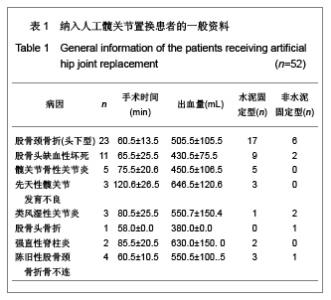
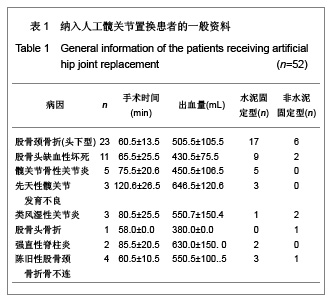
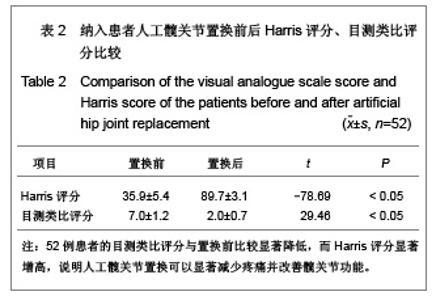
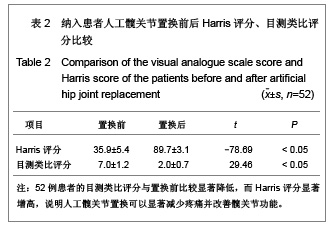
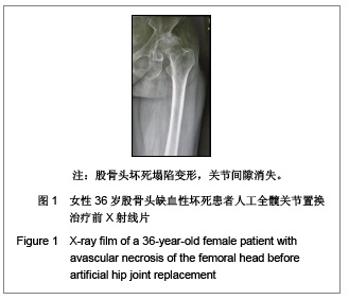
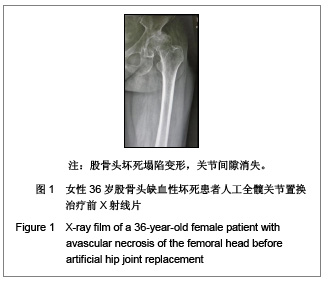
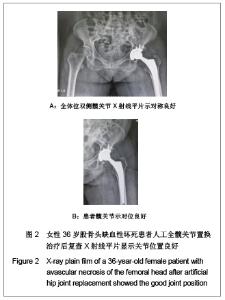
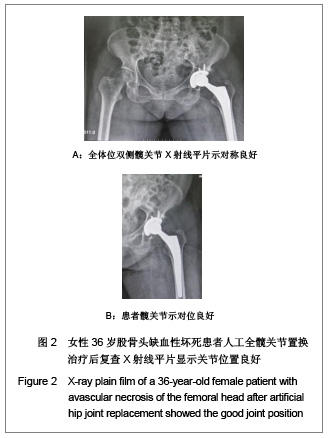
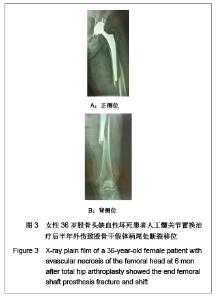
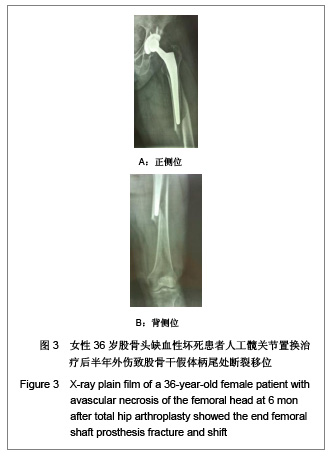
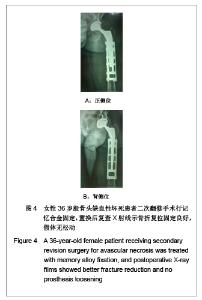
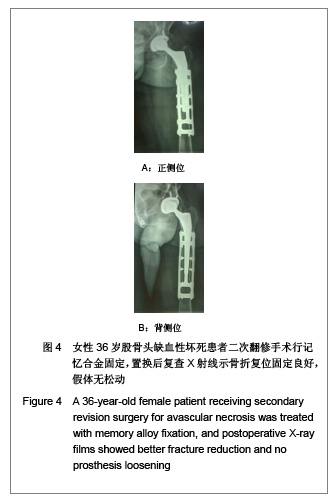
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (13): 2297-2304.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.13.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Artificial hip joint replacement for the treatment of severe hip diseases
Li Guang-wei1, 2
- 1 Zhengzhou University School of Public Health, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China
2 Second Department of Orthopedics, the Second People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou 450006, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2012-07-12Revised:2011-12-26Online:2013-03-26Published:2013-03-26 -
About author:Li Guang-wei, Attending physician, Zhengzhou University School of Public Health, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China; Second Department of Orthopedics, the Second People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou 450001, Henan Province, China lgw689@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Guang-wei. Artificial hip joint replacement for the treatment of severe hip diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(13): 2297-2304.
