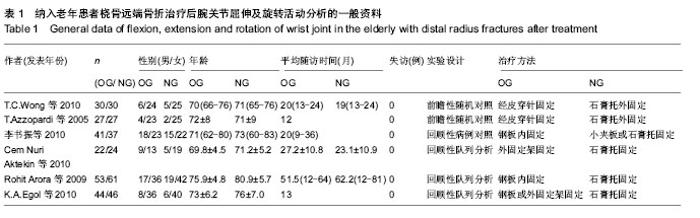
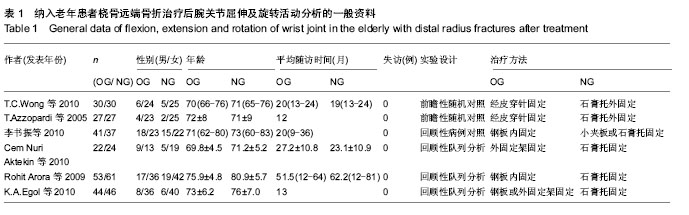
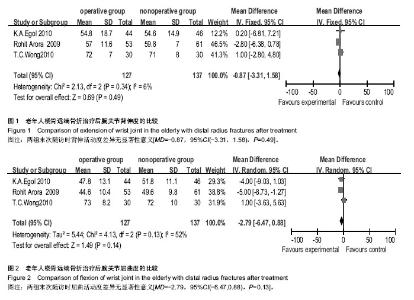
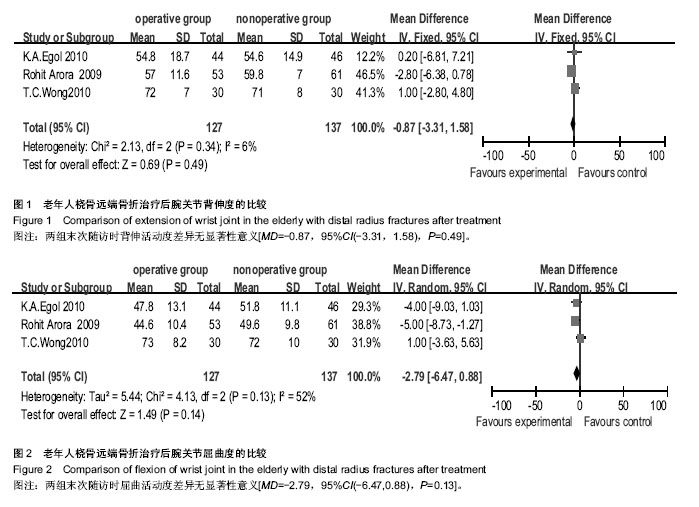
| [1] Hanel DP, Jones MD, Trumble TE. Wrist fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2002;33(1):35-57, vii.
[2] Bengnér U, Johnell O. Increasing incidence of forearm fractures. A comparison of epidemiologic patterns 25 years apart. Acta Orthop Scand. 1985;56(2):158-160.
[3] Fok MW, Klausmeyer MA, Fernandez DL, et al. Volar plate fixation of intra-articular distal radius fractures: a retrospective study. J Wrist Surg. 2013;2(3):247-254.
[4] 杨东方,金林峰.桡骨远端Barton骨折的手术治疗[J].浙江创伤外科,2008,13(5):448-449.
[5] 傅中国,姜保国,张殿英,等.尺桡骨远端粉碎性骨折外固定架的应用和临床观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2001,8(6):554-556.
[6] 安贵生,荣国威,贡小英.外固定架在桡骨远端不稳定骨折治疗中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2003,5(3):203-205.
[7] Akmaz I, Pehlivan O, Kiral A, et al. Short-term results of external fixation of unstable distal radial fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2003;37(2):126-132.
[8] Azzopardi T, Ehrendorfer S, Coulton T, et al. Unstable extra-articular fractures of the distal radius: a prospective, randomised study of immobilisation in a cast versus supplementary percutaneous pinning. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(6):837-840.
[9] 李书振,陈跃平,林宗汉,等.切开复位与闭合复位治疗老年桡骨远端骨折的对比研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(4):438- 442.
[10] Arora R, Gabl M, Gschwentner M, et al. A comparative study of clinical and radiologic outcomes of unstable colles type distal radius fractures in patients older than 70 years: nonoperative treatment versus volar locking plating. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(4):237-242.
[11] Aktekin CN, Altay M, Gursoy Z, et al. Comparison between external fixation and cast treatment in the management of distal radius fractures in patients aged 65 years and older. J Hand Surg Am. 2010;35(5):736-742.
[12] Egol KA, Walsh M, Romo-Cardoso S, et al. Distal radial fractures in the elderly: operative compared with nonoperative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(9):1851-1857.
[13] Wong TC, Chiu Y, Tsang WL, et al. Casting versus percutaneous pinning for extra-articular fractures of the distal radius in an elderly Chinese population: a prospective randomised controlled trial. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2010;35(3): 202-208.
[14] Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996b;17(1):1-12.
[15] Thomas KC, Bailey CS, Dvorak MF, et al. Comparison of operative and nonoperative treatment for thoracolumbar burst fractures in patients without neurological deficit: a systematic review. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;4(5):351-358.
[16] Knirk JL, Jupiter JB. Intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius in young adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986; 68(5):647-659.
[17] Wilcke MK, Hammarberg H, Adolphson PY. Epidemiology and changed surgical treatment methods for fractures of the distal radius: a registry analysis of 42,583 patients in Stockholm County, Sweden, 2004-2010. Acta Orthop. 2013;84(3): 292-296.
[18] Aro HT, Koivunen T. Minor axial shortening of the radius affects outcome of Colles' fracture treatment. J Hand Surg Am. 1991;16(3):392-38.
[19] Baratz ME, Des Jardins Jd, Anderson DD, et al. Displaced intra-articular fractures of the distal radius: the effect of fracture displacement on contact stresses in a cadaver model. J Hand Surg Am. 1996;21(2):183-188.
[20] Wilcke MK, Abbaszadegan H, Adolphson PY. Patient-perceived outcome after displaced distal radius fractures. A comparison between radiological parameters, objective physical variables, and the DASH score. J Hand Ther. 2007;20(4):290-298.
[21] Zhang QL, Zhu XD, Li GD, et al. Treatment of type C3 distal radius fracture resulted from high-energy injuries by volar plate in combination with external fixator. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009;122(13):1517-1520.
[22] Nijs S, Broos PL. Fractures of the distal radius: a contemporary approach. Acta Chir Belg. 2004;104(4): 401-412.
[23] Azzopardi T, Ehrendorfer S, Coulton T, et al. Unstable extra-articular fractures of the distal radius: a prospective, randomised study of immobilisation in a cast versus supplementary percutaneous pinning. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2005;87(6):837-840.
[24] Synn AJ, Makhni EC, Makhni MC, et al. Distal radius fractures in older patients: is anatomic reduction necessary. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(6):1612-1620.
[25] Moher D, Pham B, Klassen TP, et al. What contributions do languages other than English make on the results of meta-analyses? J Clin Epidemiol. 2000;53(9):964-972. |