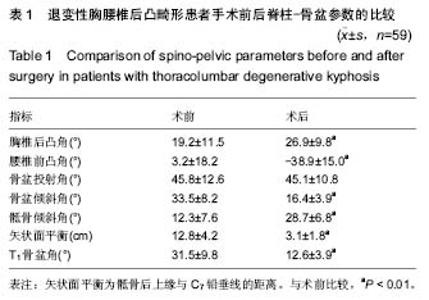
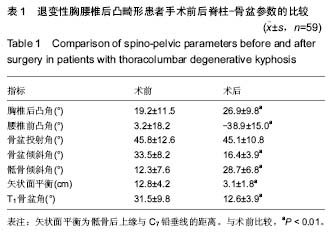
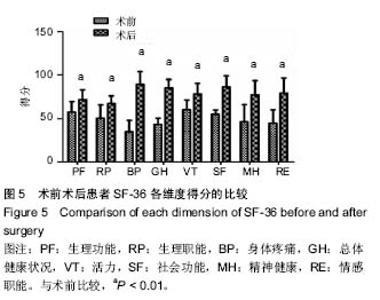
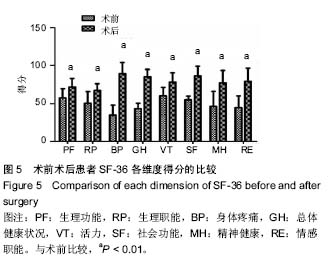
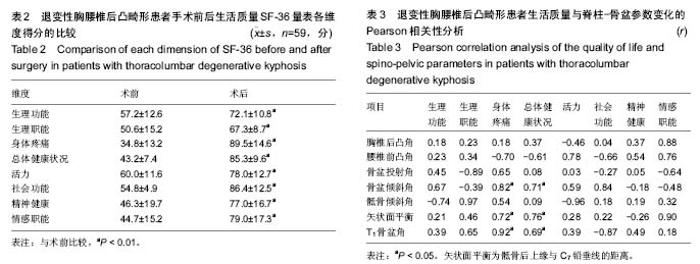
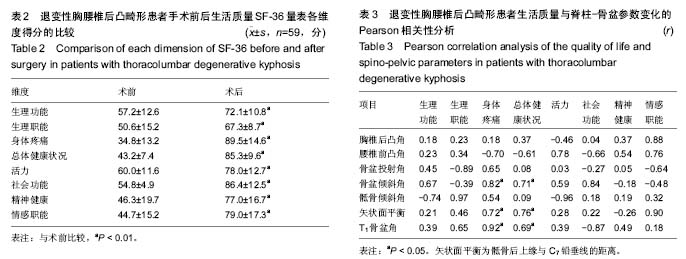
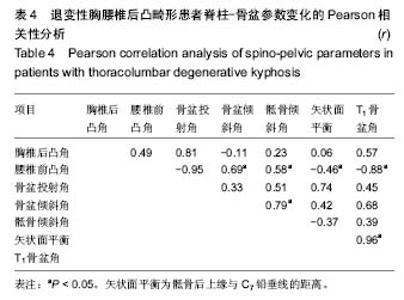
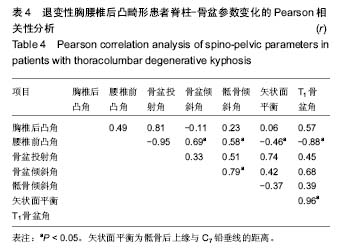
| [1] Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, et al. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(18): 2024-2029. [2] Gottfried ON, Daubs MD, Patel AA, et al. Spinopelvic parameters in postfusion flatback deformity patients. Spine J. 2009; 9(8):639-647. [3] 邱勇,朱泽章,吕锦瑜,等.强直性脊柱炎胸腰椎后凸畸形两种截骨矫形术式的疗效比较 [J].中华骨科杂志, 2002,22(12): 719-722.[4] Chang KW, Cheng CW, Chen HC, et al. Closing-opening wedge osteotomy for the treatment of sagittal imbalance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(13):1470-1477.[5] Ryan DJ, Protopsaltis TS, Ames CP, et al. T1 pelvic angle (TPA) effectively evaluates sagittal deformity and assesses radiographical surgical outcomes longitudinally. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39(15):1203-1210. [6] Wafa H, Azzouz D, Ghannouchi MM, et al. Health-related quality of life assessment on 100 Tunisian patients with ankylosing spondylitis using the SF-36 survey. Oman Med J. 2012; 27(6): 455-460.[7] Silva FE, Lenke LG. Adult degenerative scoliosis: evaluation and management. Neurosurg Focus. 2010; 28(3): E1.[8] Jang JS, Lee SH, Min JH, et al. Lumbar degenerative kyphosis: radologic analysis and classifications. Spine. 2007; 32(24): 2694-2699. [9] Chang KW, Chen YY, Lin CC, et al. Closing wedge osteotomy versus opening wedge osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis with thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(14): 1584-1593.[10] Lafage V, Schwab F, Vira S, et al. Does vertebral level of pedicle subtraction osteotomy correlate with degree of spinopelvic parameter correction? J Neurosurg Spine. 2011; 14(2):184-191.[11] Lafage V, Schwab F, Patel A,et al. Pelvic tilt and truncal inclination: two key radiographic parameters in the setting of adults with spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(17): E599-606. |