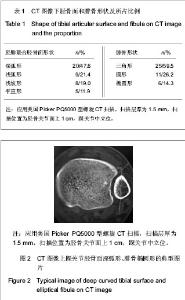
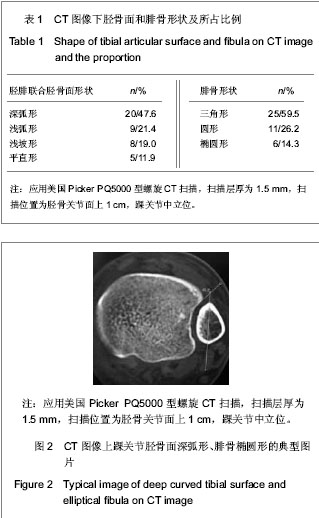
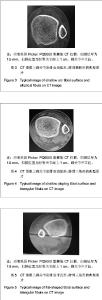
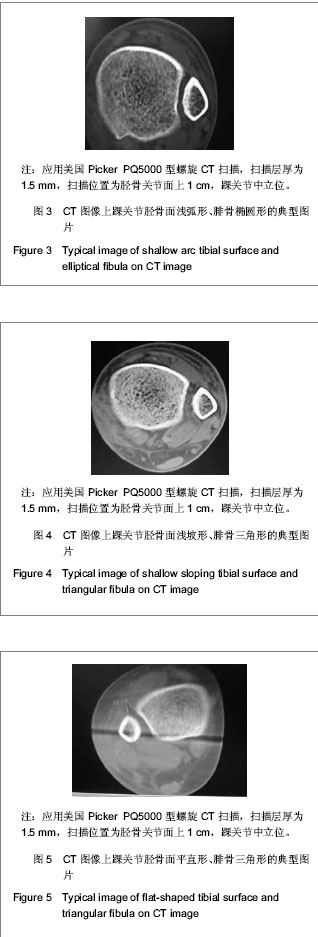
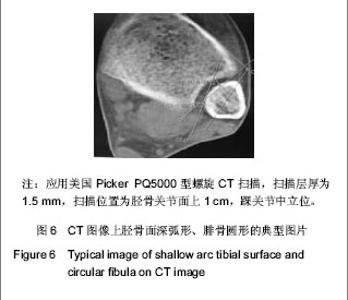
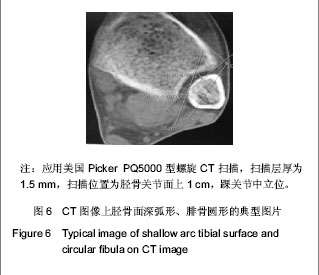
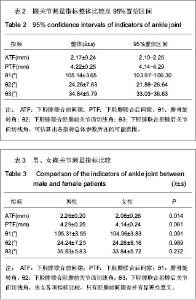
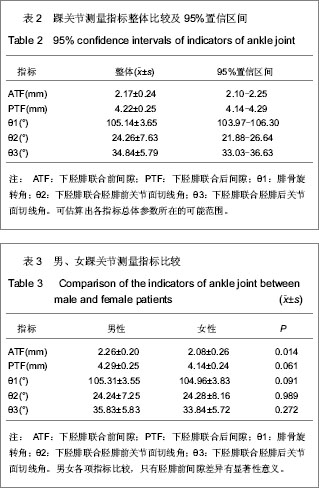
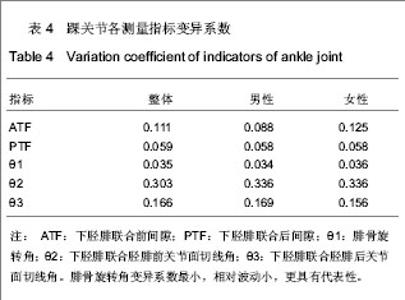
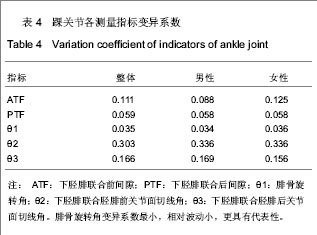
| [1] Jensen SL, Andresen BK, Mencke S, et al. Epidemiology of ankle fractures. A prospective population-based study of 212 cases in Aalborg, Denmark. Acta Orthop Scand. 1998; 69(1): 48-50.[2] Beumer A, van Hemert W L, Niesing R, et al. Radiographic measurement of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis has limited use. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;423:227-234.[3] Sagi HC, Shah AR, Sanders RW. The functional consequence of syndesmotic joint malreduction at a minimum 2-year follow-up. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(7):439-443. [4] Pei GX. Zhonghua Chuangshang Guke Zazhi. 2011; 13(12): 1-3.裴国献.数字化技术与骨科学的融汇-数字骨科学-写在中华医学会医学工程学分会数字骨科学组成立之际[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2011,13(12):1-3.[5] Sun MJ, Zhou YG, Wang Y, et al. Zhonghua Waike Zazhi. 2008;46(19): 1507-1508.孙明举,周勇刚,王岩,等.正常成人双侧下胫腓联合间隙参数指标的CT测量及临床意义[J].中华外科杂志,2008,46(19): 1507-1508.[6] Zhang Q, Hou XK, Luo JC. ZHongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2005;13(20): 1565-1567.张庆,侯筱魁,罗济程.下胫腓联合的CT测量[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(20): 1565-1567[7] Kendoff D, Citak M, Gardner MJ, et al. Intraoperative 3D imaging: value and consequences in 248 cases. J Trauma. 2009;66(1):232-238. [8] Richter M, Zech S. Intraoperative 3-dimensional imaging in foot and ankle trauma-experience with a second-generation device (ARCADIS-3D). J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(3):213- 220.[9] Ruan Z, Luo C, Shi Z, et al. Intraoperative reduction of distal tibiofibular joint aided by three-dimensional fluoroscopy. Technol Health Care. 2011;19(3):161-166.[10] Boruta PM, Bishop JO, Braly WG, et al. Acute lateral ankle ligament injuries: a literature review. Foot Ankle. 1990;11(2): 107-113.[11] Kannus P, Renstrom P. Treatment for acute tears of the lateral ligaments of the ankle. Operation, cast, or early controlled mobilization. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73(2):305-312. [12] Ferran NA, Maffulli N. Epidemiology of sprains of the lateral ankle ligament complex. Foot Ankle Clin. 2006;11(3):659-662.[13] Auleley GR, Kerboull L, Durieux P, et al. Validation of the Ottawa ankle rules in France: a study in the surgical emergency department of a teaching hospital. Ann Emerg Med. 1998;32(1):14-18.[14] Beris AE, Kabbani KT, Xenakis TA, et al. Surgical treatment of malleolar fractures. A review of 144 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;341:90-98.[15] Court-Brown CM, McBirnie J, Wilson G. Adult ankle fractures--an increasing problem?. Acta Orthop Scand. 1998; 69(1):43-47. [16] Ebraheim NA, Taser F, Shafiq Q, et al. Anatomical evaluation and clinical importance of the tibiofibular syndesmosis ligaments. