Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone cement injection for the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic fractures: Common problems in the mature technology
Han Wei-dong1, Huang Ai-jun1, Chen Li-ping2
- 1 Department of Orthopedics, the Fourth People’s Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China
2 Department of Nephrology, Second People’s Hospital of Futian District, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2012-12-15Revised:2013-04-12Online:2013-06-25Published:2013-06-25 -
Contact:Huang Ai-jun, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Fourth People’s Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China omego@qq.com -
About author:Han Wei-dong, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Fourth People’s Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China Hanwd88@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Wei-dong, Huang Ai-jun, Chen Li-ping. Bone cement injection for the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic fractures: Common problems in the mature technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.26.022.
share this article
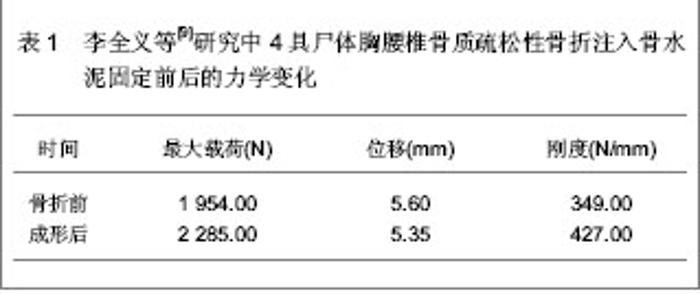
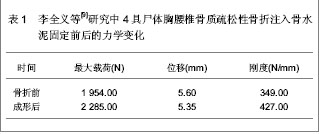
2.1 注入骨水泥治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的生物力学变化 李全义等[9]对注入骨水泥治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的生物力学变化进行了尸体标本实验。选取4具老年胸腰椎尸体标本,男女各2例,年龄58-82岁,身高160-173 mm,体质量55-64 kg,应用双能X射线吸收骨密度仪测量每个标本胸腰椎区域的骨密度,4例胸腰椎标本骨折前的骨密度分别为799,760,784,763 mg/cm。每个标本随机选取6个椎体,共24个单椎体标本,灌注聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯,固定成形后建立骨折模型,并给予载重量为200 N。每个椎体注入4 mL骨水泥。 封固后的骨水泥用5 mL注射器给予30-40 N推注力测定注射性和凝固性,结果显示压强为8-10 Psi,说明骨水泥的注射性能良好,无需添加其它成分来加强其注射性能。注射骨水泥前后的力学性能变化见表1。"
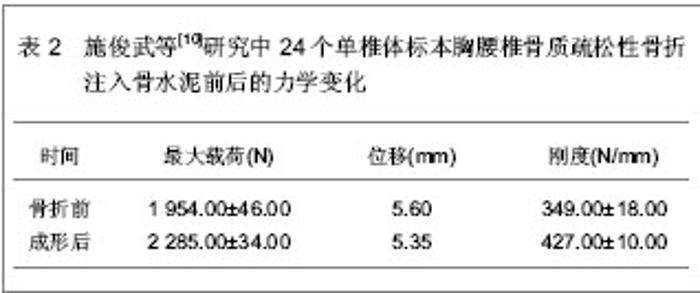
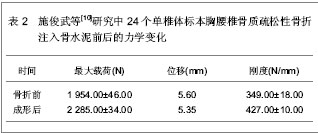
单椎体成形后的椎弓根应变变小,而刚度有较大增加,注射骨水泥成形后椎体变硬,不易发生压缩性变形。注入骨水泥前单椎体能够承受的平均载荷为 1 954.00 N,注入骨水泥成形后能够承受的平均载荷为2 285.00 N,强度增加达16.9%,并且注入骨水泥成形后单椎体的轴向刚度增加达22.1%。 施俊武等[10]同样对注入骨水泥治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的生物力学变化进行了4例老年胸腰椎标本的实验观察。标本为男女各2例,年龄65-72岁,身高162-176 cm,体质量57-66 kg,应用双能X射线吸收骨密度仪测量每个标本胸腰椎区域的骨密度,4例胸腰椎标本骨折前的骨密度分别为801,763,786,759 mg/cm。每个标本随机选取6个椎体,制备成24个单椎体标本,灌注聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯,固定成形后建立骨折模型,并给予载重量为200 N。每个椎体注入4 mL骨水泥。 封固后的骨水泥用5 mL注射器给予30,40 N推注力测定注射性和凝固性,结果显示压强为8,10 Psi,说明骨水泥的注射性能良好,无需添加其它成分来加强其注射性能。且处于骨小梁间隙内的骨水泥能够在30-45 min内凝固。注射骨水泥前后的力学性能变化见表2。"
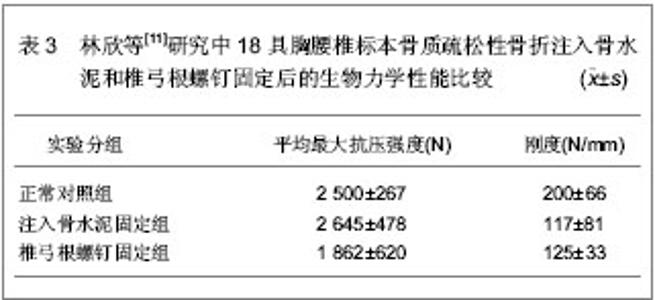
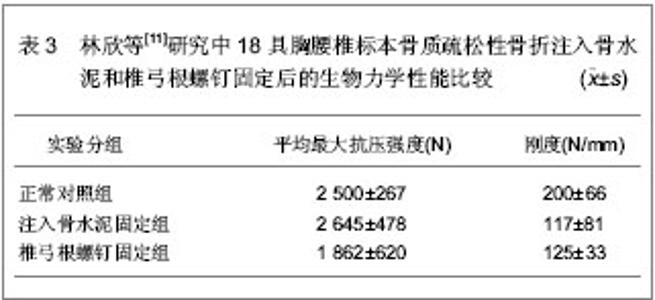
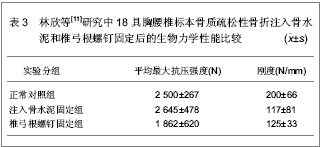
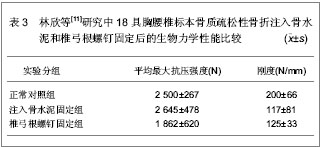
