Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (13): 2289-2296.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.13.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ceramic-on-ceramic total hip arthroplasty
Yang Xing, Wang Zheng-fei, Xue Feng, Sheng Xiao-wen, Chen Bin-qian, Qian Yu-feng, Yu Xu-dong
- The First People’s Hospital of Chanshu, Changshu 215500, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2012-09-19Revised:2012-11-11Online:2013-03-26Published:2013-03-26 -
About author:Yang Xing★, Master, Physician, the First People’s Hospital of Chanshu, Changshu 215500, Jiangsu Province, China xinghong0518@yahoo.com.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Xing, Wang Zheng-fei, Xue Feng, Sheng Xiao-wen, Chen Bin-qian, Qian Yu-feng, Yu Xu-dong. Ceramic-on-ceramic total hip arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(13): 2289-2296.
share this article
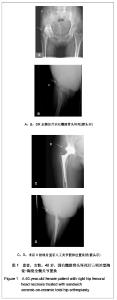
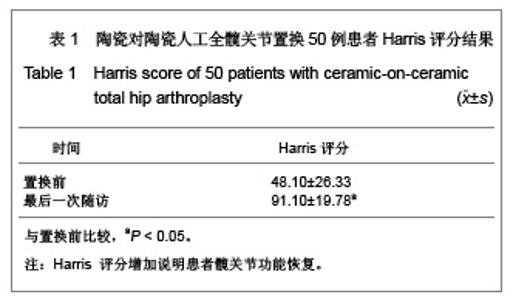
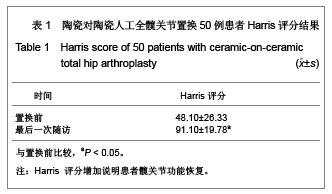
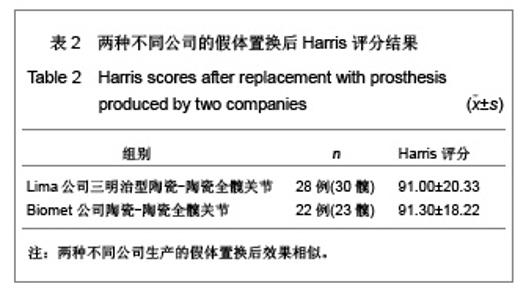
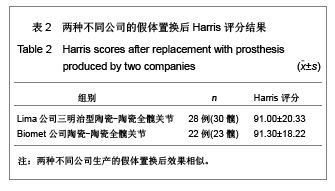
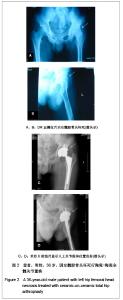
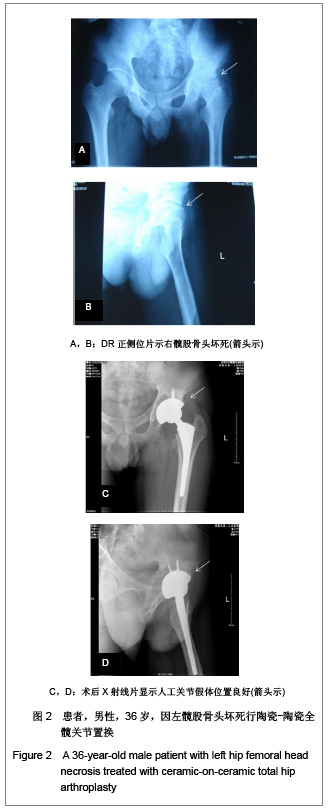
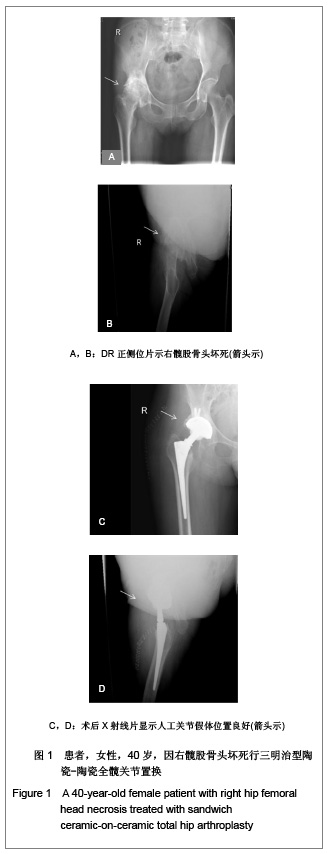
2.3 影像学评估 置换后随访测量所有假体,X射线片显示髋臼外倾角平均为(43.8±2.4)°,前倾角平均为(16.5±3.4)°。7髋出现1度异位骨化但患者活动度无影响,患者亦无任何不适表现。所有病例未发现有髋关节脱位,假体固定失败,未见假体松动、下沉、移位及碎裂发生,假体周围无透亮线形成。髋臼侧及股骨侧均见骨长入假体。股骨侧和髋臼侧均未发生骨溶解现象。股骨侧假体在股骨髓腔内充填良好,其中14例股骨峡部有明显股骨皮质增粗;股骨近端均未出现明显骨质疏松。患者均恢复日常生活,其中17例仍继续参加网球等体育活动。 2.4 并发症发生情况 所有患者无关节异响的主诉,其中1例患者剧烈运动后出现髋臼陶瓷内衬(三明治陶瓷)破碎,予以翻修后好转,现患者恢复日常生活。 2.5 典型病例分析 典型病例1:患者女,40岁,因右髋疼痛活动受限10年入院,经术前常规检查,在硬膜外麻醉下行右侧全髋关节置换,假体采用Lima公司的三明治型陶瓷-陶瓷全髋关节,其中髋臼假体内层为BIOLOX forte陶瓷内衬,陶瓷头为28 mm BIOLOX forte陶瓷球头,股骨假体为F2L假体。人工全髋关节置换前后影像学资料见图1。"
| [1] Latimer HA, Lachiewicz PF. Porous-coated acetabular components with screw fixation. Five to ten-year results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(7):975-981.[2] Unger PA. Roentgenographic scoring system for evaluating success of femoral hip implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; (284):310-312.[3] Engh CA, Hooten JP Jr, Zettl-Schaffer KF, et al. Porous-coated total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(298):89-96.[4] DeLee JG, Charnley J. Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; (121):20-32.[5] Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, et al. Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55(8): 1629-1632.[6] Harris WH, Crothers O, Oh I. Total hip replacement and femoral-head bone-grafting for severe acetabular deficiency in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59(6):752-759.[7] Hamilton HW, Gorczyca J. Low friction arthroplasty at 10 to 20 years. Consequences of plastic wear. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;(318):160-166.[8] Baxter RM, Macdonald DW, Kurtz SM,et al. Characteristics of highly cross-linked polyethylene wear debris in vivo.