Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (41): 7323-7328.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.41.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cholecystokinin and nerve repair
Chen Xuan-huang, Hu Li-bin, Li Rong-yi, Cai Han-hua
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Putian University, Putian 351100, Fujian Province, China
-
Received:2013-06-18Revised:2013-08-07Online:2013-10-08Published:2013-11-01 -
Contact:Li Rong-yi, Chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Putian University, Putian 351100, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Chen Xuan-huang★, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Putian University, Putian 351100, Fujian Province, China ptyygk@163.com -
Supported by:the General Class A Scientific Program of Fujian Educational Department, No. JA11212*; the Medical Plan of Putian City, No. 2012S03(4)*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Xuan-huang, Hu Li-bin, Li Rong-yi, Cai Han-hua. Cholecystokinin and nerve repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(41): 7323-7328.
share this article
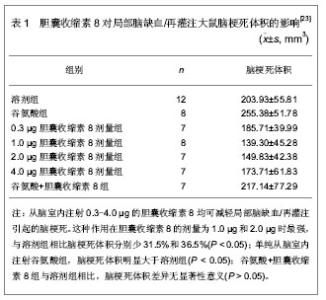
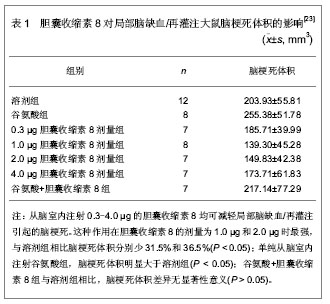
2.1 胆囊收缩素在神经损伤后的变化 Chang等[13]实验证明,猫脊髓和迷走神经、坐骨神经等周围神经内存在胆囊收缩素,受刺激后,能以与典型的神经递质及递质合成酶相近的速度向外周神经末端快速顺行传递,并作为一种神经递质,兴奋突触后膜,而且坐骨神经中胆囊收缩素传递速度比迷走神经快。Wu 等[14]也有研究证实,在鼠迷走神经切断后,背根神经节活动活跃,胆囊收缩素B受体过表达致使胆囊收缩素表达和反应能力增强,而这种改变可能是神经损伤后修复与再生开始的信号。Verge等[15]研究发现坐骨神经切断后,由于来自周围组织的神经营养信号中断,初级传入神经元胆囊收缩素表达增强,注射外源性神经生长因子可使胆囊收缩素恢复正常水平,提示神经损伤后的反应机制中,胆囊收缩素和神经生长因子有助于轴突的生长和受损神经元营养支持的重建,共同参与周围神经元的存活和再生。 2.2 胆囊收缩素与神经生长因子的相关性 胆囊收缩素可上调神经生长因子的表达:神经生长因子是一种神经营养因子,在周围和中枢神经元的生长和再生过程中发挥着重要的作用。可以调节周围感觉神经元及交感神经元的生长和分化,并在神经递质和神经肽的调制及周围神经损伤后的修复过程中发挥着重要的作用[16]。 