share this article
| [1] Mont MA,Maker DR,Smith JM,et al.Resurfacing is comparable to total hip arthroplasty at short-term follow-up. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(1):66-71.[2] Zhang XL, Jiang C, Chen YS. Beijing: The Publishing House of People’s Health. 2009:163-165. 张先龙,蒋矗,陈云苏.人工髋关节外科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社.2009:163-165.[3] Wang J, Xing HP, Liu G. Dangdai Yixue. 2012;18(9):8-10. 王俊,邢海鹏,刘刚. 全髋关节置换术治疗老年股骨颈骨折临床分析[J].当代医学,2012,18(9):8-10. [4] Tang LH, Jiao YX, Li WB. Linchuang Junyi Zazhi. 2011;39(3): 576-577. 唐丽华,焦裕霞,李五白.术中静注帕瑞昔布钠对老年患者髋关节置换术术后疼痛的影响[J].临床军医杂志,2011,39(3):576-577. [5] Tang YN, Su D. Anmo yu Kangfu Yixue. 2012;3(1):55-56. 汤艳妮,苏丹.人工全髋关节置换术后的康复治疗体会[J].按摩与康复医学,2012,3(1):55-56.[6] Zhang HN, LV CY, Xun H, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(4):626-629. 张海宁,吕成昱,徐浩,等.大直径金属/金属股骨头人工全髋关节置换治疗股骨头缺血坏死[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(4): 626-629.[7] Xie M. Yang SH, XU WH. Linchuang Guke Zazhi. 2011;14(3): 278-280. 谢卯,杨述华,许伟华.新型短柄全髋关节置换手术技术及近期疗效观察[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(3):278-280.[8] Jiang T, Zheng C, Xu JD, et al. Linchuang Guke Zazhi. 2012; 15(1):56-58. 蒋涛,郑冲,徐建达,等.金属大头全髋置换术的早期临床疗效观察[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(1):56-58.[9] Sammer DM, Shin AY. Wrist surgery: management of chronic scapholunate and lunotriquetral ligament injuries. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130(1):138e-156e.[10] Masonis JL, Bourne RB. Surgical approach, abductor function, and total hip arthroplasty dislocation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(405):46-53.[11] Wang HT, Liu WJ, Liu KG, et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2007;15(3):231-232. 王海棠,刘万军,刘可贵,等.人工髋关节置换术中的软组织平衡问题[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(3):231-232.[12] White RE Jr, Forness TJ, Allman JK, et al. Effect of posterior capsular repair on early dislocation in primary total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(393):163-167.[13] Tian H, Zhang K, Liu Y, et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2008;16(3):185-187. 田华,张克,刘岩,等.全髋关节置换术后脱位的原因分析及处理[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(3):185-187.[14] Shao M, Ge SQ, Li GL, et al. Sichuan Yixue. 2001;22(4):385- 386. 邵明,弋拾权,李贵林,等.人工股骨头置换术后髋关节疼痛原因分析[J].四川医学,2001,22(4):385-386.[15] Tang XC, Xia P. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2003;11 (3-4): 274-275. 唐希初,夏平.人工髋关节置换术后顽固性疼痛的原因分析及治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(3-4):274-275.[16] Wang YS, Chen B, Li JW, et al. Zhengzhou Daxue Xuebao (Yixueban). 2012;47(2):251-253. 王义生,陈宾,李军伟,等.人工全髋关节置换术后双下肢长度的变化[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2012,47(2):251-253.[17] Konyves A, Bannister GC. The importance of leg length discrepancy after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(2):155-157.[18] Cameron HU. Managing length: the 'too long' leg. Orthopedics. 1997;20(9):791-792.[19] Hu RY, Tian XB, Sun L, et al. Zhonghua Chuangshang Zazhi. 2011;27(7):622-626. 胡如印,田晓滨,孙立,等.93例同期双侧人工全髋关节置换术回顾性分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2011,27(7):622-626.[20] Yan L, Xia J, Wei YB. Guoji Gukexue Zazhi. 2010;31(6):340- 342. 严亮,夏军,魏亦兵.髋臼前倾角研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2010,31(6):340-342.[21] Lewinnek GE,Lewis JL,Tarr R,et al. Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978; 60(2):217-220.