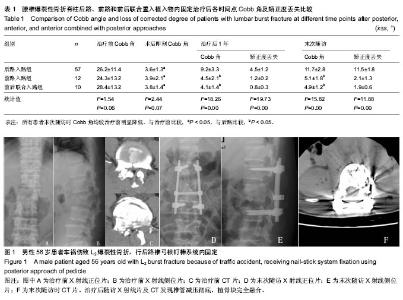
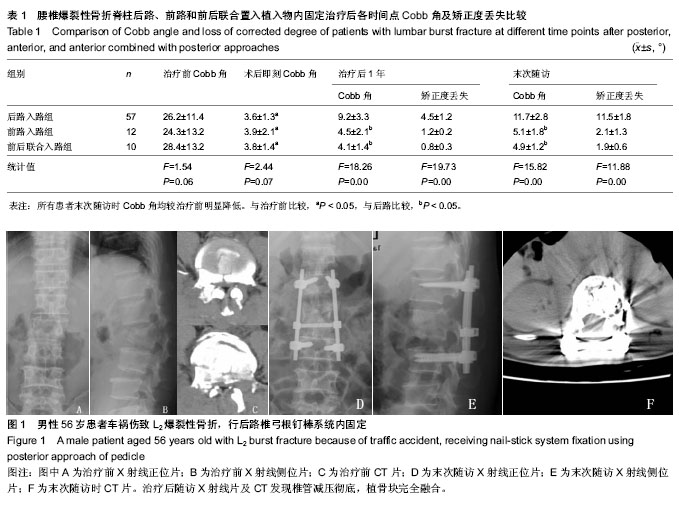
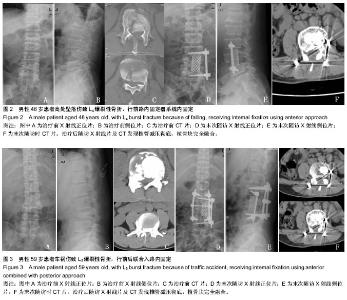
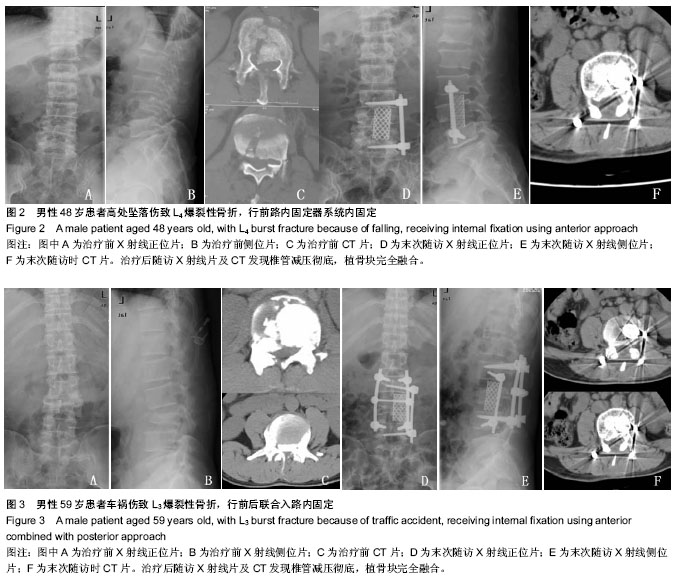
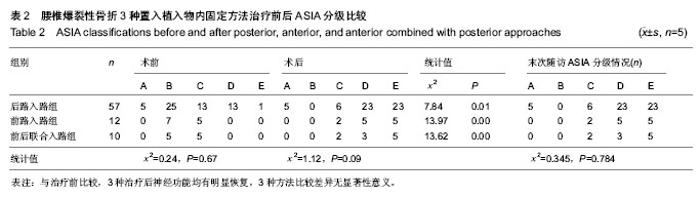
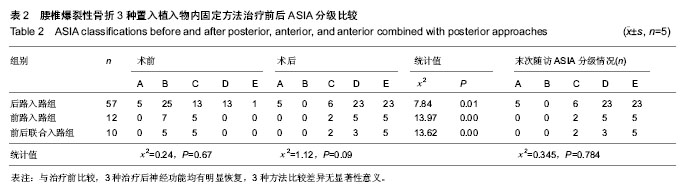
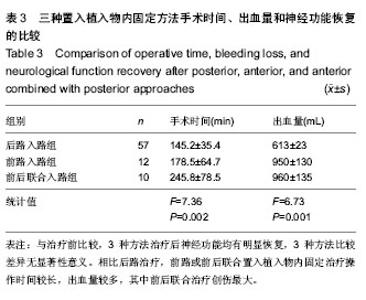
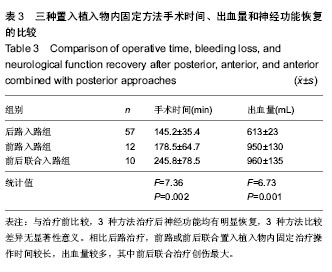
| [1] 高博,幸嵘,孔清泉,等.经后路椎体次全切除加椎间支撑植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折及骨折脱位的早期疗效观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(5):542-545.