2000至2001年,Manni等[17-18]通过给小鼠皮下注射一种神经毒素-辣椒辣素,研究胆囊收缩素与神经生长因子对感觉神经元的作用,结果发现,胆囊收缩素能引起神经生长因子的表达,并能引起化学或损伤后神经细胞功能和结构的恢复,通过在体研究证明,神经损伤后应用胆囊收缩素后可引起组织中神经生长因子蛋白质和神经生长因子mRNA含量的增加,并且这一作用仅在神经元损伤后才能发挥。 2002年,Tirassa等[19]研究6-羟多巴注射后引起交感神经障碍的动物模型,发现每天注射胆囊收缩素可使交感神经支配的虹膜部分的恢复,眼中的神经生长因子水平增加,这些数据表明,在中枢及周围神经系统遭受化学或损伤后,胆囊收缩素可阻碍神经元的丢失,并且神经生长因子参与了胆囊收缩素介导的修复过程,而在正常状态下,胆囊收缩素可能只影响了神经生长因子的基础更新率,由此可说明胆囊收缩素对周围神经损伤后的修复有促进作用,其机制可能是通过外源性胆囊收缩素介导调节神经生长因子合成和释放来完成的。 既往研究已经证明周围神经损伤与神经生长因子表达减弱或神经生长因子的合成、运输有关,而在2003年,Cahill等[20]也通过实验证明,神经生长因子对维持痛觉神经元的神经化学平衡,恢复痛觉丧失有重要意义,在坐骨神经挤压伤后给予神经生长因子鞘内注射可明显增强吗啡的镇痛作用,说明神经生长因子和胆囊收缩素之间存在一个反馈调节环路,二者互相调节,共同发挥神经保护作用。 胆囊收缩素促进神经生长因子合成的机制:胆囊收缩素受体广泛存在于外周,因此胆囊收缩素如何影响周围神经系统和外周组织神经生长因子表达的机制目前还不清楚。Kurosawa等[21]研究发现神经生长因子主要受迷走神经的影响,海马和下丘脑神经生长因子的改变是由胃迷走神经传入的选择型电刺激产生的,而迷走神经又能被外源性胆囊收缩素激活,因此,外源性胆囊收缩素调节神经生长因子的合成已被作为胆囊收缩素的生理功能之一。有人观察到胆囊收缩素B受体拮抗剂能调节神经生长因子的合成,提示胆囊收缩素调节神经生长因子合成的机制与胆囊收缩素B受体有关。Wiesenfeld-Hallin等[22]报道辣椒辣素和6-羟多巴处理后的胆囊收缩素仍然能修复神经功能障碍,说明完整的神经末梢不是必需的,局部的而不是全身的胆囊收缩素注射可激活外周胆囊收缩素受体,而且胆囊收缩素在周围神经的效应可受中枢部位的调节,由此可以推测胆囊收缩素可能从中枢对损伤的周围神经产生效应,但是胆囊收缩素通过外周途径作用的可能性也不能排除。 2.3 胆囊收缩素对神经损伤后微环境中诱导型一氧化氮合成酶表达的影响 2003年,杨世方等[23]采用线栓法建立大鼠局部脑缺血再灌注模型。随机分组如下:溶剂组为缺血前15 min从脑室内注射5 µL的人工脑脊液;不同剂量的胆囊收缩素8各组均于缺血前15 min从脑室内注射以5 µL人工脑脊液胆囊收缩素8,剂量分别为0.3,1.0,2.0和4.0 µg;谷氨酸组:缺血前15 min从脑室内注射谷氨酸;谷氨酸+胆囊收缩素8组为脑缺血前20 min先从脑室内注射谷氨酸,5 min后从脑室内注射胆囊收缩素8,观察侧脑室注射胆囊收缩素8或其受体拮抗剂-谷氨酸对脑缺血1 h再灌注24 h大鼠脑梗死体积的影响,各组动物例数及结果,见表1。"
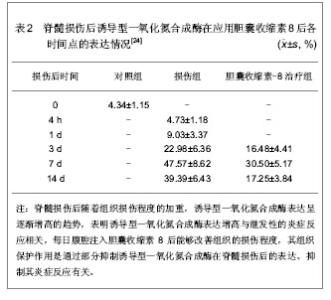
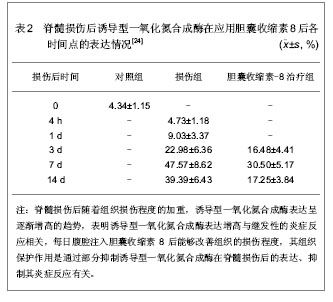
2005年,李德生等[24]在脊髓水平上,将胆囊收缩素对神经损伤后诱导型一氧化氮合成酶表达的影响进行了进一步研究。将36只SD大鼠随机分成3组:对照组4只,仅行椎板切开术,不损伤脊髓;损伤组20只,脊髓损伤后每天腹腔内注入生理盐水1 mL,分别于伤后4 h,1,3,7,14 d取材;胆囊收缩素8治疗组12只,脊髓损伤后每日腹腔内注入1 mL的胆囊收缩素8,分别于伤后3,7,14 d取材,参照改良的Gruner法建立大鼠T9脊髓损伤模型,用免疫组化研究损伤后不同时间点诱导型一氧化氮合成酶的表达变化;选取3个表达最强时间点应用胆囊收缩素8腹腔内注射观察诱导型一氧化氮合成酶的表达变化,结果见表2。"

