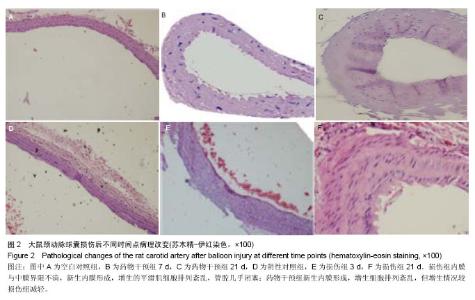
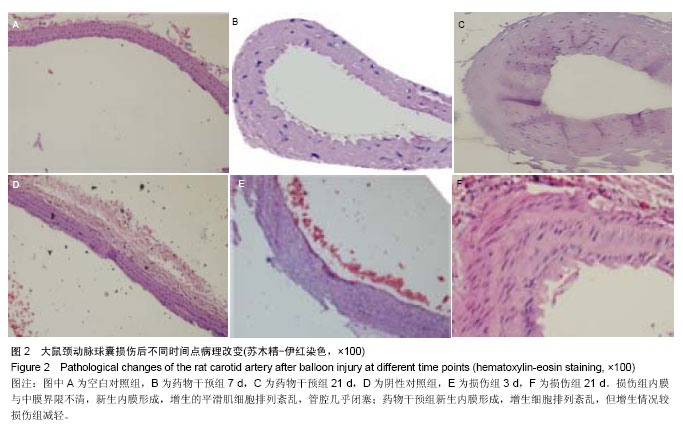
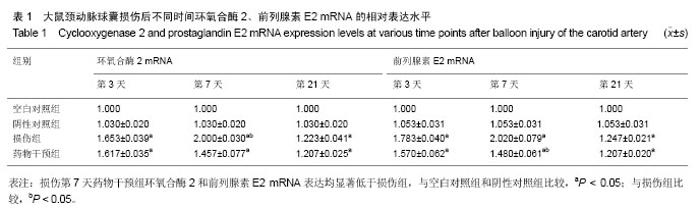
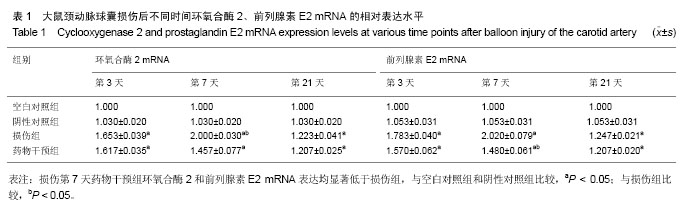
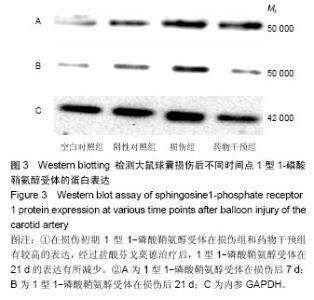
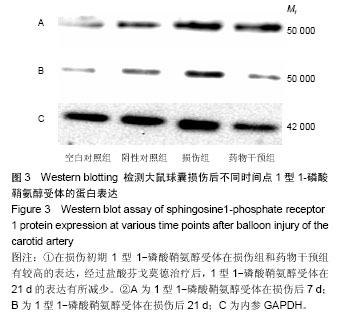
| [1] Dehmer GJ, Smith KJ.Drug-eluting coronary artery stents. Am Fam Physician. 2009;80(11):1245-1251.[2] Simon DI.Inflammation and vascular injury: basic discovery to drug development. Circ J.2012;76(8):1811-1818.[3] Ni HF, Chen JF, Zhang MH, et al.FTY720 attenuates tubulointerstitial inflammation and fibrosis in subtotally nephrectomized rats. Ren Fail. 2013;35(7):996-1004.[4] Edelman ER, Rogers C. Pathobiologic responses to stenting. Am J Cardiol. 1998;81(7A):4E-6E.[5] 束波,范芳. 骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠血管成形术后内膜增生及炎症因子表达的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2012,32(14):2989-2992.[6] 张云飞,董颀,熊龙根.辛伐他汀与环孢素A对大鼠经皮动脉血管成形术术后再狭窄作用的比较[J].广东医学,2012,(7):879-882.[7] 熊龙根,黎德恩,董颀. 球囊扩张术后大鼠腹主动脉钙调神经磷酸酶、血浆MCP-1的变化[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志,2012,20(3):231-234.[8] 董少红,罗特丹,刘华东,等. 颈动脉球囊损伤大鼠白细胞介素6、白细胞介素10及白细胞介素17A mRNA表达:罗格列酮干预的意义[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13 (48):9570-9574.[9] 张春炳,朱健,张秋玉,等. Cyr61、TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β与颈动脉损伤后再狭窄的关系[J]. 上海交通大学学报:医学版,2008, 28(11): 1410-1415.[10] 布伦,贾国良,张薇,等. 罗格列酮对大鼠颈动脉球囊损伤后新生内膜及炎症因子的影响[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志,2007, 15(2):103-106.[11] 李绍冰,傅向华,王春梅,等. 罗格列酮或氯沙坦及二者合用对大鼠血管损伤后再狭窄影响的研究[J].中国老年学杂志,2005, 25(5):546-548.[12] Guo Q, Li QF, Liu HJ,et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 gene transfer reduces postoperative peritoneal adhesion in an experimental model.Br J Surg. 2008;95(2):252-258.[13] Uhlig S, Yang Y.Sphingolipids in acute lung injury. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013;(216):227-246.[14] Takeshita H, Kitano M, Iwasaki T,et al.Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P)/S1P receptor 1 signaling regulates receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) expression in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 419(2):154-159.[15] Kitano M, Hla T, Sekiguchi M, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate/sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 signaling in rheumatoid synovium: regulation of synovial proliferation and inflammatory gene expression. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(3): 742-753.[16] Hsieh HL, Wu CB, Sun CC,et al.Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces COX-2 expression via PI3K/Akt and p42/p44 MAPK pathways in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 2006;207(3):757-766.[17] Ki SH, Choi MJ, Lee CH, et al. Galpha12 specifically regulates COX-2 induction by sphingosine 1-phosphate. Role for JNK-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of IkappaBalpha. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(3):1938-1947.[18] Jarving R,Jarving I,Kurg R,et al.On the evolutionary origin of cyclooxygenase (COX) isozymes: characterization of marine invertebrate COX genes points to independent duplication events in vertebrate and invertebrate lineages. