Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (46): 8049-8055.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.46.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Radiation metabolomics of minimally invasive urine biomarkers for X-ray radiation exposure in mice
Wang Min1, Pan Xiao-jing1, Liu Bin 1, 2, Zhang Hong2
- 1 Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 2 Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Science, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China
-
Online:2013-11-12Published:2013-11-30 -
Contact:Liu Bin, Professor, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Science, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China liubkq@lzu.edu.cn -
About author:Wang Min☆, M.D., Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China wangmin@lzu.edu.cn -
Supported by:Major State Basic Research Development Program of China, No. 2010CB834202*; Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 10835011*; General Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30770639*; Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Lanzhou University, No. lzujbky-2012-154*; Support Fund Project of Lanzhou University School of Stomatology, No.120653*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Min, Pan Xiao-jing, Liu Bin, Zhang Hong. Radiation metabolomics of minimally invasive urine biomarkers for X-ray radiation exposure in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(46): 8049-8055.
share this article
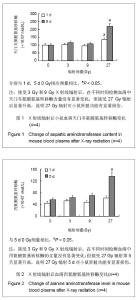
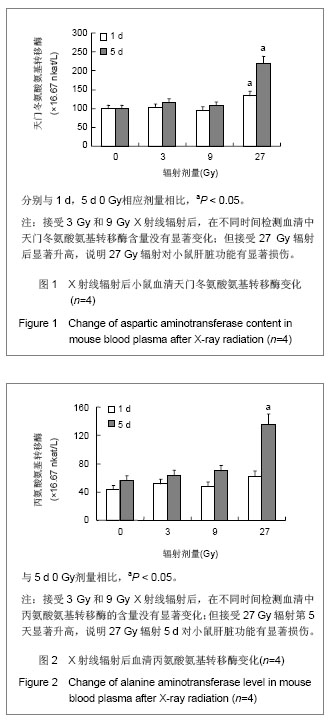
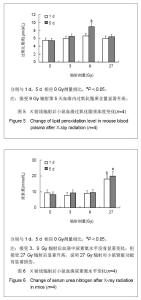
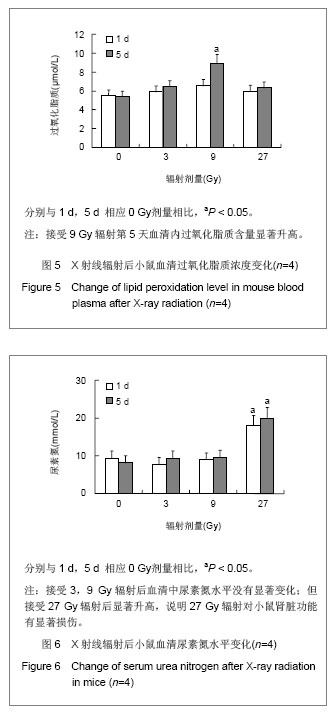
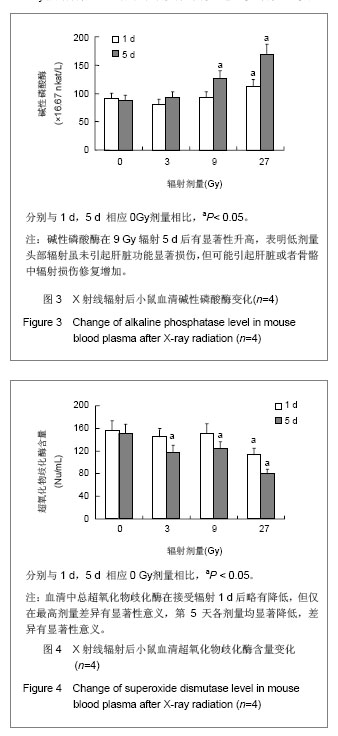
碱性磷酸酶在9 Gy辐射后显著升高,表明低剂量头部辐射虽未引起肝脏功能显著损伤,但可能引起肝脏或者骨骼中辐射损伤修复增加,见图3。血清中总超氧化物歧化酶在辐射后24 h没有显著改变,见图4,但在第5天超氧化物歧化酶显著降低。血清内过氧化脂质含量显著升高,见图5,表明虽然小鼠仅接受头部辐射,但引起了全身过氧化物增多和氧化应激效应。血清中肌酸磷酸激酶和尿素氮水平没有显著变化,见图6,表明局部低剂量辐射并未造成心脏和肾脏功能的显著损伤。但小鼠在接受头部辐射27 Gy剂量后,各项生化指标均发生显著改变,小鼠自发活动减少,毛色枯槁,尿量减少,表明该辐射剂量对小鼠的存活产生严重影响,但9 Gy和27 Gy辐射剂量之间的详细变化需要进一步研究证实。"
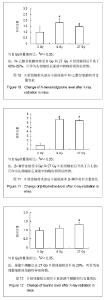
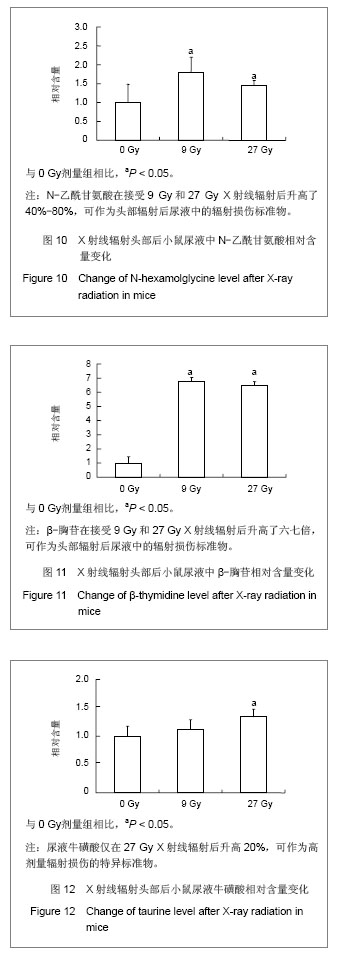
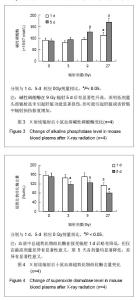
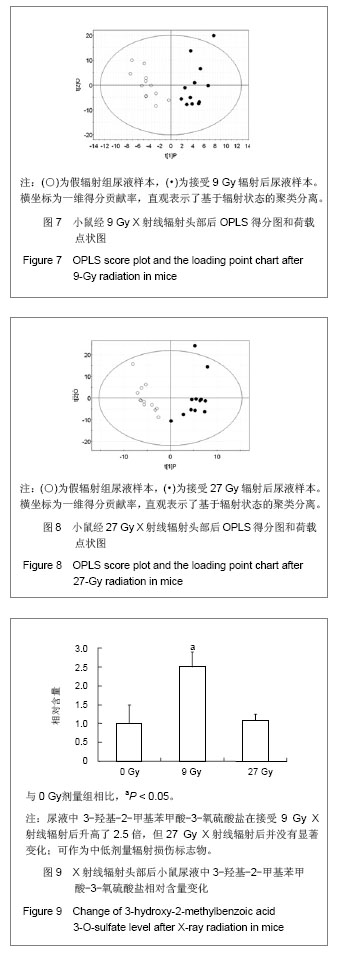
小鼠经27 Gy X射线辐射或假辐射后收集0-24 h尿液,辐射组收集尿液减少,但与假辐射组比较没有统计学差异。依然运用监督的OPLS分析方法,将数据分为辐射组和假辐射组,图8展示了27Gy X射线辐射或假辐射后OPLS得分柱状图。辐射后有3个明确的标志物,分别是N-乙酰甘氨酸,牛磺酸和β-胸苷。 尿液中3-羟基-2-甲基苯甲酸-3-氧硫酸盐在接受 9 Gy X射线辐射后升高了2.5倍,但27Gy X射线辐射后并未变化,见图9;N-乙酰甘氨酸在接受9 Gy和27Gy X射线辐射后升高了40%-80%,见图10;β-胸苷在接受 9 Gy和27 Gy X射线辐射后升高了六七倍,见图11,尿液牛磺酸仅在27 Gy X射线辐射后升高20%,见图12。"
