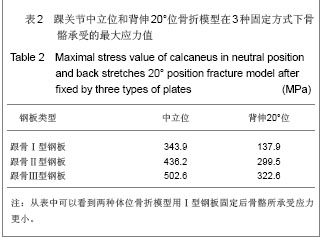
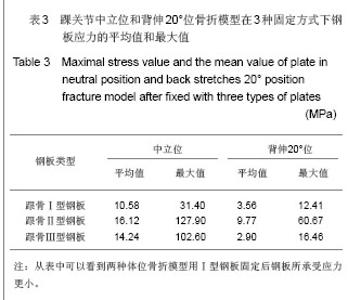
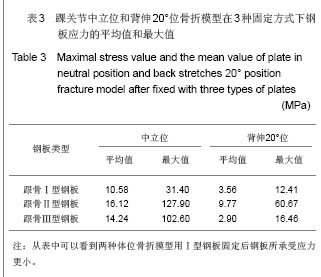
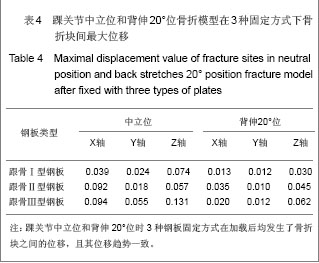
| [1] Fu CM, Yang ZH, Qian CS, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011; 15(9):1686-1689.付昌马,杨祖华,钱春生,等.可塑性钛钢板置入治疗有移位的跟骨关节内骨折[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(9): 1686-1689.[2] Han MJ, Wang ZJ, Zou YW, et al. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2011; 31(4): 335-338.韩明建,王志杰,邹云雯,等.锁定跟骨钢板治疗新鲜跟骨骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(4):335-338. [3] Huang ZH, Li J, Chen RQ, et al. Zhongguo Gushang. 2012; 25(2): 97-101.黄诸侯,李俊,陈日齐,等.跟骨三维有限元模型的建立及其骨折发生机制[J].中国骨伤,2012, 25(2): 97-101.[4] Liu LF, Cai JF, Liang J. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2003; 11(8): 557-558.刘立峰,蔡锦方,梁进.跟骨骨折内固定方法的有限元模拟比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(8):557-558.[5] Liu LF, Cai JF, Liang J. Gu yu Guanjie Shunshang Zazhi. 2003; 18(7): 458-460.刘立峰,蔡锦方,梁进.畸形愈合的跟骨在不同步态位相应力分布的三维有限元研究[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2003, 18(7): 458-460.[6] Surendran S, Kwak DS, Lee UY,et al. Anthropometry of the medial tibial condyle to design the tibial component for unicondylar knee arthroplasty for the Korean population. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15(4):436-442.[7] Cheung JT, Zhang M, An KN. Effect of Achilles tendon loading on plantar fascia tension in the standing foot. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2006;21(2):194-203.[8] Cheung JT, Zhang M, An KN. Effects of plantar fascia stiffness on the biomechanical responses of the ankle-foot complex. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2004;19(8):839-846.[9] Nakamura S, Crowninshield RD, Cooper RR. An analysis of soft tissue loading in the foot--a preliminary report. Bull Prosthet Res. 1981;10-35:27-34.[10] Siegler S, Block J, Schneck CD.The mechanical characteristics of the collateral ligaments of the human ankle joint.Foot Ankle. 1988;8(5):234-242.[11] Wright DG, Rennels DC.A study of the elastic properties of plantar fascia.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964;46:482-492.[12] Athanasiou KA, Liu GT, Lavery LA,et al. Biomechanical topography of human articular cartilage in the first metatarsophalangeal joint.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(348): 269-281.[13] Lemmon D, Shiang TY, Hashmi A,et al. The effect of insoles in therapeutic footwear--a finite element approach. J Biomech. 1997;30(6):615-620.[14] Du JW. Fuzhou: Fujian Collage of TCM, 2008.杜景文.跟骨的三维有限元分析及临床意义[D].福州:福建中医学院,2008.[15] Chen XM, Ma HS, Liu YZ, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(39): 7331-7335.陈晓明,马华松,刘玉增,等.克氏针撬拨结合钢板置入内固定与局部植骨治疗跟骨关节内骨折[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(39):7331-7335.[16] Little JP, Taddei F, Viceconti M,et al. Changes in femur stress after hip resurfacing arthroplasty: response to physiological loads.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2007;22(4):440-448.[17] Li SQ, Li DS, Qi X, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(9):1785-1788.李叔强,李冬松,齐欣,等.不同骨质密度下生物型及骨水泥型股骨假体置入后的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(9):1785-1788.[18] Bevill G, Keaveny TM.Trabecular bone strength predictions using finite element analysis of micro-scale images at limited spatial resolution. Bone. 2009;44(4):579-584.