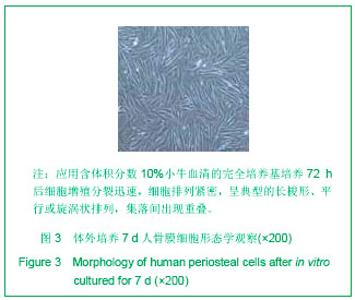
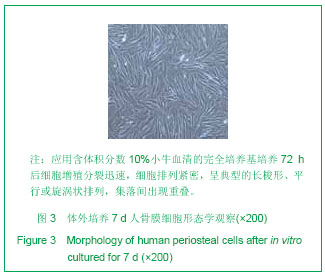
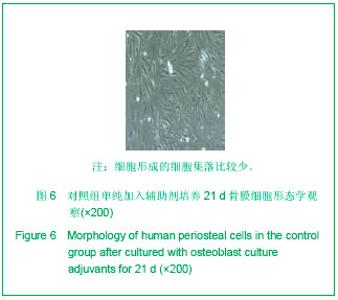
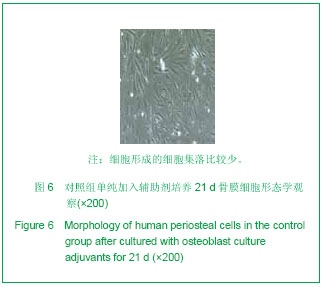
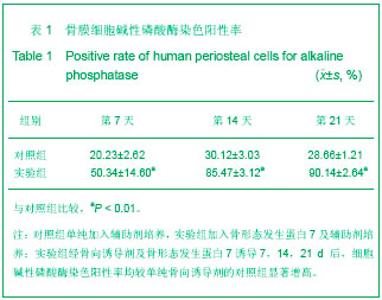
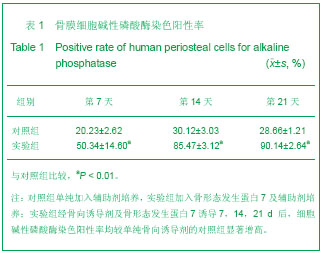
| [1] 宋守礼,朱盛修,孙翠萍,等.骨膜细胞移植修复股骨头缺血性坏死的实验研究[J].中华医学杂志,1998,78(1):52-54. [2] 宋守礼,朱盛修, 张伯勋,等. 经皮注射 自体骨膜细胞修复骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1997,17(11):696-698. [3] Akihiko T,Yukie K,Kiyonori H,et al.Osteogeneic potential of cultured periosteal cells in distracted bone gap in rabbits.J Sur Res.1998;78(1):68-77. [4] 贝抗胜,刘建平.人骨膜细胞体外培养的实验研究与临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004, 9(17):1329-1331. [5] Wozney JM. The bone morphogenetic protein family : multifunctional cellular regulators in the embryo and adult.Eur J Oral Sci.1998;106(Suppl1):160-166. [6] 胡丽玲,李晓霞,张镜宇,等.BMP2与BMP7嵌合表达产物可诱导成骨细胞分化[J].天津医药,2009,37(10):820-822. [7] 温学红,郭若霖,程瑞芳,等.BMP-2和地塞米松对成人成骨细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].临床检验杂志,2005,23(1):34-37. [8] 祝联,陈付国,刘伟,等.骨髓基质干细胞转染腺病毒BMP7后的成骨改变[J].中华整形外科杂志,2006,22(3):59-62. [9] Reddi AH. Morphogenesis and tissue engineering of bone and carti-lage :inductive signals, stem cells and biomimetic biomaterials. Tissue Eng.2000;6 :351-359. [10] 张子军,卢世璧,王继芳,等.骨缺损中内源性BMP的分布及其作用[J].中华外科杂志,1996,34:596-597. [11] Reddi AH.Bone morphogenetic proteins , bone marrow st romal cells , and mesenchymal stem cells. Clin Orthop.1995; 313: 115-119. [12] Bosch P,Musgrave DS,Lee J Y,et al. Osteoprogenitor cells with in skeletal muscle. J Orthop Res.2000;18 :933-944. [13] 轩昆,杨富生,文玲英,等.BMP3、BMP4、BMP7在犬牙根发育过程中的表达研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2006,22(6):807-810. [14] 彭丽萍,姚程,姜振宇.正常人骨髓基质支持造血的试验研究[J].中华血液学杂志,2001,22(12):659-660. [15] 刘忠厚.骨质疏松学[M].北京: 科学出版社,1998:87-88. [16] Thomas AO, Michael A, Victoria S, et al. Progressive development of the rat osteoblast phenotype in vit ro:reciprocal relationship in expression of genes associated with osteoblast proliferation and differentiation during formation of the bone extracelluar matrix. J Cell Physiol. 1990;143-420. |