| [1]Garaj-Vrhovac, V, Kopjar N. The alkaline comet assay as biomarker in assessment of DNA damage in medical personnel occupationally exposed to ionizing radiation. Mutagenesis.2003; 18:265-271. [2]Blakely WF, Prasanna PG, Grace MB, et al. Miller. Radiation exposure assessment using cytological and molecular biomarkers. Radiation Protection Dosimetry.2001;97: 17-23. [3]Budhwar R, Bihari VN, Mathur A, et al. DNA-protein cross links as a biomarker of exposure to solar radiation: a preliminary study in brick-kiln workers. Biomarkers.2003;8: 162-166. [4]Porciani S, Lanini A, Balzi M, et al. Polyamines as biochemical indicators of radiation injury. Phys. 2001;17 : ( Suppl. 1) 187-188. [5]Menard C, Johann D, Lowenthal MT, et al. Discovering clinical biomarkers of ionizing radiation exposure with serum proteomic analysis. Cancer Res.2006;66:1844-1850. [6]Arun S, Laila MP, Thekkelnaycke MR, et al. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression.Nature. 2009;457(7231):910-914. [7]Wolfram, RM., Budinsky AC, Palumbo B, et al. Radioiodine therapy induces dose-dependent in vivo oxidation injury: evidence by increased isoprostane 8-epi-PGF.Nucl Med. 2002;43:1254-1258. [8]Wang LF, Hu XJ, Peng RY, et al. Application of 1H-NMR-based metabolomics for detecting injury induced by long-term microwave exposure in Wistar rats' urine. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012; 404(1):69-78. [9]John BT, Andrew DP, Kristopher WK, et al. Radiation metabolomics:1. Identification of minimally invasive urine biomarkers for gamma-radiation exposure in mice. Radiation Research.2008;170(1):1-14. [10]John BT, Andrew DP, Kristopher WK, et al. Radiation metabolomics:2. Dose- and time-dependent urinary excretion of deaminated purines and pyrimidines after sublethal gamma-radiation exposure in mice. Radiat Res.2009; 172(1):42-57. [11]Christian L, Andrew DP, Josef S, et al. Radiation Metabolomics:3. Biomarker discovery in the urine of gamma-irradiated rats using a simplified metabolomics protocol of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry combined with random forests machine learning algorithm. Radiation Research.2009;172(2):198-212. [12]Johnson CH,Patterson AD,Krausz KW,et al.Radiation metabolomics.4. UPLC-ESI-QTOFMS-Based metabolomics for urinary biomarker discovery in gamma-irradiated rats. Radiation Research. 2011;175(4):473-484. [13]Johnson CH, Patterson AD, Krausz KW, et al. Radiation metabolomics. 5. Identification of urinary biomarkers of ionizing radiation exposure in nonhuman primates by mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Radiat Res. 2012;178(4): 328-340. [14]Coy SL, Cheema AK, Tyburski JB, et al. Radiation metabolomics and its potential in biodosimetry. Int J Radiat Biol.2011;87(8):802-823. [15]Ma Z, Huo C, Zhou S, et al. Metabonomic study on siwu tang in radiation-induced blood deficient mice. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.2012;37(9):1289-1295. [16]霍超,王穆,马增春,等.辐射损伤所致血虚证小鼠模型及四物汤反证的代谢组学研究[J]. 天津中医药,2010,27(3):233-235 [17]Wang M, Rang W, Zhang Q, et al. NMR-spectroscopy-based metabonomic approach to analysis of Siwutang, a novel prescription, treated blood deficiency in mice. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.2010;35(5):630-634. [18]Huo C, Ma Z, Wang M, et al. NMR-spectroscopy-based metabonomic study on mouse model of blood deficiency syndrome induced by compound method of bleeding, starved feeding and exhausting and effect of siwu tang. