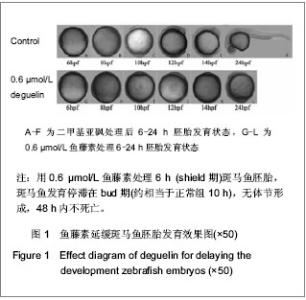
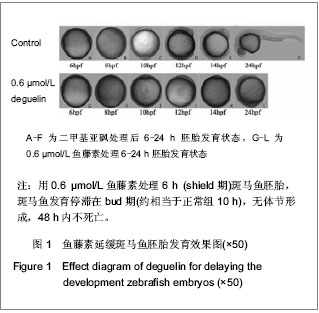
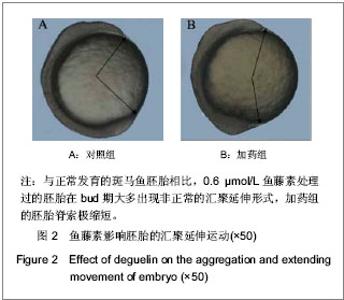
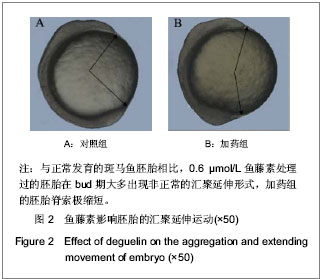
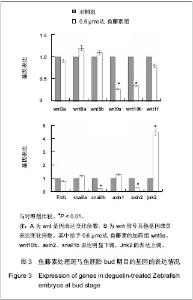
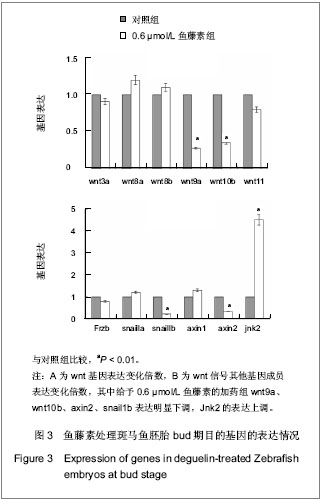
| [1] |
Xu Guofeng, Li Xuebin, Tang Yifan, Zhao Yin, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun.
The role of autophagy in ossification of the human ligamentum
flavum
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1174-1181.
|
| [2] |
Huang Cheng, Liu Yuanbing, Dai Yongping, Wang Liangliang, Cui Yihua, Yang Jiandong.
Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
overexpressing glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor gene for spinal cord
injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1037-1045.
|
| [3] |
Han Bo, Yang Zhe, Li Jing, Zhang Mingchang .
Regulation of limbal stem cells via Wnt signaling in the
treatment of limbal stem cell deficiency
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1057-1062.
|
| [4] |
Song Xudong, He Yunwu, Li Yonglin, Chen Jing, Hu Junlan.
Ultrasound-guided paravertebral nerve block for
zoster-associated pain: a Meta-analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1797-1804.
|
| [5] |
Zhong Qiusheng1, Xia Weichao1, Guo Meizhen1, Zhu Haiqing1, Zhong Cuiqiong1, Shao Jieqi1, He Xiaohong2, Chen Xiumin2.
Sandwiched Moxibustion plus Bushen Quhan recipe for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5670-5675.
|
| [6] |
Chen Kairui, Bao Chongyun, Liu Xian, Xiao Yu, Tan Yanlin, Liu Xiupiao, Xiong Bokai, Zhang Qiang.
Effects of tricalcium phosphate materials with different microstructures on the expression of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway-related markers
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5430-5435.
|
| [7] |
Xiong Fei1, Wei Yishan2.
Reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip in rabbits: expression levels of Caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in acetabular chondrocytes
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4974-4978.
|
| [8] |
Li Xianan, Tian Shaoqi, Wang Yuanhe, Liu Jiangjun, Ding Tao, Chu Guoqing, Sun Kang.
Hydrogen sulfide protects articular cartilage in rabbit models of knee osteoarthritis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4992-4997.
|
| [9] |
Chen Dongmei, Xu Lili, Zhou Jianwei.
Curcumin regulates odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells through Wnt signaling pathway
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(25): 4018-4024.
|
| [10] |
Ding Huan1, Chen Lihong1, Chen Yujing1, Yue Rongzhao1, Yang Min1, Xu Guihua2 .
Efficacy of different scraping protocols in the intervention of rat models of lumbar disc herniation based on urine metabolomics
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3654-3659.
|
| [11] |
Fan Chaoqun1, Xu Kai2, Nie Mingjian1, Xu Wenfeng1, Wang Mei1.
Evaluation of the cardiopulmonary endurance: cardiopulmonary exercise test versus 6-minute two-step test
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3686-3691.
|
| [12] |
Yang Na1, Bao Pingping2, Lei Tao2.
Adiponectin levels in plasma and periodontal tissue of mouse models of diabetic periodontitis treated by adiponectin
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3692-3697.
|
| [13] |
Li Xiaoju, Song Guangbao, Yang Jianzhen, Wei Bo, Wu Bin.
Effect of concentrated growth factors on proliferation and differentiation of human gingival fibroblasts
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3342-3348.
|
| [14] |
Xu Qing, Fang Haolin, Liu Yang, Zhang Cunxin, Tian Baofang.
Proanthocyanidins inhibit high glucose-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells in a rabbit
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3426-3431.
|
| [15] |
Liu Yan, Yu Xi, He Hongchen, He Chengqi, He Jing.
Biological therapy in rotator cuff injury
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(20): 3248-3254.
|