[2] 焦根龙,李志忠,潘永勤,等.后路开窗减压、伤椎短节段固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折效果观察[J].山东医药,2013,53(5):15-17.
[3] 罗一,邓展生,陈静.不同植骨融合方式对胸腰椎爆裂性骨折疗效的影响[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(11):1302-1307.
[4] 李同相,肖睿,官清,等.改良法经病椎植钉复位椎弓根植骨后路钉棒治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012, 26(5):546-549.
[5] 赵文明,柴俊,毛立彪,等.后路短节段钉棒系统结合经伤椎置钉固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2013,16(5):487- 489.
[6] 崔鑫,王文革,李仕臣,等.前路减压钛网重建脊柱治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].北方药学,2014,11(1):115-116.
[7] 鄢文发.Ⅰ期前后联合入路和Ⅰ期后入路治疗严重腰椎爆裂骨折疗效对比分析[J].河南外科学杂志,2013,19(6):98-99.
[8] 冯永洪,卢国樑,李真,等.经后外侧入路椎间融合内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(8):730-732.
[9] 顾华,付建,易难,等.AF椎弓根螺钉内固定系统治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折:30个月随访的中远期效果分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(13):2378-2381.
[10] 周其璋,黄福立,严坚强,等.经椎弓根减压配合脊柱后路内固定术治疗胸腰椎新鲜爆裂性骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013, 15(7): 622-623.
[11] 元虎,郑光彬,陈继良,等.前路减压融合结合前路或后路固定治疗严重的胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(14): 1041-1044.
[12] Korovessis P, Baikousis A, Zacharatos S, et al. Combined anterior plus posterior stabilization versus posterior short-segment instrumentation and fusion for mid-lumbar (L2-L4) burst fractures. Spine. 2006;31 (8):859-868.
[13] 孙先润,唐涛,赵晓芳,等.不稳定性胸腰椎骨折合并脊髓损伤的治疗体会[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(2):158-161.
[14] 成红兵,李佳.CD2椎弓根螺钉置入内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(39):7402-7406.
[15] 侯永洋,庞施义,徐亚斌,等.伤椎固定椎体内复位植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(2):149-152.
[16] Wood KB,Bohn D,Mechbod A.Anterior versus posterior treatment of stable thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic deficit: a prospective, randomized study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(suppl):S15-23.
[17] Harrington RM, Budorick T, Hoyt J, et al.Biomechanics of indirect reduction of bone retropulsed into the spinal canal in vertebral fracture. Spine.1993;18(6):692-699.
[18] 曾祥一,刘元禄,王伟,等.蛋壳技术在胸腰椎爆裂骨折手术治疗中应用的临床研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2009,11(6):167-168.
[19] Wei YD.Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractire by lateral and anterior decompression from posterior incision. Chin J Orthop Trauma. 2004;6(2):227-229.
[20] 李同相,肖睿,官清,等.改良法经病椎植钉复位椎弓根植骨后路钉棒治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012, 26(5):546-549.
[21] 戴力扬,蒋雷生,沈雷,等.多发伤患者胸腰椎骨折的手术时机[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2004,6(1):84-87.
[22] Fehlings MG, Vaccaro A, Wilson JR, et al. Early versus delayed decompression for traumatic cervical spinal cord injury: results of the Surgical Timing in Acute Spinal Cord Injury Study (STASCIS).PLoS One.2012;7(2):e32037.
[23] 易国良,宋西正,王文军,等.脊柱外固定器治疗相邻双节段腰椎骨折的生物力学测试[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(9):1586- 1591. |