Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (18): 2841-2847.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.18.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis infection after renal transplantation
Li Guo-wen, Hu Jian-min, Liu Yong-guang, Fan Li-pei, Li Liu-yang, Zhao Ming
- Department of Organ Transplantation, Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510282, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2014-02-20Online:2014-04-30Published:2014-04-30 -
Contact:Zhao Ming, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Organ Transplantation, Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510282, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Li Guo-wen, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Organ Transplantation, Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510282, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Guo-wen, Hu Jian-min, Liu Yong-guang, Fan Li-pei, Li Liu-yang, Zhao Ming. Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis infection after renal transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(18): 2841-2847.
share this article
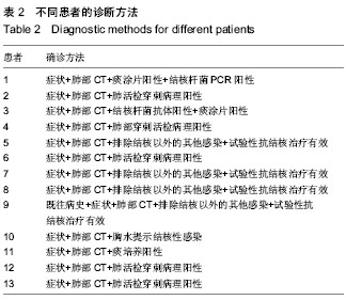
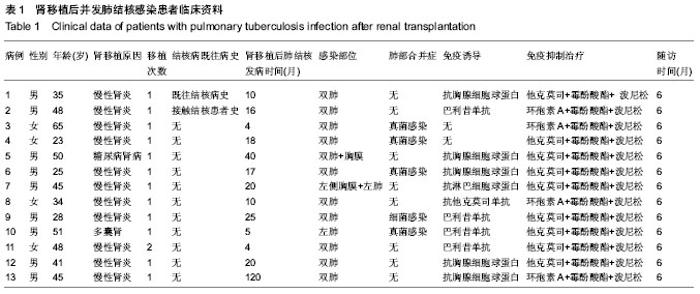
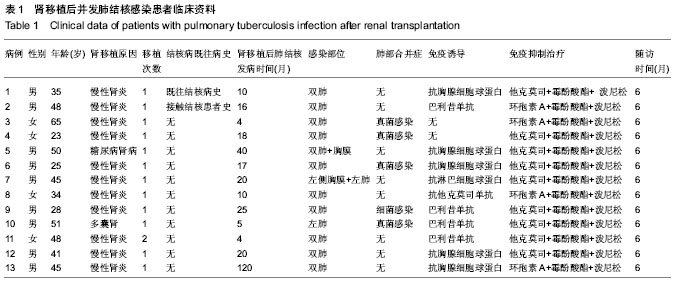
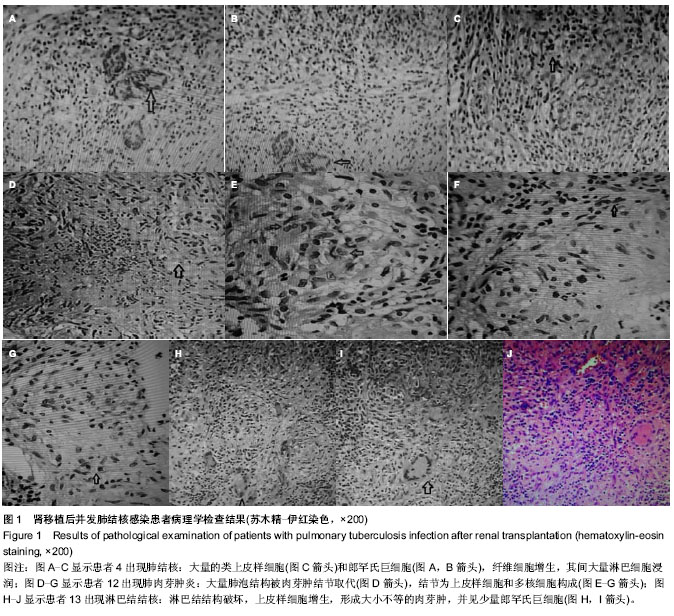
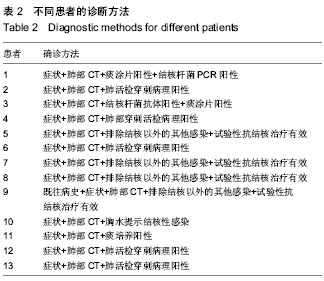
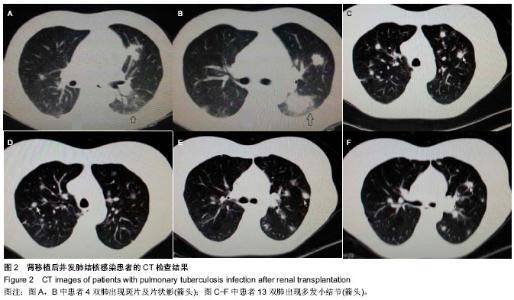
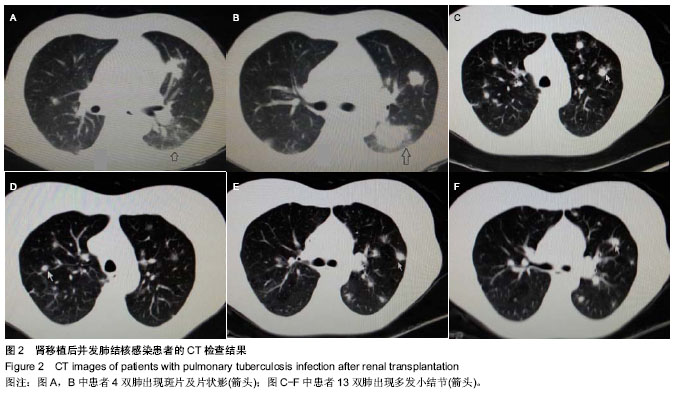
2.1 肾移植后并发肺结核感染患者临床资料 所有患者均进入结果分析,无脱失。13例患者的一般资料见表1。 2.2 肾移植后并发肺结核感染患者的发病时间 结核病患者发病时间为肾移植后4-120个月,其中发病时间为肾移植后5个月以内3例,肾移植后6-20个月7例,肾移植后20个月以后3例;62%(8/13)患者于移植肾移植后18个月内发病。 2.3 肾移植后并发肺结核感染患者的临床表现 2.3.1 发热 是最常见的表现,实验纳入的患者中有8例患者表现为不明原因的低热,体温37.8 ℃上下波动,午后及傍晚多见。 2.3.2 咳嗽、咳痰 多比较轻,痰量偏少,实验纳入的患者中有2例患者以咳嗽为首发症状。 2.3.3 其他表现 胸骨后疼痛1例,头痛1例。 2.4 肾移植后并发肺结核感染患者的实验室检查结果 13例患者予痰涂片查抗酸杆菌,其中阳性3例,阴性10例;1例痰涂片阴性者痰培养结核杆菌阳性,痰结核杆菌PCR阳性1例。抗结核抗体阳性1例,阴性12例。结核菌素试验实验均阴性。菌阴者行组织病理学检查5例,其中肺结核3例,1例提示肺内结核性慢性肉芽肿炎,1例肺结核合并淋巴结核。1例行胸腔穿刺查胸水常规提示结核感染;13例均有不同程度血沉加快。病理图片见图1。 2.5 肾移植后并发肺结核感染患者的影像学检查结果 13例患者均行胸部X射线和CT检查,其中呈小结节病变5例,斑点、斑片状病变3例。胸部CT见图2。 2.6 肾移植后并发肺结核感染患者的诊断 所有患者均经病原学或组织病理学或类表方法确诊,表2。"
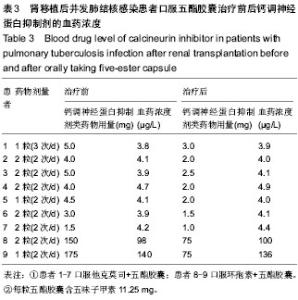
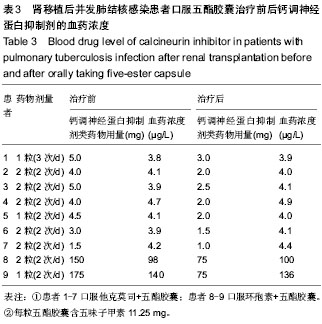
2.7 肾移植后并发肺结核感染患者的治疗经过 结核病采用异烟肼(丹东医药公司)[或对氨基水杨酸异烟肼(重庆华邦公司)]、利福平(哈药集团)[或利福喷丁(四川明欣公司)]、乙胺丁醇(江苏克胜公司)、吡嗪酰胺(广州华南公司)四联抗结核治疗,疗程6-10个月。 在治疗前2-4个月采用异烟肼(或对氨基水杨酸异烟肼)0.3 g、利福平(或利福喷丁)0.45 g、乙胺丁醇0.75 g、吡嗪酰胺1.5 g,早晨一次顿服;而后改为异烟肼(或对氨基水杨酸异烟肼)0.3 g、利福平(或利福喷丁)0.45 g维持治疗6-8个月;其中9例患者口服五酯胶囊(四川禾正公司)护肝治疗。 治疗过程中每2-4周复查测肝肾功能、尿常规、尿酸、血脂水平及(他克莫司或环孢素)全血药物浓度,及时调整免疫抑制剂方案;同时每8-12周复查胸部CT评估肺结核转归情况。患者口服五酯胶囊前后钙调神经蛋白抑制剂药物的血药变化见表3。"