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(14):13624-13633.[19] Fosslien E. Molecular pathology of cyclooxygenase-2 in neoplasia. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2000;30(1):3-21.[20] Huh YH, Kim SH, Kim SJ,et al. Differentiation status-dependent regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E2 production by epidermal growth factor via mitogen-activated protein kinase in articular chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(11):9691-9697.[21] Rimarachin JA, Jacobson JA, Szabo P, et al. Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in aortic smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994;14(7):1021-1031.[22] Escargueil-Blanc I, Meilhac O, Pieraggi MT, et al. Oxidized LDLs induce massive apoptosis of cultured human endothelial cells through a calcium-dependent pathway. Prevention by aurintricarboxylic acid. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17(2):331-339. [23] Wang K, Tarakji K, Zhou Z, et al. Celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, decreases monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression and neointimal hyperplasia in the rabbit atherosclerotic balloon injury model. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2005;45(1):61-67. [24] Liu Z, Zhang C, Dronadula N,et al. Blockade of nuclear factor of activated T cells activation signaling suppresses balloon injury-induced neointima formation in a rat carotid artery model. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(15):14700.[25] Chang W, Lim S, Song H, et al.Cordycepin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008; 597(1-3):64-69.[26] Pernomian L, Gomes M, de Oliveira A. Balloon catheter injury abolishes phenylephrine-induced relaxation in the rat contralateral carotid. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163(4):770-781.[27] Liu B, Han M, Wen JK. Acetylbritannilactone Inhibits Neointimal Hyperplasia after Balloon Injury of Rat Artery by Suppressing Nuclear Factor-{kappa}B Activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;324(1):292-298.[28] Capper EA, Roshak AK, Bolognese BJ, et al. Modulation of human monocyte activities by tranilast, SB 252218, a compound demonstrating efficacy in restenosis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;295(3):1061-1069.[29] Chen YL, Hu CS, Lin FY, et al.Salvianolic acid B attenuates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in vitro in LPS-treated human aortic smooth muscle cells and in vivo in the apolipoprotein-E- deficient mouse aorta. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98(3):618-631.[30] Zhang J, Zou F, Tang J, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostaglandin E(2) promotes injury-induced vascular neointimal hyperplasia through the E-prostanoid 3 receptor. Circ Res. 2013;113(2):104-114.[31] Gardell SE, Dubin AE, Chun J.Emerging medicinal roles for lysophospholipid signaling. Trends Mol Med.2006;12(2): 65-75.[32] Tsunemi S, Iwasaki T, Kitano S, et al. Effects of the novel immunosuppressant FTY720 in a murine rheumatoid arthritis model. Clin Immunol. 2010;136(2):197-204. |