[22] Barrack RL. Dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: implant design and orientation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;11(2): 89-99. [23] D'Lima DD, Urquhart AG, Buehler KO, et al. The effect of the orientation of the acetabular and femoral components on the range of motion of the hip at different head-neck ratios. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(3):315-321.[24] Wan DD, You J, Jiang WX. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2012;20(3):220-223. 万东东,尤佳,姜文学.全髋关节置换术后撞击征[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(3):220-223.[25] Berkes MB, Cross MB, Shindle MK, et al. Traumatic posterior hip instability and femoroacetabular impingement in athletes. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2012;41(4):166-171.[26] Malik A, Wan Z, Jaramaz B, et al. A validation model for measurement of acetabular component position. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(5):812-819.[27] Wan Z, Malik A, Jaramaz B, et al. Imaging and navigation measurement of acetabular component position in THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(1):32-42.[28] Zai JL, Weng XS. Zhonghua Waike Zazhi. 2011;49(4):366- 368. 翟吉良,翁习生. 髋关节置换术后腹股沟区疼痛研究进展[J].中华外科杂志,2011,49(4):366-368.[29] Li JY, Guan GH, Li XF, et al. Zhongguo Gushang. 2012;25(1): 74-77. 李建有,管国华,李雄峰,等. 全髋关节置换术治疗Crowe Ⅳ型髋关节发育不良患者及围手术期并发症分析[J].中国骨伤,2012, 25(1):74-77.[30] Liu HP, Ge CL, Li JM, et al. Zhongguo Shiyong Yiyao. 2012; 7(10):68-69. 刘汉平,葛崇林,李家民,等. 96 例人工全髋关节置换术的临床分析[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(10):68-69. |
| [1] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [2] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [3] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [4] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [5] | Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun. The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [8] | Zhou Wu, Wang Binping, Wang Yawen, Cheng Yanan, Huang Xieshan. Transforming growth factor beta combined with bone morphogenetic protein-2 induces the proliferation and differentiation of mouse MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3630-3635. |
| [9] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [10] | Feng Guancheng, Fang Jianming, Lü Haoran, Zhang Dongsheng, Wei Jiadong, Yu Bingbing. How does bone cement dispersion affect the early outcome of percutaneous vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3450-3457. |
| [11] | Yang Li, Li Xueli, Song Jinghui, Yu Huiqian, Wang Weixia. Effect of cryptotanshinone on hypertrophic scar of rabbit ear and its related mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3150-3155. |
| [12] | Sun Yiqiang, Xing Jianqiang, Li Xuecheng, Wang Xin, Tian Shenglan, Zhao Zihao, Geng Xiaopeng. Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture in the elderly: a comparison of vertebral height recovery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2851-2855. |
| [13] | Li Qiang, Li Jun, Luan Jian, Jin Canghai, Hao Meng, Lin Yong. Bone cement distribution of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2466-2471. |
| [14] | Tian Lin, Shi Xiaoqing, Mao Jun, Zhang Nongshan, Zhang Li, Xing Runlin, Wang Peimin. Meta-analysis of vacuum-sealing drainage combined with antibiotic bone cement in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2618-2624. |
| [15] | Liu Zige, Liu Xinrui, Li Yan, Song Guorui, Zhang Chen, Chen Desheng. In vitro experiment of tetrandrine on the model of osteolysis induced by wear particles around the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2358-2363. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||