2.4 胆囊收缩素对神经保护的作用机制 胆囊收缩素发挥神经保护的作用机制仍不明确,具有充分说服力的证据很少。但已有的资料提示胆囊收缩素可能通过某几种直接或间接的方式起作用:①胆囊收缩素可减少一氧化氮的合成。Tamura等[25]对培养的神经细胞的研究发现,一氧化氮介导了谷氨酸的细胞毒性,即谷氨酸激活N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体引起Ca2+内流,Ca2+和钙调素结合进而激活一氧化氮合酶,一氧化氮大量合成并扩散到临近细胞引起细胞损伤,同时胆囊收缩素对N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体激活引起的Ca2+内流无影响,但可通过胞内某种信号转导系统抑制Ca2+和钙调素复合体的形成或一氧化氮合酶的激活,减少一氧化氮合成,最终拮抗谷氨酸的神经毒性作用。②Kapás等[26]研究发现胆囊收缩素或其类似物可降低体温和脑温,降低体温或脑温对脑缺血神经元具有明显的保护作用。③胆囊收缩素可减少脑缺血时K+的大量外流,脑缺血时,梗死区三磷腺苷严重耗竭,细胞内外离子稳态破坏,大量外流并在细胞外积聚,梗死区高浓度的K+向周边半暗区扩散引起扩撒抑制样去极化,进一步加重了代谢负荷,使半暗区向不可逆损伤转化。胆囊收缩素可抑制离体海马脑片中间神经元静息状态下K+电导,减少K+外流,抑制梗死周围去极化可缩小缺血梗死体积。④胆囊收缩素可刺激神经生长因子的表达和释放。Tirassa等[27]研究发现小鼠腹腔注射胆囊收缩素8,15 min后可使下丘脑和垂体神经生长因子水平增加3倍,海马神经生长因子水平增加60%,因此,推测神经生长因子的升高可能是胆囊收缩素对缺血脑产生保护作用的机制之一。⑤胆囊收缩素可调控脑氨基酸类神经递质的释放。 2.5 胆囊收缩素的神经保护作用 胆囊收缩素在细胞水平的神经保护作用:Katsuura等[28]研究发现,胆囊收缩素8、胆囊收缩素类似物蓝肽、胃泌素1分别和谷氨酸同时加入到培养的神经细胞中,均可抑制谷氨酸引起的标志细胞损伤或死亡的乳酸脱氢酶的释放,且呈浓度依赖性。随后Akaike 等[29]也报道了胆囊收缩素8、胆囊收缩素类似物蓝肽可以通过作用于胆囊收缩素-B抑制N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体介导的谷氨酸对培养的大鼠大脑皮层神经元的毒性作用,且胆囊收缩素及其类似物的有效保护浓度远低于N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体拮抗MK-801或氯胺酮的浓度。梁英武[30]等观察胆囊收缩素8对谷氨酸神经毒性作用所致神经元病理损害的影响。采用扫描及透射电镜技术分别观察经不同因素处理后的原代培养的大鼠大脑皮质神经元和经侧脑室注射药物后的大鼠海马CA1区神经元的形态学变化 ,同时应用生物体视学计量分析法对细胞内线粒体各指标的变化进行比较。结果显示,胆囊收缩素8在体内外均能明显改善谷氨酸所致神经元胞体、细胞膜肿胀及破溃,轴、树突断裂、丢失或线粒体肿胀、数目减少等病理损害。因此,胆囊收缩素8在体内外具有拮抗谷氨酸神经毒性作用。 胆囊收缩素在器官水平的神经保护作用:Minamoto等[31]通过实验研究中观察到胆囊收缩素预处理可以明显加重缺血所致的海马CA1区神经元突触钱峰电位幅度的下降,且具有剂量依赖性。与此相反,Yasui等[32]在类似的模型上观察到胆囊收缩素可以明显加快缺血引起的海马CA1区神经元群体峰电位消失后的恢复。产生这两种不同的结果,认为有可能是方法学的不同造成的,如所用动物种属、缺血时间、观察指标的不同。 胆囊收缩素对脊髓损伤的保护作用:急性创伤性脊髓损伤后的炎症反应是继发性损伤的主要机制,核因子кB是众多细胞因子和炎症介质表达的主要转录因子之一,核因子кB的活化可诱导产生大量的肿瘤坏死因子a,白细胞介素1等促炎因子,在许多炎症疾病中起着非常重要的作用[33]。核因子кB是参与脊髓继发性炎症反应的一个重要信号转导分子[34],寻找有效的核因子кB抑制剂,是治疗的关键。扈玉华等[35]探讨了胆囊收缩素作用于脊髓的机制,使用电泳迁移率变动分析技术及免疫印记法分析胆囊收缩素8对急性创伤性脊髓损伤后核因子кB活性的影响。