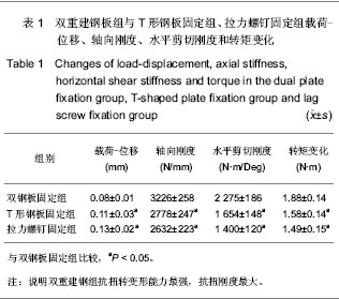
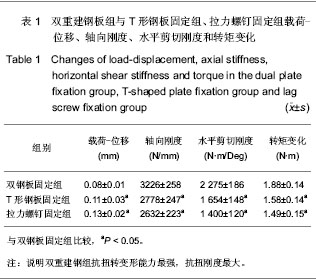
| [1] Browner DD, Jupiter JB, Levine AM, et al. Skeletal Trauma (2nd Revised Edition). CD, Published 1998:1998:2150[2] Wang YC.Beijing: Beijing:People’s Medical Publishing House. 2001:1033.王亦璁.骨与关节损伤[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2001: 1033.[3] Horwitg DS,Bachus KN,Craig MA.A biomechanical analysis of internal fixation of complex tibial plateau fractures.J rthop Trauma.1999.13(8):545-549. [4] Rockwood TA,Green D,Bucholz R,et al.Fracture in adults.4rd ed.Philadelphia :Lippincott.1996:1919.[5] Wang ZC,Wang CC.Zhongguo Zhongyi Gushangke Zazhi. 1996;4(2):24.王战朝,王春成.胫骨平台骨折远期疗效临床72 例分析[M].中国中医骨伤科杂志,1996,4(2):24. [6] Chiu KY,Zhang SD,Zhang GH.Posterior slope of tibial plateau in Chinese.J Anhroplasty,2000,15:224-227.[7] Zhang GZ,Jiang XY,Wang MY.Zhonghua Chuangshang Guke Zazhi. 2006;8 (4) :326:329.张国柱,蒋协远,王满宜.CT扫描对胫骨平台骨折分型及治疗的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(4):326:329.[8] Bhattacharyya MDL,Mitchell B,Suzanne M,et al.The Posterior Shearing Tibial Plateau Fracture:Treatment and Results via a Posterior Approach.J Orthop Trauma.2005,19(5):305-311.[9] Zhang DY,Jiang BG,Fu ZG,et al.Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2001;8(3):253.张殿英,蒋保国,傅忠国,等.AO 技术治疗胫骨平台骨折疗效探讨[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2001,8(3):253.[10] Li YS,Zhong SR,Cao DL,et al.Linchuang Guke Zazhi. 1999;2 (4):281.李永山,周素仁,曹德良,等.43例胫骨平台骨折的手术治疗[J].临床骨科杂志,1999,2(4):281.[11] Schatzker J, Tile M. The rationale of operative care. Berlin: SpringerVerlag.1987;279.[12] Kenedy JC,Bailey WH.Experimental tibial plateau fractures.J Bone Joint Surg 1969,50A:1522-1934.[13] Shen Y, Ye JJ. Gu yu Guanjie Sunshang Zazhi.2004;19(9): 628.沈扬,叶建军.屈曲型胫骨平台骨折诊断与治疗[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2004,19(9):628.[14] Kennedy JC, Weinberg HW, Wilson AS. The anatomy and function of the anterior cruciate ligament. As determined by clinical and morphological studies. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974 ;56(2):223-235.[15] Bhattacharyya MDL,Mitchell B,Suzanne M,et al.The Posterior Shearing Tibial Plateau Fracture:Treatment and Results via a Posterior Approach.J Orthop Trauma.2005,19(5):305-311.[16] Gardner MJ,Yacoubian S, Geller D, et al.The incidence of soft Tissue Injury in Operative Tibial Plateau Fractures:A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Analysis of 103 Patients.J Orthop Trauma. 2005.19(2):79-85.[17] Vanek J.Posteromedial fracture of the tibial plateau is not an avulsion injury.A case report and experimental study.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1994,6(2):290-292. |