,内固定治疗可以降低骨不连率(图1)。 2.2.2 骨折畸形愈合率 共4篇随机对照试验报道了骨折畸形愈合率[19-20,22-23]。Meta分析结果表明,研究效应量同质(I2=0%,P=0.76),采用固定效应模型。两组相比差异有显著性意义[RR=0.15,95%CI(0.07,0.34),P < 0.000 01],认为与保守治疗相比,内固定治疗可以降低畸形愈合率 (图2)。 2.2.3 骨折延迟愈合率 共4篇随机对照试验报道了骨折延迟愈合率[19-21,24]。Meta分析结果表明,研究效应量同质(I2=41%,P=0.18),采用固定效应模型。两组相比差异有显著性意义[RR=0.20,95%CI(0.06,0.70),P=0.01],认为与保守治疗相比,内固定治疗可以降低骨折延迟愈合率(图3)。 2.2.4 神经并发症发生率 共6篇随机对照试验报道了神经症状发生率[19-24],其中5篇纳入研究。Meta分析结果表明,研究效应量同质性明显(I2=0%,P=0.51),采用固定效应模型。两组相比差异无显著性意义[RR=0.63,95%CI (0.06,0.70),P=0.22],与保守治疗相比,尚不能认为内固定治疗可以降低神经症状发生率(图4)。 2.2.5 治疗后1年残余疼痛发生率 共4篇随机对照试验报道了治疗后1年残余疼痛发生率[19,22-24]。Meta分析结果表明,研究效应量同质性明显(I2=19%,P=0.30),采用固定效应模型。两组相比差异有显著性意义[RR=0.24,95%CI(0.12,0.51),P=0.000 2],认为与保守治疗相比,内固定治疗可以降低治疗后1年残余疼痛发生率(图5)。 2.2.6 CS评分 共2篇随机对照试验中关于CS评分的数据可以使用[19-20]。Meta分析结果表明,研究效应量同质性明显(I2=34%,P=0.22),采用固定效应模型。两组相比差异有显著性意义[MD=3.68,95%CI(1.61,5.76),P=0.000 5],认为与保守治疗相比,内固定治疗可以提高CS评分(图6)。"
| [1] Robinson C. Fractures of the clavicle in the adult. Epidemiology and classification. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80(3):476-484.
[2] Postacchini F, Gumina S, De Santis P, et al. Epidemiology of clavicle fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2002;11(5):452-456.
[3] Jeray KJ. Acute midshaft clavicular fracture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007; 15(4):239-248.
[4] Neer CS 2nd. Nonunion of the clavicle. J Am Med Assoc. 1960;172:1006-1011.
[5] Rowe CR. An atlas of anatomy and treatment of midclavicular fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1968;58:29-42.
[6] Nowak J, Holgersson M, Larsson S. Can we predict longterm sequelae after fractures of the clavicle based on initial findings? A prospective study with nine to ten years of follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2004;13(5):479-486.
[7] Robinson CM, Court-Brown CM, McQueen MM, et al. Estimating the risk of nonunion following nonoperative treatment of a clavicular fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(7):1359-1365.
[8] Hill JM, McGuire MH, Crosby LA. Closed treatment of displaced middle-third fractures of the clavicle gives poor results.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(4):537-539.
[9] Mueller M, Burger C, Florczyk A, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing of midclavicular fractures in adults: 32 patients followed for 1-5 years. Acta Orthop. 2007; 78(3): 421-423.
[10] Eden L, Doht S, Frey SP, et al. Biomechanical comparison of the Locking Compression superior anterior clavicle plate with seven and ten hole reconstruction plates in midshaft clavicle fracture stabilisation. Int Orthop. 2012; 36(12):2537-2543.
[11] Thyagarajan DS, Day M, Dent C, et al. Treatment of mid-shaft clavicle fractures: a comparative study. Int J Shoulder Surg. 2009;3(2):23-27.
[12] Sohn HS, Shin SJ, Kim BY. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using anterior-inferior plating of clavicular midshaft fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(2): 239-244.
[13] Deeks JJ, Altman DG, Bradburn MJ. Statistical methods for examining heterogeneity and combining results from several studies in meta-analysis. Systematic reviews in health care: metaanalysis in context, 2nd ed. BMJ Publishing Group, London, 2008: 285-312.
[14] 康德英,洪旗.如何评价Meta分析的统计分析结果[J].中国循证医学, 2001,1(2):106-108.
[15] Jadad AR,Moore RA,Carroll D,et al.Assessing the Quality of Reports of Randomized Clinical Trials:Is Blinding Necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17:1-12.
[16] Altamimi SA, McKee MD, Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90 Suppl 2 Pt 1:1-8.
[17] Stegeman SA, de Jong M, Sier CF, et al. Displaced midshaft fractures of the clavicle: non-operative treatment versus plate fixation (Sleutel-TRIAL). A multicentre randomised controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:196.