| [1] 全国结核病流行病学抽样调查技术指导组.第四次全国结核病流行病学抽样调查报告[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2002,25(1): 6-10. [2] 陆再英,钟南山.内科学[M].7版.北京:人民卫生出版社.2007. [3] 郭巍.肾移植术后肺部感染28例诊治分析[J].器官移植,2010, 1(6):352-355. [4] 安丹,韩梦霞,张韬.肾移植术后并发肺结核11例临床分析[J].人民军医,2008,51(6):390. [5] 齐隽,殷金龙,闵志廉,等.肾移植后结核并发症的诊断与治疗(附14例报告)[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,1994,3(3):185-188. [6] 唐斌,刘东,吴家清,等.肾移植术后结核感染13例临床分析[J].新医学,2006,37(4):242-243. [7] 林俊,郭宏波,唐雅望,等.肾移植术后肺结核的临床特点及早期诊断的单中心经验[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2013,12(9):680- 682. [8] 刘京,吴雄飞,刘宏.肾移植术后结核感染的临床分析[J].第三军医大学学报,2005,27(11):1134-1135. [9] 傅红梅,王云南,刘龙山,等.肾移植术后并发结核病的诊断与治疗——附33例报告[J].新医学,2008,39(5):311-313. [10] 王必佺,张爱民,刘泽成,等.CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检对肺部周围型肿物的诊断价值探讨(附108例分析)[J].福建医药杂志,2010, 32(5):70-74. [11] 顾钱峰,任能,陈俊波.多层螺旋CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检的应用[J].中国乡村医药,2010,17(12):59-60. [12] 尹广.器官移植患者感染合并症诊断治疗方面的某些进展[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2000,9(5):476-481. [13] North RJ, Jung YJ. Immunity to tuberculosis. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:599-623. [14] el-Agroudy AE, Refaie AF, Moussa OM, et al. Tuberculosis in Egyptian kidney transplant recipients: study of clinical course and outcome. J Nephrol. 2003;16(3):404-411. [15] 谭毅刚,谭守勇,冯宝玲.肾移植术后合并结核病临床分析(附16例报告)[J].临床肺科杂志,2005,10(3):305-306. [16] 潘纪戍.成人胸部结核的CT诊断[J].中华放射学杂志,2000,34(9): 583. [17] 黄建业,武光明,卢永红.胸部CT在肺结核诊断中的作用[J].中外医学研究,2013(1):56-57. [18] 朱彬,周岗鹏,李勇毅.螺旋CT胸部增强扫描对肺结核的诊断价值[J].航空航天医学杂志,2013,24(2):167-168. [19] 姜晓静,范华君,吴晓丽.肺结核的CT诊断分析[J].中国现代药物应用,2013,7(11):58-59. [20] 孟家晓,李品林,龙显荣,等.多层螺旋CT在活动性菌阴肺结核诊断中的价值[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2013,11(3):64-66. [21] 张海燕,李锋.肺结核不典型CT表现及误诊分析[J].中国医药导报,2013(36):98-99,102. [22] ]戴轶,徐春明,杨伟.CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检对肺周围性肿块诊断价值的探讨[J].临床肺科杂志,2013,18(1):11-13. [23] 叶永青,赵祥玲,林承奎,等.CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检在肺部占位性病变诊断中的诊断价值[J].临床肺科杂志,2013,18(2): 233-235. [24] 范洪涛,洪原城,黄鑫成,等.CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检120例临床分析[J].临床肺科杂志,2013,18(3):568-570. [25] 侯晓玮,庄兴俊,宋谦,等.CT引导经皮肺穿刺活检检测晚期非小细胞肺癌表皮生长因子受体基因突变[J].介入放射学杂志,2013, 22(2):125-128. [26] 钱麒钰,马希涛,张晓菊,等.CT引导下经皮肺穿刺的诊断价值[J].