Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hip surface replacement and total hip arthroplasty: Meta-analysis on the efficacy
Zhang Pi-jun, Hong Gu-qi, Wang Gang
- Department of Orthopedic Trauma, Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2013-01-15Revised:2013-02-22Online:2013-06-25Published:2013-06-25 -
Contact:Wang Gang, Master, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedic Trauma, Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China wgfr@163.com -
About author:Zhang Pi-jun★, Studying for master’s degree, Physician, Department of Orthopedic Trauma, Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Pi-jun, Hong Gu-qi, Wang Gang. Hip surface replacement and total hip arthroplasty: Meta-analysis on the efficacy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.26.017.
share this article
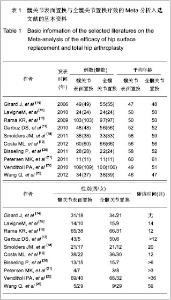
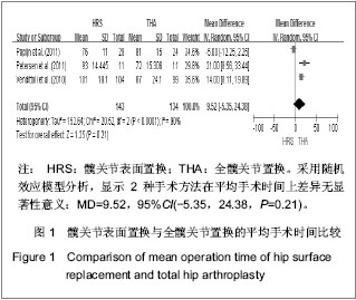
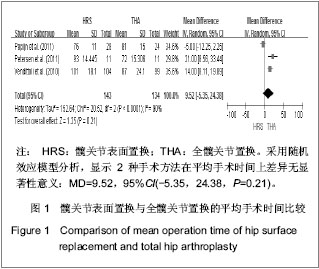
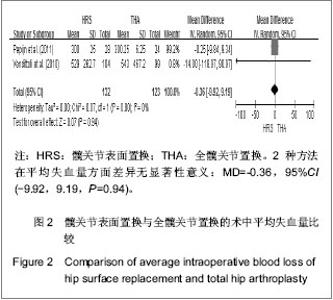
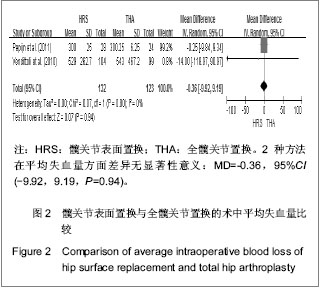
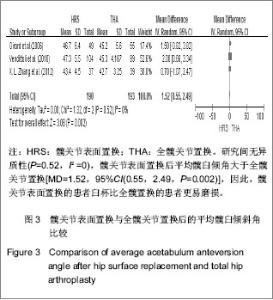
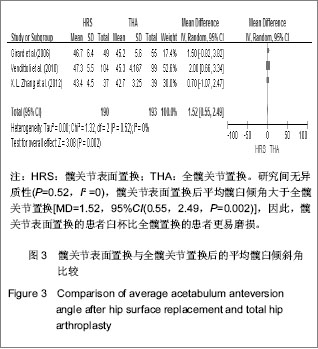
2.1 文献检索结果 采用双人平行摘录方法,由2位研究者独立阅读文献题目和摘要,在排除明显不符合纳入标准的试验后,对可能符合纳入标准的试验阅读全文以最终确定是否符合纳入要求。2位评价者交叉核对试验结果,对有分歧而难以确定是否纳入的试验通过讨论或由第3位评价者决定其是否纳入。初检并阅读题录后获文献534篇,经过阅读文章摘要后得到文献67篇,进一步阅读全文后,剔除57篇不符合纳入标准的文献。根据筛选标准,10篇文献符合这次Meta分析的标准,发表时间为2006年至2012年,均为随机对照试验[14-23]。共包括1 006例患者1 012髋,其中采用髋关节表面置换的患者504例507髋,全髋关节置换的患者502例505髋,见表1。"
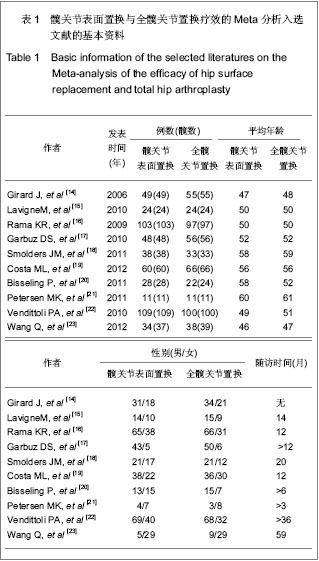
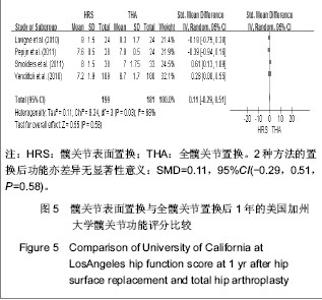
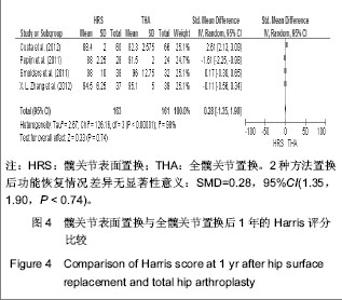
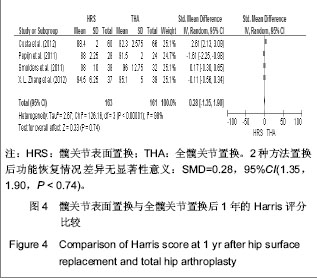
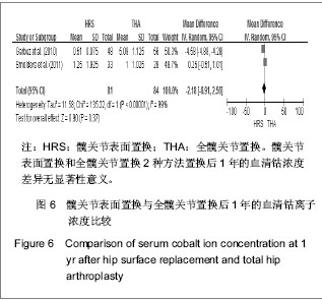
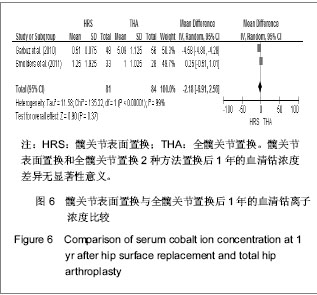
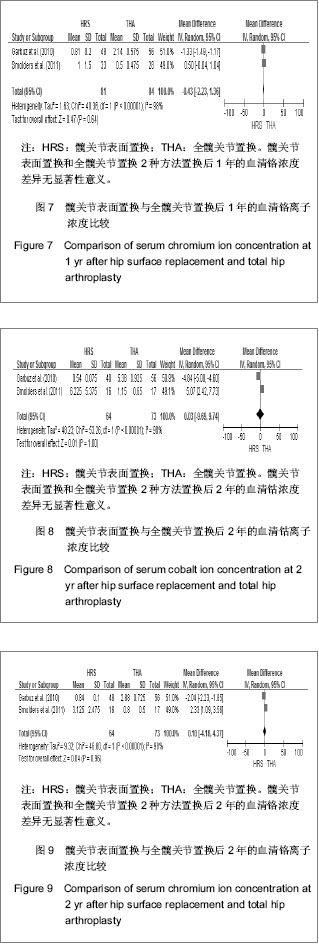
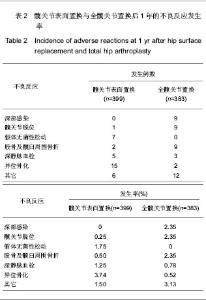
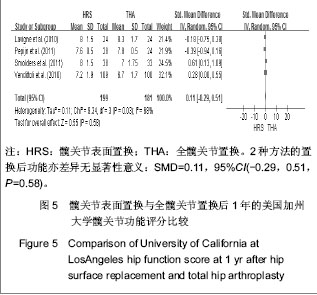
2.2.5 置换后1年美国加州大学髋关节功能评分 美国加州大学髋关节功能评分(University of California Los Angeles,UCLA)对患者手术前后疼痛、步行、功能、活动进行评分,每项记分为1-10分,10分为最佳。35-40分为优,29-34分为好,22-28分为一般,< 22分为差。4个研究根据置换后1年随访的美国加州大学髋关节功能评分评估置换后的髋关节功能恢复情况[18-20,23]。分析结果显示2种方法的置换后功能亦差异无显著性意义:SMD=0.11,95%CI(-0.29,0.51,P=0.58),见图5。UCLA评分显示髋关节表面置换后和全髋置换后的患者疼痛、步行、功能及活动等方面无明显差异。"
| [1] Liu P. Nartong Daxue Xuebao: Yixue Ban.2007;27(3):157-159.刘璠.人工全髋表面置换技术的历史与现状[J].南通大学学报(医学版),2007,27(3):157-159.[2] dela Rosa MA, Silva M, Heisel C, et al. Range of motion after total hip resurfacing. Orthopedics. 2007;30(5):352-357.[3] Abraham A, Hajipour L,Innes AR, et al. Are nationalguidelines for total hip replacement in the UK reflected in practice? Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2006;88 (2):108-115.[4] Ahmad R, Gillespie G, Annamalai S, et al. Leg length and offset following hip resurfacing and hip replacement. Hip Int. 2009;19(2):136-140.