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006;28(2):142-149. [17] Grass R, Rammelt S, Biewener A, et al. Peroneus longus ligamentoplasty for chronic instability of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int. 2003;24(5):392-397. [18] Dikos GD, Heisler J, Choplin RH, et al. Normal tibiofibular relationships at the syndesmosis on axial CT imaging. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(7):433-438.[19] Williams GN, Allen EJ. Rehabilitation of syndesmotic (high) ankle sprains. Sports Health. 2010;2(6):460-470.[20] Zhang P. Diagnosis and treatment for distal tibiofibular diastasis in the malleolus joint injuries. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2009b;22(2):137.[21] Blomfldt R, Tomkvist H, Ponzer S, et al. Comparison of internal fixation with total hip replacement for displaced femoral neck fractures. Randomized, controlled trial performed at four years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87: 1680-1688.[22] Qin Y, Henry DeGroot Ⅲ. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2008,16(22):1685-1688.秦煜,Henry DeGroot Ⅲ. Suture Button装置修复下胫腓联合损伤的初步报告[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2008,16(22):1685-1688.[23] Yang SD, Zhu Y, Deng ZS, et al. Zhongguo Xiandai Yixue Zazhi. 2005;15(13):1962-1964.杨慎达,朱勇,邓展生,等. 下胫腓联合钩栓的研制及其生物力学比较研究[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2005,15(13):1962-1964. [24] Tiemstra JD. Update on acute ankle sprains. Am Fam Physician. 2012;85(12):1170-1176. [25] Rammelt S, Zwipp H, Grass R. Injuries to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: an evidence-based approach to acute and chronic lesions. Foot Ankle Clin. 2008;13(4):611-33, vii-viii. [26] Norkus SA, Floyd RT. The anatomy and mechanisms of syndesmotic ankle sprains. J Athl Train. 2001;36(1):68-73. [27] Beumer A, Valstar ER, Garling EH, et al. Effects of ligament sectioning on the kinematics of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: a radiostereometric study of 10 cadaveric specimens based on presumed trauma mechanisms with suggestions for treatment. Acta Orthop. 2006;77(3):531-540.[28] Yu XH, Fang QS, Ji HQ. Treatment of trimalleolar fracture by fibular approach for exposing post malleolus. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2009;22(2):138-139.[29] Watson DJ, Weatherby BA, Womack JW. Dunking the knot in suture button fixation for distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: technique tip. Foot Ankle Int. 2012;33(8):686-688.[30] Ebraheim NA, Lu J, Yang H, et al. Radiographic and CT evaluation of tibiofibular syndesmotic diastasis: a cadaver study. Foot Ankle Int. 1997;18(11):693-698. [31] Elgafy H, Semaan H B, Blessinger B, et al. Computed tomography of normal distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Skeletal Radiol. 2009;39(6):559-564.[32] Gerber JP, Williams GN, Scoville C R, et al. Persistent disability associated with ankle sprains: a prospective examination of an athletic population. Foot Ankle Int. 1998; 19(10):653-660. [33] Childs SG. Syndesmotic ankle sprain. Orthop Nurs. 2012; 31(3): 177-184. |