胆囊收缩素及其受体在脊髓的广泛分布,是应用胆囊收缩素8治疗急性脊髓损伤的重要生理基础。已经有大量实验支持损伤早期神经系统中有氧自由基增加核细胞膜脂质过氧化。已知氧化应激是核因子кB激活的重要途径,而胆囊收缩素8可提高血液超氧化物酶歧化酶活性,具有抗氧化效应[36],从而间接的抑制核因子кB的激活,核因子кB与抑制蛋白I-кB集合成无活性的形式存在于胞质中,当其受氧化剂、细菌、毒素等刺激后被激活,从而使Rel蛋白的核定位信号暴露,导致核因子кB快速移至核内,结合在北诱导基因启动子序列上与之相同的кB位点,致转录增加,蛋白质合成增加。可以推测抑制I-кB的降解是胆囊收缩素8发挥作用的主要机制。其分子机制可能是胆囊收缩素8通过抗氧化及诱导cAMP增加的方式来抑制I-кB的磷酸化,使IкB-NF-кB复合物结构趋于稳定,从而最大程度上减轻了急性脊髓损伤后的继发性损害。 胆囊收缩素临床应用于神经保护的前期实验研究:陈宣煌[37,38-39]创新性地将胆囊收缩素应用于动物周围神经损伤方面的研究,观察大鼠失神经改变情况及再生神经的大体形态;步态分析测定坐骨神经功能指数恢复率;检测坐骨神经复合神经动作电位、感觉神经动作电位和腓肠肌复合肌肉动作电位,分别记录潜伏期、波幅和神经传导速度;切取损伤远端神经,半薄切片行苏木精-伊红及固绿髓鞘染色,观察再生神经的组织学变化,测定再生有髓神经纤维计数恢复率;对比腓肠肌湿重恢复率。综合各种指标比较全面地进行效果评价,认为胆囊收缩素能有效地促进周围神经损伤后的修复,有利于再生神经纤维传导功能及肢体运动功能的恢复,且再生纤维数量及质量优,能有效防止神经损伤后骨骼肌萎缩。刘合庆[40]认为陈宣煌通过实验研究证实胆囊收缩素能促进大鼠坐骨神经再生这一发现,为临床修复神经缺损开辟了一个新方法。在此基础上,其进一步用外源性胆囊收缩素在大鼠坐骨神经缺损端聚乳酸-聚羟基乙酸共聚物导管制成的再生室内给药,研究胆囊收缩素和聚乳酸-聚羟基乙酸共聚物导管共同构成的复合组织导管(即人工神经)对神经缺损的修复效果,证实在周围神经缺损端局部应用胆囊收缩素时,也能够表现出胆囊收缩素促神经修复与再生的作用。以上前期实验的成功,为临床应用胆囊收缩素促进神经再生提供了理论依据,预示着胆囊收缩素神经保护广阔的实践应用前景。"

| [1] Noble F,Wank SA,Crawley JN,et al.International Union of Pharmacology.XXI.Structure,distribution,and unctions of cholecystokinin receptors.Pharmacol Rev.1999;51(4): 745-781.
[2] 黄江.周围神经损伤的基因治疗[J].广西医学,2006,28(9): 1420-1423.
[3] 李培建,李兵仓.基因治疗在周围神经损伤修复中的应用前景[J].现代康复,2001,5(7):46-47.
[4] 孙小单,李羽佳.神经生长因子促神经再生作用的研究进展[J].辽宁医学院学报,2010,31(4):377-380.
[5] 刘丽丽,周江堡,肖农.胆囊收缩素在周围神经损伤中的作用[J].国际神经病学神经外科学杂志,2006,33(1):82-84.
[6] 陈宣煌,吴献伟,张国栋,等.胆囊收缩素促大鼠坐骨神经再生的初步研究[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2011,5(24):7242-7247.
[7] 梁英武,宋爱芹,曹勇,等.NMDA诱导神经元胆囊收缩素mRNA表达及其机制研究[J].济宁医学院学报,2002,25(4):1-3.
[8] 文迪,闫玉仙,丛斌,等.胆囊收缩素对中枢阿片系统的调节作用[J].中国药物依赖性杂志,2010,19(3):167-170.
[9] Ma L,Lei L,Eng SR,et al.Brn3a regulation of TrkA/NGF receptor expression in developing sensory neurons. velopment.2003;130(15):3525-3534.