[5] Daniel J, Pynsent PB, McMinn DJ. Metal-on-metal resurfacing of the hip in patients under the age of 55 years with osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(2):177-184.[6] Amstutz HC, Beaulé PE, Dorey FJ, et al. Metal-on-metal hybrid surface arthroplasty:two to six-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(1):28-39.[7] Treacy RB, McBryde CW, Pynsent PB. Birmingham hip resurfacing arthroplasty. A minimum follow-up of five years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(2):167-170.[8] Wang Q, Zeng BF. Guowai Yixue: Gukexue Fence. 2005;26 (1): 58-59.王琦,曾炳芳.髋关节表面置换术[J].国外医学:骨科学分册, 2005, 26(1):58-59.[9] Chan FW, Bobyn JD, Medley JB, et al. The Otto Aufranc Award. Wear and lubrication of metal-on-metal hip implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1999;(369):10-24.[10] Medley JB, Chan FW, Krygier JJ, et al. Comparison of alloys and designs in a hip simulator study of metal on metal implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(329Suppl):S148-159.[11] Springer BD, Connelly SE, Odum SM, et al. Cementless femoral components in young patients:review and meta-analysis of total hip arthroplasty and hip resurfacing. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(6 Suppl):2-8.[12] Smith TO, Nichols R, Donell ST, et al. The clinical and radiological outcomes of hip resurfacing versus total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Orthop. 2010;81(6):684-695.[13] Huo MH, Dumont GD, Knight JR, et al. What’s new in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;19;93(20): 1944- 1950.[14] Girard J, Lavigne M, Vendittoli P-A, et al. Biomechanical reconstruction of the hip. A randomised study comparing total hip resurfacing and total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2006;88 (6):721-726.[15] Lavigne M, Therrien M, Nantel J, et al. The John Charnley Award:The functional outcome of hip resurfacing and large-head THA is the same.A randomised double-blind study. Clin Orthop. 2010;(468):326-336.[16] Rama KR, Vendittoli PA, Ganapathi M, et al. Heterotrophic ossification after surface replacement arthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty. A randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24(2):256-262.[17] Garbuz DS, Tanzer M, Greidanus NV, et al. Metal-onmetal hip resurfacing versus large-diameter head metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty. A randomized clinical trial. Clin Orthop. 2010: (468):318-325.[18] Smolders JM, Hol A, Rijnberg WJ, et al. Metal ion levels and functional results after either resurfacing hip arthroplasty or conventional metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2011;82(5):559-566.