医药论坛杂志,2013(2):53-54. [27] 毕惠君,段慧萍,宋承平,等.CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检在菌阴肺结核诊断中的意义[J].山西医药杂志,2013,42(7):394-395. [28] 段慧萍,罗宏,吴吉丽,等. CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检105例分析[J].山西医科大学学报,2013,44(8):610-612. [29] 王舰涛.CT引导下肺穿刺活检术临床应用[J].医学理论与实践, 2013(20):2749-2750. [30] 王学忠,张锦华,徐光辉,等. CT引导下56例经皮肺穿刺活检分析[J].医学理论与实践,2013(18):2471-2472. [31] 张春芳,陆珍凤,印洪林,等.642例CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检病理诊断分析[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2011,27(4):376-378,381. [32] 盛景春,付跃波,王立非,等.CT引导下经皮肺活检对肺部疾病诊断的临床意义[J].中国医药指南,2011,9(10):40-50. [33] 孟家晓,王建华,李品林,等.经皮肺穿刺活检+组织培养在菌阴肺结核诊断中的价值[J].当代医学,2011,14(3):60-62. [34] 王薇,李鸿霞.CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检在28例疑难肺结核诊断中的临床应用[J].农垦医学,2011,33(4):312-314. [35] 高福平.CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检诊断疑难肺结核病9例临床病理分析[J].临床肺科杂志,2012,17(4):672-673. [36] 雷伟,张建生,黄建安.CT引导下经皮肺穿刺并发气胸的危险因素分析[J].江苏医药,2013(4):414-416. [37] 黄勇,杨云辉,吕天甫,等.CT引导下经皮胸肺穿刺活检安全性和准确性分析[J].实用医学影像杂志,2013,14(1):65-67. [38] 王舰涛.CT引导下经皮肺穿刺活检术的并发症及其危险因素分析[J].临床合理用药杂志,2013,6(30):62-63. [39] 解放军肾脏病研究所学术委员会.肾移植术后结核菌感染[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2005,14(1):94-98. [40] 许世阳.利福喷丁治疗肺结核的临床疗效[J].北方药学,2013(8): 36-37. [41] 徐学昌.利福喷丁与利福平在肺结核治疗中的药效比较及安全性评价[J].海峡药学,2012,24(4):85-86. [42] 张学群,王洪霞,覃茂玉.利福喷丁治疗肺结核的疗效观察[J].临床肺科杂志,2005,10(1):54-55. [43] 彭浩.利福喷丁、利福平在初治涂阳肺结核患者治疗中的疗效比较[J].临床肺科杂志,2013,18(7):1331-1332. [44] 郝峥,高秋莲.利福喷丁联合左氧氟沙星治疗初治菌阳肺结核近期疗效观察[J].临床肺科杂志,2013,18 (10):1848-1849. [45] 牛海军,岳双宝,陈俊红.利福喷丁在肺结核患者治疗中的疗效分析[J].当代医学,2013(32):149-150. [46] 翟广,李波,李玉芹,等.利福喷丁与利福平治疗肺结核疗效和安全性的Meta分析[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2011,37(3):523-528. [47] 赵冠人,李国栋,冯端浩.利福喷丁与利福平治疗肺结核的Meta分析[J].中国药物应用与监测,2012,9(2):73-77. [48] 邓家英,彭浩.利福喷丁与利福平对肺结核患者肝功能影响的比较[J].临床肺科杂志,2012,17(6):1081-1082. [49] 朱路平,罗君,李喜.利福喷丁与利福平在治疗肺结核中的临床疗效分析[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(28):146-147. [50] 马飞,范霞.对氨基水杨酸异烟肼治疗复治菌阳肺结核疗效评价[J].临床肺科杂志,2005,10(4):443-444. [51] 陈蕾,吴桂辉,何畏,等.对氨基水杨酸异烟肼联合左氧氟沙星、丙硫异烟胺治疗复治结核临床疗效观察[J].临床肺科杂志,2011, 16(7):1048-1049. [52] 赵丽.对氨基水杨酸异烟肼、利福喷丁治疗难治性肺结核疗效观察[J].中国医药指南,2011,9(26):109-110. [53] 胡建东,林君,李建枝.复治涂阳肺结核2种治疗方案疗效分析[J].职业卫生与病伤,2012,27(3):169-171. [54] 文锦荣.耐多药肺结核病60例临床分析[J].中国医药指南,2012 (36):551-552. [55] Lucey MR, Kolars JC, Merion RM, et al. Cyclosporin toxicity at therapeutic blood levels and cytochrome P-450 IIIA. Lancet. 