[19] Abdul-Kadir MR, Hansen U, Klabunde R,et al. Finite element modelling of primary hip stem stability: the effect of interference fit.J Biomech. 2008;41(3):587-594.[20] Janssen D, van Aken J, Scheerlinck T,et al. Finite element analysis of the effect of cementing concepts on implant stability and cement fatigue failure.Acta Orthop. 2009;80(3): 319-324.[21] Beillas P, Lee SW, Tashman S,et al. Sensitivity of the tibio-femoral response to finite element modeling parameters. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2007;10(3): 209-221. [22] Mesfar W, Shirazi-Adl A. Computational biomechanics of knee joint in open kinetic chain extension exercises. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2008;11(1):55-61.[23] Chantarapanich N, Nanakorn P, Chernchujit B,et al. A finite element study of stress distributions in normal and osteoarthritic knee joints. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009;92 Suppl 6:S97-103.[24] Zelle J, Van der Zanden AC, De Waal Malefijt M,et al. Biomechanical analysis of posterior cruciate ligament retaining high-flexion total knee arthroplasty.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009;24(10):842-829.[25] Guess TM, Thiagarajan G, Kia M,et al. A subject specific multibody model of the knee with menisci.Med Eng Phys. 2010;32(5):505-515.[26] Gíslason MK, Stansfield B, Nash DH. Finite element model creation and stability considerations of complex biological articulation: The human wrist joint. Med Eng Phys. 2010; 32(5):523-531.[27] Frehill B, Crocombe A, Cirovic S,et al. Initial stability of type-2 tibial defect treatments. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010;224(1): 77-85.[28] Chong DY, Hansen UN, Amis AA. Analysis of bone-prosthesis interface micromotion for cementless tibial prosthesis fixation and the influence of loading conditions. J Biomech. 2010; 43(6): 1074-1080.[29] Hopkins AR, New AM, Rodriguez-y-Baena F,et al. Finite element analysis of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.Med Eng Phys. 2010;32(1):14-21.[30] Gefen A. Optimizing the biomechanical compatibility of orthopedic screws for bone fracture fixation. Med Eng Phys. 2002;24(5):337-347.[31] Liu LF,Cai JF. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2003; 11(11): 786-789.刘立峰,蔡锦方.跟骨骨折的生物力学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2003,11(11):786-789.[32] Huang HJ, Wan J, Ma JX, et al. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2010; 30(3): 282-286.黄海晶,王捷,马建雄,等.跟骨三维有限元模型的建立与静态分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2010, 30(3): 282-286.[33] Liao T, Zhang JX. Zhongguo Zhongyi Gushangke Zazhi. 2008; 16(2): 64-66.廖铦,张建新.跟骨骨折的生物力学实验研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2008, 16(2): 64-66.[34] Liao T, Zhang JX. Zhongguo Zhongyi Gushangke Zazhi. 2009; 17(7): 7-8.廖铦,张建新.跟骨的三维光弹实验与跟骨骨折发生机制[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2009, 17(7): 7-8. [35] Niu WX, Ding ZQ. Yiyong Shengwu Lixue. 2007; 22(4): 345-350.牛文鑫,丁祖泉.三种三维有限元建模方法在跟骨模型建立中的应用和比较[J].医用生物力学,2007,22(4): 345-350.[36] Du MK, Wang QG, Zhang QL, et al.Yiyong Shengwu Lixue. 2007; 22(1): 94-98.杜明奎,王秋根,张秋林,等.锁定加压钢板固定骶骨不稳定骨折的三维有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2007, 22(1): 94-98. |