[19] Costa ML, Achten J, Parsons NR, et al. Total hip arthroplasty versus resurfacing arthroplasty in the treatment of patients with arthritis of the hip joint: single centre, parallel group, assessor blinded, randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2012; 344:e2147.[20] Bisseling P, Smolders JM, Hol A, et al. No clear influence of preference bias on satisfaction and early functional outcome in resurfacing hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2011;82(2): 161-165.[21] Petersen MK, Andersen NT, Mogensen P, et al. Gait analysis after total hip replacement with hip resurfacing implant or Mallory-head Exeterprosthesis:a randomised controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2011;35(5):667-674.[22] Vendittoli PA, Ganapathi M, Roy AG, et al. A comparison of clinical results of hip resurfacing arthroplasty and 28 mm metal on metal total hip arthroplasty: a randomised trial with 3-6 years follow-up. Hip Int. 2010;20(01):1-13.[23] Wang Q, Zhang XL, Chen YS, et al. Resurfacing arthroplasty for hip dysplasia:a prospective randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(6):768-773.[24] Li J, Wang JL. Zhonghua Yixue Zazhi.2001;81(1):53-55.李静,王家良.系统评价的方法与评价原则[J].中华医学杂志, 2001,81(1):53-55.[25] Silva M, Lee KH, Heisel C, et al. The biomechanical results of total hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86-A(1):40-46.[26] Loughead JM, Chesney D, Holland JP, et al. Comparison of offset in Birmingham hip resurfacing and hybrid total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(2):163-166.[27] Doorn PF, Mirra JM, Campbell PA, et al. Tissue reaction to metal on metal total hip prostheses. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(329 Suppl):S187-205.[28] Doorn PF, Campbell PA, Worrall J, et al. Metal wear particle characterization from metal on metal total hip replacements: transmission electron microscopy study of periprosthetic tissues and isolated particles. J Biomed Mater Res. 1998; 42(1):103-111.[29] Schmalzried TP. Preoperative templating and biomechanics in total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2005;28:S849-851.[30] Beaul PE, Campbell PA, Hoke R, et aI. Notching of the femoralneck during resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip:a vascular study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(1):35-39.[31] Lewis CG, Stmderman FW Jr. Metal carcinogenesis in total joint arthroplasty. Animal models. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996:(329 Suppl):S264-268.[32] Moroni A, Savarino L, Hoque M, et al. Do Ion Levels In Hip Resurfacing Differ From Metal-on-metal THA at Midterm? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(1):180-187. |