[10] Broberger C,Holmberg K,Shi TJ,et al.Expression and regulation of cholecystokinin and cholecystokinin receptors in rat nodose and dorsal root ganglia.Brain Res.2001;903 (1-2): 128-140.
[11] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-5-15. https://www.cnki.net
[12] SCI数据库.Web of Sciencevia ISI Web of Knowledge[DB/OL]. 2013-5-15.http://ip-science.thomsonreuters.com/mjl
[13] Chang TM,Thagesen H,Lee KY,et al.ine vagus nerve stores cholecystokinin-58 and -8 but releases only cholecystokinin-8 upon electrical vagal stimulation.Regul Pept.2000;87(1-3): 1-7.
[14] Wu HE,Schwasinger ET,Hong JS,et al.Pretreatment with antiserum against dynorphin, substance P, or cholecystokinin enhances the morphine-produced anti-allodynia in the sciatic nerve ligated mice.Neurosci Lett.2005;386(1):46-51.
[15] Verge VM,Richardson PM,Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z,et al.Differential influence of nerve growth factor on neuropeptide expression in vivo: a novel role in peptide suppression in adult sensory neurons.J Neurosci. 1995; 15(3):2081-2096.
[16] Donnerer J.Improved neurochemical recovery of 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned postganglionic sympathetic neurons by nerve growth factor in the adult rat.Neurosci Lett.1996;221(1):33-36.
[17] Manni L,Lundeberg T,Tirassa P,et al.Cholecystokinin-8 enhances nerve growth factor synthesis and promotes recovery of capsaicin-induced sensory deficit.Br J Pharmacol. 2000;129(4):744-750.
[18] Manni L,Aloe L,Tirassa P,et al.Cholecystokinin-8 promotes recovery of sympathectomy induced by 6-hydroxydopamine in adult mice.Neuroreport.2001;12(8):1621-1627.
[19] Tirassa P,Manni L,Aloe L,et al.Cholecystokinin-8 and nerve growth factor: two endogenous molecules working for the upkeep and repair of the nervous system.Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord.2002;1(5):495-510.
[20] Cahill CM,Dray A,Coderre TJ.Intrathecal nerve growth factor restores opioid effectiveness in an animal model of neuropathic pain.Neuropharmacology.2003;45(4):543-552.
[21] Kurosawa M,Bucinskaite V,Taniguchi T,et al.Response of the gastric vagal afferent activity to cholecystokinin in rats lacking type A cholecystokinin receptors.J Auton Nerv Syst.1999; 75(1):51-59.
[22] Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z,de Araúja Lucas G,Alster P,et al. Cholecystokinin/opioid interactions.Brain Res.1999;848(1-2): 78-89.
[23] 杨世方,凌亦凌,段国辰.胆囊收缩素与神经保护[J].中国病理生理杂志,2003,19(1):134-138.
[24] 李德生,许百男,王世波,等.八肽胆囊收缩素抑制大鼠脊髓损伤后诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(9):24-25.
[25] Tamura Y,Sato Y,Akaike A,et al.Mechanisms of cholecystokinin-induced protection of cultured cortical neurons against N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated glutamate cytotoxicity.Brain Res.1992;592(1-2):317-325.
[26] Kapás L,Obál F Jr,Alföldi P,et al.Effects of nocturnal intraperitoneal administration of cholecystokinin in rats: simultaneous increase in sleep, increase in EEG slow-wave activity, reduction of motor activity, suppression of eating, and decrease in brain temperature.Brain Res.1988;438(1-2): 155-164.
[27] Tirassa P,Stenfors C,Lundeberg T,et al.Cholecystokinin-8 regulation of NGF concentrations in adult mouse brain through a mechanism involving CCK(A) and CCK(B) receptors.Br J Pharmacol.1998;123(6):1230-1236.
[28] Katsuura G,Shinohara S,Shintaku H,et al.Protective effect of CCK-8 and ceruletide on glutamate-induced neuronal cell death in rat neuron cultures: possible involvement of CCK-B receptors.Neurosci Lett.1991;132(2):159-162.
[29] Akaike A,Tamura Y,Sato Y,et al.Cholecystokinin-induced protection of cultured cortical neurons against glutamate neurotoxicity.Brain Res.1991;557(1-2):303-307.
[30] 梁英武,张国荣,单巍松,等.胆囊收缩素八肽拮抗谷氨酸神经毒性作用的病理研究[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志,1997,23(4): 210-212.