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010;35(23):3194-3198. [19]Chen C, Brenner DJ, Brown TR. Identification of urinary biomarkers from X-irradiated mice using NMR spectroscopy. Radiat Res. 2011;175(5):622-630. [20]Neerathilingam M, Volk DE, Sarkar S, et al. 1H NMR-based metabonomic investigation of tributyl phosphate exposure in rats. Toxicol Lett.2010;199(1):10-16. [21]Schoedl K,Schuhmacher R, Forneck A.Correlating physiological parameters with biomarkers for UV-B stress indicators in leaves of grapevine cultivars Pinot noir and Riesling. Journel of Agriculture Science.2013;151(2):189-200. [22]Lake JA, Field KJ, Davey MP, et al. Metabolomic and physiological responses reveal multi-phasic acclimation of Arabidopsis thaliana to chronic UV radiation. Plant Cell Environ. 2009;32(10):1377-1389. [23]Kim S, Yun EJ, Hossain MA, et al. Global profiling of ultraviolet-induced metabolic disruption in Melissa officinalis by using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem.2012;404(2):553-562. [24]Smutná M, Beňová K, Dvo?ák P, et al. Protein carbonyls and traditional biomarkers in pigs exposed to low-dose gamma-radiation. Research in Veterinary Science.2013, 94(2):214-218. [25]Liu H, Wang Z, Zhang X, et al. Selection of candidate radiation biomarkers in the serum of rats exposed to gamma-rays by GC/TOFMS-based metabolomics. Radiat Prot Dosimetry.2013;154(1):9-17. [26]Gruber F, Bicker W, Oskolkova OV, et al. A simplified procedure for semi-targeted lipidomic analysis of oxidized phosphatidylcholines induced by UVA irradiation. J Lipid Res. 2012;53(6):1232-1342. [27]赵娟,朱一婧,曾露,等.作用于FTase 和Raf-1 激酶的新型抗肿瘤药物的设计[J]. 药学学报,2011,46 (2): 170−178. [28]Bott R, Dublineau I, Gourmelon P, et al. The metabolomic approach identifies a biological signature of low-dose chronic exposure to cesium 137. J Radiat Res. 2012; 53(1):33-43. [29]张芳玲,邵蔚.牛磺酸对NMDA诱导的视网膜神经节细胞损伤的保护作用[J]. 江苏医药,2013,39(3):263-265. [30]陆彩玲,宋凌勇,唐深,等.牛磺酸改善染锰大鼠学习记忆能力的海马蛋白质组学研究[J]. 营养学报,2012,34(6):553-557. [31]杨曦,陆彩玲,郭松超,等.牛磺酸对锰中毒大鼠学习记忆的影响[J].中国药物与临床,2010,10(2):128-130. [32]成兰云,门秀丽,张连元,等.内质网应激诱导的细胞凋亡在大鼠肢体缺血再灌注后肺损伤中的作用及牛磺酸的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2010,26( 9) : 1776-1780. [33]李腾,彭靖,吕尚军,等.甘氨酸对烧伤大鼠心肌细胞能量代谢的影响[J].重庆医学,2012,41(33):3476-3478. [34]Manna SK, Krausz KW, Bonzo JA, et al. Metabolomics Reveals Aging-associated Attenuation of Noninvasive Radiation Biomarkers in Mice: Potential Role of Polyamine Catabolism and Incoherent DNA Damage-repair. J Proteome Res. 2013;12(5):2269-2281. |
| [1] | Li Qin, Mao Shuangfa, Li Min, Cheng Jiyan. Protective effect and mechanism of dendrobium on fibroblasts damaged by ultraviolet B [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1228-1233. |