| [1] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [3] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [4] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [5] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [6] | Liu Lihua, Sun Wei, Wang Yunting, Gao Fuqiang, Cheng Liming, Li Zirong, Wang Jiangning. Type L1 steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through femoral head and neck junction decompression by fenestration: a single-center prospective clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 906-911. |
| [7] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| [8] | Zhang Yu, Feng Shuo, Yang Zhi, Zhang Ye, Sun Jianning, An Lun, Chen Xiangyang. Three-dimensional gait of patients with developmental dysplasia of hip undergoing total hip arthroplasty with high hip center [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 350-355. |
| [9] | Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Hu Weifan, Tang Jinlong, Zhao Fengchao. Risk assessment of contralateral knee arthroplasty after unilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 374-379. |
| [10] | Tian Kechao, Wang Lei, Tao Yong, Yao Tao. Proximal femoral nail antirotation combined with posteromedial wall reconstruction for the treatment of type A2 intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3337-3342. |
| [11] | Lin Tianye, Yang Peng, Xiong Binglang, He Xiaoming, Yan Xinhao, Zhang Jin, He Wei, Wei Qiushi . Comparison of preoperative three-dimensional reconstruction simulation and intraoperative drawing of femoral osteotomy to measure rotation angle in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3349-3353. |
| [12] | Peng Chao, Liu Yunpeng, Hua Guojun, Yang Jiaji, Wang Xingliang, Wang Xiaolong. Imaging evaluation of the hip-knee-ankle angle and osteoarthritis progression before and after partial meniscectomy for degenerative medial meniscus posterior root tear [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3368-3373. |
| [13] | Fu Panfeng, Shang Wei, Kang Zhe, Deng Yu, Zhu Shaobo. Efficacy of anterolateral minimally invasive approach versus traditional posterolateral approach in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3409-3415. |
| [14] | Su Mingzhu, Ma Yuewen. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy regulates the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells in the hippocampus via Notch1/Hes1 pathway after cerebral ischemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3009-3015. |
| [15] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||