1990;335(8680):11-15. [56] Prasad TN, Stiff DD, Subbotina N, et al. FK 506 (Tacrolimus) metabolism by rat liver microsomes and its inhibition by other drugs. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1994;84(1): 35-46. [57] 余凌虹,刘耕陶.黄皮酰胺类化合物及五味子素衍化物对小鼠肝细胞色素P-450的诱导作用[J].中国药学杂志,2000,35(7): 16-18. [58] 吴雪,蔡林,石姗平,等.五酯胶囊对肾移植患者他克莫司血药浓度的影响[J].中国药房,2013(43):4095-4097. [59] 唐薇,胡丹,杨荆艳.肾移植受者联合应用五酯胶囊与FK506的药物经济学研究[J].护理实践与研究,2011(4):13-14. [60] 郭晓伟,陈刚,朱兰,等.五酯胶囊对肾移植患者他克莫司血药浓度的影响[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2011(1):95-97. [61] 辛华雯,李罄,吴笑春,等.五酯胶囊与他克莫司合用对肾移植受者的成本与效果评估研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2011,27(4): 295-298. [62] 谢申平,晏强,陈怀周,等.五酯胶囊在肾移植术后的临床应用研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2011,31(9):1213-1215. [63] 郭晓伟.五酯胶囊对肾移植受者他克莫司血药浓度的影响[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2011. |
| [1] | Fu Shuanhu, Qin Kai, Lu Dahan, Qin Haibiao, Gu Jin, Chen Yongxi, Qin Haoran, Wei Jiading, Wu Liang, Song Quansheng. Lumbar spinal tuberculosis implanted with artificial bone with streptomycin sulfate and percutaneous pedicle screw under transforaminal endoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 493-498. |
| [2] | Ye Haimin, Ding Linghua, Kong Weihao, Huang Zutai, Xiong Long. Role and mechanism of hierarchical microchanneled bone scaffolds in promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 621-625. |
| [3] | Wang Xiaobo, Wang Changan, Han Jianle, Yang Qingyan, Yang Shuaiping, Yang Junwei. Influence of conversion from cyclosporine to tacrolimus on glucose metabolism and cardiovascular risk profiles in stable kidney transplant patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2236-2240. |
| [4] | Liu Junchang, Gao Xiaolin, Jiang Taimao. Correlation of CY3A5 genetic polymorphism with concentration/dosage of tacrolimus and individualized administration of tacrolimus after kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1740-1744. |
| [5] | Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, Zhu Xiangqing, Li Ye, He Jie, Tian Chuan, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on thymus structure and function in the aging macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 13-19. |
| [6] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Pan Xinghua. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treating systemic lupus erythematosus in a tree shrew model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 90-95. |