| [2] | Li Chenkai, Qin Wen, Liu Chun, Chen Wenyang, Zhao Hongbin. Three-dimensional electrohydrodynamic printing of attapulgite/polycaprolactone scaffolds and osteogenic differentiation ability in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5459-5464. |
| [3] | Zheng Weipeng, Hu Weijian, Zhao Guoyuan, Wei Hewei, Liu Zhijun, Wan Lei, Chen Sheng, Liao Zhihao. Effects of Bushen Jianpi Huoxue Recipe on cell proliferation and alkaline phosphatase activity in Beclin-1 overexpressing and silencing MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4650-4655. |
| [4] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [5] | Jiang Shengyuan, Li Dan, Jiang Jianhao, Shang-you Yang, Yang Shuye. Biological response of Co2+ to preosteoblasts during aseptic loosening of the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3292-3299. |
| [6] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [7] | Ailimaierdan·Ainiwaer, Wang Ling, Gu Li, Dilidaer•Taxifulati, Wang Shan, Yin Hongbin. Effect of transforming growth factor-beta3 on the proliferation and osteogenic capability of osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2664-2669. |
| [8] | Luo Yicai, Li Hao. Effect of enhanced aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression on inflammatory response and healing of alveolar bone defects in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2166-2171. |
| [9] | Chen Qiang, Zhuo Hongwu, Xia Tian, Ye Zhewei . Toxic effects of different-concentration isoniazid on newborn rat osteoblasts in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1162-1167. |
| [10] | Qiao Jiutao, Guan Dehong, Wang Dongyan, Liu Aiyun. Zuogui Pill has protective effect against oxidative stress injury in osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1052-1056. |
| [11] | Wu Qi, Liao Ying, Sun Guanghua, Zhou Guijuan, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Zhong Peirui, Cheng Guo, Deng Chengyuan, Wang Tiantian. Changes of subchondral bone in rat models of knee osteoarthritis treated by elcatonin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 709-715. |
| [12] | Zhang Huxiong, Li Wei, Yang Wupeng, New Suyaratu. 3D-printed icariin/decalcified bone matrix material promotes the repair of femoral condyle defects in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5461-5466. |
| [13] | Bai Zhenjun, Liu Tong, Wang Zirun, Zhang Huiyu, Xu Peng. Effect of “Lumbar Three Needles” on expression of oxidative stress factors in rats with multifidus muscles injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5145-5150. |
| [14] | Yan Caiping, Chen Lu, Deng Changgong, Chen Qian, Jiang Ke, Yi Yuanyuan, Li Yuling. Beta-ecdysterone promotes in vitro proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4605-4612. |
| [15] | Wang Yanling, Shao Zhe, He Wei. Micro-arc oxidation and osteoblast proliferation and osteogenic differentiation ability on titanium surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(22): 3486-3490. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||