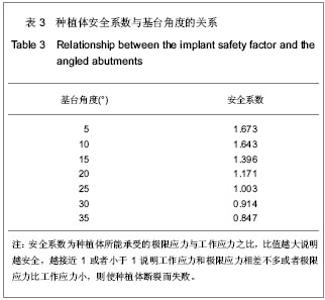
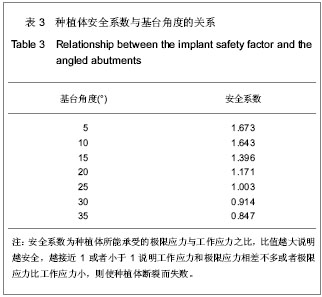
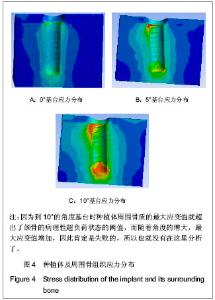
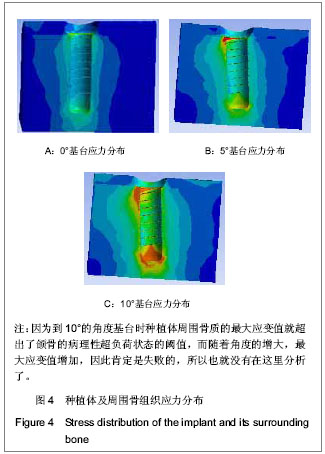
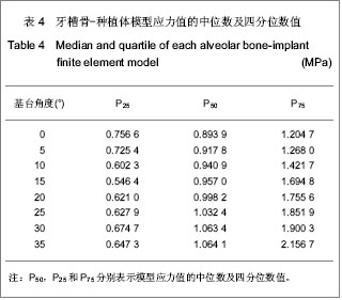
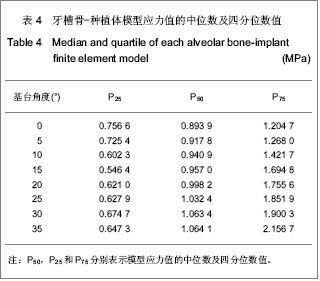
| [1] 邹德荣,蒋欣泉,张志愿.上颌窦提升同期种植的研究现状[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2010,20(1):49-52.[2] Thomas A, Raman R. A comparative study of the pneumatization of the mastoid air cells and the frontal and maxillary sinuses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1989;10(5 Suppl): S88.[3] 王丽萍,张树标,范长斌.倾斜种植体联冠桥修复上颌后牙游离缺失伴骨量不足的临床研究[J].广东牙病防治,2010,18(4): 183-186.[4] Eberhardt JA, Torabinejad M, Christiansen EL. A computed tomographic study of the distances between the maxillary sinus floor and the apices of the maxillary posterior teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1992;73(3):345-346.[5] Kwak HH, Park HD, Yoon HR, et al. Topographic anatomy of the inferior wall of the maxillary sinus in Koreans. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;33(4):382-388.[6] 张卉卉.上颌后牙区严重骨萎缩的种植修复设计[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2009,14(2):136-137.[7] 顾章愉,黄健,阮宏,等.两个种植体倾斜植入联合修复时应力分布的初步研究[J].中国临床医学,2007,14(6):906-908.[8] 陈祖贤,王超,王立军,等.上颌前牙区非埋入式种植体不同角度基台的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(30):5591-5595.[9] 皮昕.口腔解剖生理学[M].5版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2003:257.[10] Lin D, Li Q, Li W, e al. Dental implant induced bone remodeling and associated algorithms. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2009;2(5):410-432. [11] O'Mahony AM, Williams JL, Spencer P. Anisotropic elasticity of cortical and cancellous bone in the posterior mandible increases peri-implant stress and strain under oblique loading. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001;12(6):648-657.[12] Kayaba?? O, Yüzbas?o?lu E, Erzincanl? F. Static, dynamic and fatigue behaviors of dental implant using finite element method. Adv Eng Softw. 2006;37:649–658.[13] Borchers L, Reichart P. Three-dimensional stress distribution around a dental implant at different stages of interface development. J Dent Res. 1983;62(2):155-159.[14] Kao HC, Gung YW, Chung TF, et al. The influence of abutment angulation on micromotion level for immediately loaded dental implants: a 3-D finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008;23(4):623-630.[15] Tada S, Stegaroiu R, Kitamura E, et al. Influence of implant design and bone quality on stress/strain distribution in bone around implants: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003;18(3):357-368.[16] 吕渭莉,石红光.应力与牙槽骨的吸收和改建[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2003,12(2):86-88.[17] 黎小坚,Harold M Frost,朱绍舜,等.基础骨生物学新观[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2001,7(3):253-261.[18] Robling AG, Castillo AB, Turner CH. Biomechanical and molecular regulation of bone remodeling. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2006;8:455-498.[19] Korioth TW, Hannam AG. Deformation of the human mandible during simulated tooth clenching. J Dent Res. 1994;73(1): 56-66. |