[18] Longo UG, Banerjee S, Barber J, et al. Conservative management versus open reduction and internal fixation for mid-shaft clavicle fractures in adults--the Clavicle Trial: study protocol for a multicentre randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2011;12:57.
[19] Virtanen KJ, Remes V, Pajarinen J, et al. Sling compared with plate osteosynthesis for treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2012;94(17):1546-1553.
[20] Smekal V, Irenberger A, Struve P, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing versus nonoperative treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fracturesa randomized, controlled, clinical trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(2): 106-112.
[21] Judd DB, Pallis MP, Smith E, et al. Acute operative stabilization versus nonoperative management of clavicle fractures. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2009;38(7):341–345.
[22] Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1):1-10.
[23] Mirzatolooei F. Comparison between operative and nonoperative treatment methods in the management of comminuted fractures of the clavicle. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2011;45(1):34-40.
[24] Robinson CM, Goudie EB, Murray IR, et al. Open reduction and plate fixation versus nonoperative treatment for displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(17): 1576-1584.
[25] Liu GD, Tong SL, Ou S, et al. Operative versus non-operative treatment for clavicle fracture: a meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2013;37(8):1495-1500.
[26] 谷贵山,张进,王铁军,等.锁骨骨折手术与非手术治疗的Meta分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2009, 15(3):161-165.
[27] Rehn CH, Kirkegaard M, Viberg B, et al. Operative versus nonoperative treatment of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures in adults: a systematic review. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013. [Epub ahead of print]. |
| [1] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [2] | Li Jing, Yang Long, Wang Jian-ji, Liu Qin, Zou Qiang, Sun Yu, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Three-dimensional reconstruction based on DICOM data and its application for orthopedic implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1046-1051. |
| [3] | Liu Jian-kun, Deng Shu-cai. Status and role of three-dimensional printing technology in spine surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1131-1136. |
| [4] | Ye Xiang-yang, Sun Xiang, Tang Li-xin, Zhen Ping, Geng Bin, Wang Hua-lei, Zhao Yu-guo. Acetabular liner wear of cross-linked versus conventional polyethylene for total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1143-1148. |
| [5] | Sheng Xiao-lei, Yuan Feng, Li Zhi-duo, Yang Yu-ming, Lu Hai-tao, Zhang Jun-wei. Comparison of the accuracy of lower cervical anterior transpedicular screws between three-dimensional printing assembly navigation template and free hand placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 406-411. |
| [6] | Lu Zhong-lin, Cao Zhi-qiang, Gao Guo-liang, Jing Qing-ling, Zhang Wei, Huang Yong. Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis during waiting period before operation for calcaneal fractures by ultrasound elastography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 423-427. |
| [7] | Wu Min-hao, Sun Wen-chao, Yan Fei-fei, Xie Yuan-long, Hou Zhi-qiang, Feng Fan, Cai Lin . Treatment research and new progress of early-onset scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 433-439. |
| [8] | Zou Wei, Xiao Jie, Long Hao, Zhang Yang, Wu Chen, Du Yu-hui, Feng Ming-xing, Zhou Chang-jun. Screw placement selection of minimally invasive percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 356-361. |
| [9] | Chen Lu-yao, Hu Shi-qiang, Wang Xiao-ping, Wu Wei-wei, Wei Zhan-tu, Huang Jian. Accuracy of digital orthopedic three-dimensional reconstruction for thoracolumbar pedicle screw placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 373-377. |
| [10] | Du Shi-yao, Zhou Feng-jin, Ni Bin, Chen Bo, Chen Jin-shui. Finite-element analysis of a novel posterior atlantoaxial restricted non-fusion fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 383-389. |
| [11] | Liu Jun, Liao Su-ping. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of Kirschner nails and external fixation for Bennett fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 390-395. |
| [12] | Zhang Tai-liang, Zhang Lei, Lian Zhi-ming, Yang Guang-zhong. Effect of remnant preservation on recovery of knee proprioception in arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 471-477. |
| [13] | Wang Lei, Wang Feng-feng, Ma Yan-hui, Zhang Jie, Hu Fang, Ma Gai-ping, Liu Mei-mei, Ma Zhang-wen. Meta analysis of clinical outcome of intramedullary nails versus locking plates for two-part proximal humerus fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 478-484. |
| [14] | Zha Yuan-yu, Yang Yang, Chen Shu-zhen, Wei Ren-xiong, Zhang Shu-wei, Jin Wei. Meta-analysis of posterior laminectomy and instrumented fusion versus laminoplasty in treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 485-492. |
| [15] | Yang Min, Ma Xiang-yang, Yang Jin-cheng, Chen Shu-jin, Zou Xiao-bao. Biomechanical properties of a novel automatic anti-rotation posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation system: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 3031-3037. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||