单椎体成形后的椎弓根应变变小,而刚度有较大增加,注射骨水泥成形后椎体变硬,不易发生压缩性变形。注入骨水泥前单椎体能够承受的平均载荷为 (1 954.00±46.00)N,注入骨水泥成形后能够承受的平均载荷为(2 285.00±34.00)N,强度增加达16.92%,并且注入骨水泥成形后单椎体的轴向刚度增加达22.31%。 以上2组实验的结果均显示,注入骨水泥前单椎体能够承受的平均载荷为1 954.00 N左右,注入骨水泥成形后的平均载荷为2 285.00 N左右,骨折前载荷位移为5.6 mm,注入骨水泥成形后载荷位移为5.35 mm,刚度增加22.3%左右。 为了进一步证明注入骨水泥治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的生物力学性能,林欣等[11]对注入骨水泥与椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的生物力学变化进行了对比。实验选取18具胸腰椎标本,测定骨密度为0.6-1.0 g/cm2,年龄50-65岁,身高158-172 cm,体质量58-63 kg。将标本随机分为3组,注入骨水泥固定组,椎弓根螺钉固定组和正常对照组,注入骨水泥固定组和椎弓根螺钉固定组椎体标本给予建立胸腰椎骨折模型。注入骨水泥固定组每个椎体标本注入骨水泥5 mL,椎弓根螺钉固定组的胸腰椎骨折标本按标准的椎弓根螺钉固定方式给予固定,固定后2组标本给予力学性能测定,具体结果见表3。"
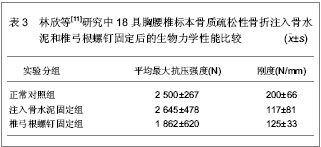
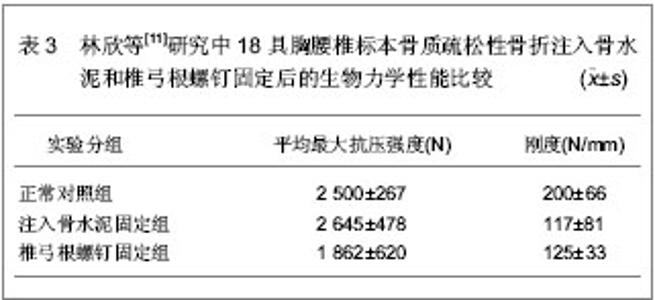
各组结果之间进行比较发现,注入骨水泥固定组最大抗压强度明显高于椎弓根螺钉固定组,且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),而注入骨水泥固定组与椎弓根螺钉固定组之间刚度结果比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);注入骨水泥固定组最大抗压强度和刚度与正常对照组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);椎弓根螺钉固定组最大抗压强度和刚度均低于正常对照组,且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 林欣等[11]研究中的实验结果说明,注入骨水泥固定胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的力学性能优于椎弓根螺钉固定胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的力学性能,进一步证明了注入骨水泥固定胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折良好的生物性能。 国内学者对注入骨水泥固定胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的生物力学变化进行了研究分析,国外也有学者对此进行了研究。Lim等[12]对30具胸腰椎标本骨质疏松性骨折的生物力学性能进行了研究,实验选取T2-L1之间的椎体标本,应用双能X射线骨密度仪测定骨密度为0.56-0.89 g/cm2,将实验标本随机分为3组,磷酸钙骨水泥组、聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯组以及对照组,各组间椎体标本的大小和注入骨水泥的量相似,结果显示注入聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯组的失败率明显高于磷酸钙骨水泥组,注入磷酸钙骨水泥以及注入注入聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯后椎体恢复高度分别为3.56%和2.01%。研究显示出磷酸钙骨水泥治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折良好的生物性能。Belkoff等[13]对胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折骨水泥的注入量与生物力学变化进行了研究,研究选取T6-L5节段椎体标本,结果显示注入2 mL骨水泥时,能恢复所有骨折椎体的强度,要完全恢复骨质疏松骨折椎体的刚度,应用Orthocomp骨水泥时,胸部以及胸腰部椎体需要注入4 mL骨水泥,腰部椎体需要注入6 mL骨水泥;应用Simplex 20骨水泥时,胸部及腰部椎体需要注入4 mL骨水泥,而胸腰部椎体需要注入8 mL骨水泥才能够完全恢复椎体的强度和刚度。 2.2 注入骨水泥治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的病例分析 病例资料:来自深圳市福田区人民医院骨科胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折患者60例,男11例,女49例,平均年龄68. 5岁,均伴有伤椎区域疼痛症状,无明显脊髓和神经根受压的症状及体征,经MRI检查证实有椎体压缩性骨折。患者病程为3-21 d,平均9.6 d,伤椎部位T10-L3,行CT检查排除椎体爆裂性骨折、后壁不完整或椎管内明显受累的骨折类型以及椎体肿瘤或炎症、脊柱侧凸超过40°,排除手术部位感染、椎间盘炎和发热。 病例分组:按随机数字法将60例患者分为2组,一组为对照组,行经皮椎体成形治疗;另一组为实验组,行闭合复位及经皮椎体成形治疗。全部患者由同一组医生完成固定操作。 治疗方法:实验组患者俯卧于手术床上,给予基础麻醉及止痛药物,在患者胸部及骨盆处各垫2个枕头,见图1,以伤柱棘突为中心按压腰背部,借助前纵韧带通过过伸复位,常规术野消毒、铺巾,C 型臂X射线机下正位透视双侧椎弓根形状对称,双侧“牛眼”(相邻椎体小关节处)显像清晰,棘突位于正中。确认病变相应椎体,在后正中线旁开2.5 cm 以1%利多卡因做全层浸润麻醉,将穿刺针于“牛眼”外上象限水平成矢状角10°-15°穿刺进入椎弓根,穿刺针可自行站立时改侧位透视,观察进针水平角度及进针深度,微调进针水平方向,C型臂X射线机荧幕上预测进针方向,缓慢进针至椎体前中1 /3 处,针尖斜面朝对侧。调聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥,C型臂X射线机下监视水泥扩散方向,如遇骨水泥有沿血管扩散至椎体外时暂停推入水泥或调整进针方向,同时防止骨水泥扩散至椎体后缘,且如有骨水泥扩散时暂停注入。注入骨水泥时持续按压直至拨出穿刺针。操作完成后患者取仰卧位,腰部垫枕2 h。注入骨水泥后第2天,佩戴胸腰骶矫形支具下床活动。"