| [7] | Guo Juan, Zheng Shan, Xie Hui, Hu Yahui. An analysis of pathogenic bacteria infection in 422 kidney transplant recipients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5198-5202. |
| [8] | Zhang Xuhan, Wang Li, Tang Baolin, Wan Xiang, Yao Wen, Song Kaidi, Sun Zimin. Pretreatment of unrelated umbilical cord blood transplantation without antithymocyte globulin for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia: follow-up evaluation of 306 cases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4986-4993. |
| [9] | Liu Luhao, Fang Jiali, Zhang Lei, Li Guanghui, Xu Lu, Lai Xingqiang, Xiong Yunyi, Chen Rongxin, Ma Junjie, Chen Zheng. Clinical assessment criteria of donor pancreas transplants for simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4157-4161. |
| [10] | Weng Rui, Ye Linqiang, Huang Xuecheng, Yao Zhensong, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Tang Jingjing, Cai Zhuoyan. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 combined with autologous bone grafting and fusion in the treatment of thoracolumbar tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3609-3614. |
| [11] | Zhang Helong, Wang Huiyan, Li Zhuo, Gao Jianguo, Zhai Qian. In vitro anti-tuberculosis effect of chitosan-gelatin/poly(lactic acid co-glycolic acid) combined with drug-loaded hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(22): 3480-3485. |
| [12] | He Xiaoming, Gong Shuidi, Zheng Xiaolong, Shen Yingshan, Pang Fengxiang, Chen Lixin, Li Weifeng, Yang Fan, Liu Shaojun, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Trends in global research on bone and joint tuberculosis: bibliometrics and visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(20): 3234-3239. |
| [13] | Feng Yang, Yan Xu, Wang Yongkui, Yang Tengyue, Shang Lijie, Zhang Chunlin. Relationship between degenerative lumbar disc disease and peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(17): 2630-2635. |
| [14] |
Yin Zhenyu, Song Jingang, Cui Yikun, Pu Jinsong.
Spinal stability in patients with lumbar spinal tuberculosis with anterior
double titanium mesh support bone grafting and posterior pedicle screw fixation
|
| [15] | Li Xiang, Si Jianwei. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of spine tuberculosis debridement treated by single-segment fixation with short pedicle screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4552-4557. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||