[31] Minamoto Y,Tanaka T,Shibata S,et al.Neuroprotective effect of cholecystokininB receptor antagonist on ischemia-induced decrease in CA1 presynaptic fiber spikes in rat hippocampal slices.Neurosci Lett.1994;167(1-2):81-84.
[32] Yasui M,Kawasaki K.CCKB receptor activation protects CA1 neurons from ischemia-induced dysfunction in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats hippocampal slices.Neurosci Lett.1995;191(1-2):99-102.
[33] Baldwin AS Jr.The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights.Annu Rev Immunol.1996;14: 649-683.
[34] Bethea JR,Castro M,Keane RW,et al.Traumatic spinal cord injury induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation.J Neurosci. 1998;18(9):3251-3260.
[35] 扈玉华,张庆俊,李建峰,等.胆囊收缩素-8对大鼠急性脊髓损伤核因子-κB活性的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2001, 23(6): 345-347.
[36] 凌亦凌,黄善生,张君岚,等.胆囊收缩素对内毒素性休克大鼠SOD、MDA及吞噬细胞发光的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 1997,5(13):483-486.
[37] 陈宣煌.八肽胆囊收缩素(CCK-8)促进大鼠坐骨神经再生的实验研究[D].福建:福建医科大学,2007:1-46.
[38] 陈宣煌,郑祖高,占鲤生,等.胆囊收缩素对大鼠坐骨神经损伤后修复的影响[J].南昌大学学报:医学版,2012,52(7):4-7.
[39] 陈宣煌,郑祖高,占鲤生,等.胆囊收缩素促大鼠坐骨神经再生的电生理检测及意义[J].海南医学院学报,2012,18(7):869-871.874
[40] 刘合庆.CCK-8构建人工神经桥接修复大鼠坐骨神经缺损的实验研究[D].山东:泰山医学院,2010:1-53. |
| [1] | Wang Qin, Shen Cheng, Liao Jing, Yang Ye. Dapagliflozin improves renal injury in diabetic nephropathy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1216-1222. |
| [2] | Xiao Yang, Gong Liqiong, Fei Jing, Li Leiji. Effect of electroacupuncture on nerve growth factor and its receptor expression in facial nerve nucleus after facial nerve injury in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1253-1259. |
| [3] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [4] | Wen Xiaoyu, Sun Yuhao, Xia Meng. Effects of serum containing Wuzang Wenyang Huayu Decoction on phosphorylated-tau protein expression in Alzheimer’s disease cell model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1068-1073. |
| [5] | Dong Miaomiao, Lai Han, Li Manling, Xu Xiuhong, Luo Meng, Wang Wenhao, Zhou Guoping. Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3/cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1 in rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 749-755. |
| [6] | Xu Jing, Yan Yongmin, Cai Mengjie . miR-373 inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by downregulating transforming growth factor beta type II receptor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 756-761. |
| [7] | Fan Danyang, Fu Runze, Mi Jiajing, Liu Chunyan. Expression and role of cannabinoid receptors during bone remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 283-288. |
| [8] | Xu Lin, Qi Hongshun, Ge Rucun, Li Peipei, Zhen Lixiao, Feng Xiaoya. Effects of minimally invasive surgery combined with metformin on inflammatory responses in rabbits with intracerebral hemorrhage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1741-1746. |
| [9] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [10] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [11] | Zhi Jiajia, Du Chaozheng, Wang Yuze. Pyroptosis in the progression of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5204-5209. |
| [12] | Ye Erbai, Xiao Xiaoling, He Ziyu, Yang Chun, Du Yikuan. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor signaling pathway is involved in the metabolic regulation of obesity by intestinal flora and brown adipose tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5222-5226. |
| [13] | Huang Zhusong, Lin Yu, Chen Xiang, Lan Jinfu, Guan Yong, Gao Xi. Alcohol extract of Morinda officinalis improves lipid metabolism and bone metabolism in ovariectomized obese rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 205-210. |
| [14] | Chen Yutong, Li Chenchen, Liu Yang, Zheng Yaqin, Yang Xihua, An Meiwen. Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model in Wistar rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 237-241. |
| [15] | Fan Siqi, Zeng Ping, Nong Jiao, Liu Jinfu, Qian Xiaofen. Effect of Tongluo Shenggu Capsule-containing serum on osteoclasts and Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2155-2160. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||