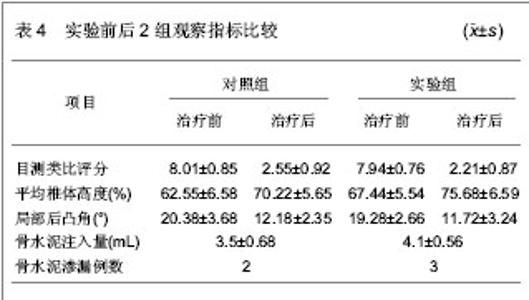
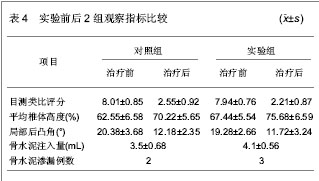
统计学分析:采用SPSS13.0对数据进行统计学分析。数值均用x(_)±s表示。对于计量资料采用独立样本t 检验,组间比较采用方差分析,计数资料采用χ2检验,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。 治疗结果:所有患者均在局麻下完成治疗操作,平均操作时间为每个椎体45 min,骨水泥注入量为2.0-5.5 mL,平均4.0 mL。共有5例出现无临床症状的骨水泥渗漏,无脊髓神经损伤、血管栓塞、肺栓塞、感染以及心脑血管意外等严重并发症发生。共有54例患者得到长达6个月以上的随访。 治疗后对照组和实验组患者目测类比疼痛评分均较治疗前明显降低,2组结果差异无显著性意义 (P > 0.05);椎体高度较治疗前明显提高,2组结果差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);局部后凸角较治疗前明显下降,2组结果差异仍有显著性意义(P < 0.05);骨水泥注入量对照组2.2-5.5 mL,平均(3.5± 0.68) mL,实验组2.0-5.2 mL,平均(4.1±0.56) mL,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。骨水泥渗漏对组照2例,实验组3例,渗漏率为8.33%,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),具体结果见表4。"
| [1] Rao RD, Singrakhia MD. Painful osteoporotic vertebral fracture. Pathogenesis, evaluation, and roles of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in its management. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(10):2010-2022.[2] 郑召民,李佛保.经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术—问题与对策[J].中华医学杂志,2006,86(27):1878-1880.[3] 刘艺.经皮椎体扩张成形术治疗胸腰椎压缩性骨折患者的护理[J].实用临床医药杂志:护理版,2008,4(6):73.[4] Lane JM, Riley EH, Wirganowicz PZ. Osteoporosis: diagnosis and treatment. Instr Course Lect. 1997;46:445-458.[5] Wardlaw D, Cummings SR, Van Meirhaeghe J, et al. Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty compared with non-surgical care for vertebral compression fracture(FREE): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;373(9668):1016-1024.[6] Hiwatashi A, Westesson PL, Yoshiura T, et al. Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty produce the same degree of height restoration. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(4):669-673.[7] 史成富,邹方亮,荆玉峰.经皮穿刺椎体注入骨水泥治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].华北煤炭医学院学报,2009,11(2): 226-227.[8] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-2-20.https://www. cnki.net[9] 李全义,李彩铃,刘时璋.骨质疏松伴胸腰椎骨折行自固骨水泥灌注成形术的力学研究[J].延安大学学报:医学科学版,2008,6(1): 27.[10] 施俊武,胡艇,池永龙,等.胸腰椎骨质疏松骨折行CPC灌注成形的力学实验[J].实用骨科杂志,2006,12(4):316-319.[11] 林欣,李家谋,张昆亚,等.经皮椎体成形术与椎弓根螺钉固定治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2006,8(9):861-863.[12] Lim TH, Brebach GT, Renner SM, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an injectable calcium phosphate cement for vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(12): 1297-1302.[13] Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Jasper LE, et al. The biomechanics of vertebroplasty. The effect of cement volume on mechanical behavior. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1537-1541.[14] 金波,韩贵和,赖震.PVP与PKP治疗老年骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折临床研究[J].浙江中西医结合杂志,2012,22(1):32-34.[15] 王松,王清,康建平,等.经横突-椎弓根单侧穿刺椎体后凸成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012, 22(7): 622-626.[16] 李晓东,江汉,江毅,等.椎体后凸成型术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(3):241-243.[17] 陈伟,李鹏,陈是煌,等.经皮穿刺球囊扩张椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折[J].江苏医药,2012,38(8):960-961.[18] 刘东,孙远新,张克非,等.微创经皮椎弓根固定联合伤椎椎体成形术治疗中老年骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折36例[J].中国老年学杂志, 2012,32(12):2641-2642.[19] 王洪,易小波,陈晓东,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折375例[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(7): 589-591.[20] 何卫斌,冉学军.经皮球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松性胸、腰椎压缩性骨折61例疗效分析[J].重庆医学,2012,41 (15): 1499-1500.[21] 柳申鹏,刘中何,赵斌,等.骨水泥植入经皮椎体成形治疗胸腰椎体骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(29):5465-5468.[22] 杨峰,唐淼,许康永.椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(6):484-485.[23] 许峰,杨小龙.PVP联合软组织封闭治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折疗效观察[J].颈腰痛杂志,2012,33(1):43-44.[24] Lindsay R, Silverman SL, Cooper C, et al. Risk of new vertebral fracture in the year following a fracture. JAMA. 2001;285(3):320-323.[25] Belkoff SM, Maroney M, Fenton DC, et al. An in vitro biomechanical evaluation of bone cements used in percutaneous vertebroplasty. Bone. 1999;25(2 Suppl): 23S-26S.[26] Cloft HJ, Jensen ME. Kyphoplasty: an assessment of a new technology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(2):200-203. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [3] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [4] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [5] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [6] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [7] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [8] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| [9] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [10] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [11] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [12] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [13] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [14] | Gao Yan, Zhao Licong, Zhao Hongzeng, Zhu Yuanyuan, Li Jie, Sang Deen. Alteration of low frequency fluctuation amplitude at brain-resting state in patients with chronic discogenic low back pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1160-1165. |
| [15] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||