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013. [Epub ahead of print][9] Malem D, Nagy MT, Ghosh S,et al. Catastrophic failure of ceramic-on-ceramic total hip arthroplasty presenting as squeaking hip.BMJ Case Rep. 2013. [Epub ahead of print][10] Karam JA, Tokarski AT, Ciccotti M,et al. Revision total hip arthroplasty in younger patients: indications, reasons for failure, and survivorship.Phys Sportsmed. 2012;40(4):96-101. [11] Min BW, Lee KJ, Song KS,et al. Highly cross-linked polyethylene in total hip arthroplasty for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a minimum 5-year follow-up study.J Arthroplasty.2013;28(3):526-530.[12] Kuo FC, Liu HC, Chen WS,et al.Ceramic-on-ceramic total hip arthroplasty: incidence and risk factors of bearing surface-related noises in 125 patients.Orthopedics. 2012; 35(11):e1581-e1585.[13] Sehatzadeh S, Kaulback K, Levin L. Metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty: an analysis of safety and revision rates.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2012;12(19):1-63.[14] van der Veen HC, van den Akker-Scheek I, Bulstra SK,et al. Wear, bone density, functional outcome and survival in vitamin E-incorporated polyethylene cups in reversed hybrid total hip arthroplasty: design of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:178.[15] Qi G, Wayne SF, Mann KA, et al. Random damage and characteristics of debris particles are two important and yet ignored factors in the mechanical integrity of the stem-cement interface of a total hip replacement: influence of the surface finish of the metal stem. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(4): 1385-1392.[16] Ramaniraka NA, Rakotomanana LR, Leyvraz PF. The fixation of the cemented femoral component. Effects of stem stiffness, cement thickness and roughness of the cement-bone surface. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(2):297-303.[17] Ramaniraka NA, Rakotomanana LR, Rubin PJ,et al. Noncemented total hip arthroplasty: influence of extramedullary parameters on initial implant stability and on bone-implant interface stresses. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2000;86(6):590-597.[18] Boutin P.Total arthroplasty of the hip by fritted aluminum prosthesis. Experimental study and 1st clinical applications. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1972;58(3): 229-246.[19] Bozic KJ, Kurtz S, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of bearing surface usage in total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(7):1614-1620.[20] Bizot P, Hannouche D, Nizard R, et al. Hybrid alumina total hip arthroplasty using a press-fit metal-backed socket in patients younger than 55 years. A six- to 11-year evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(2):190-194.[21] Streit MR, Schröder K, Körber M,et al. High survival in young patients using a second generation uncemented total hip replacement.Int Orthop. 2012;36(6):1129-1136.[22] Schroder D, Bornstein L, Bostrom MP,et al. Ceramic-on-ceramic total hip arthroplasty: incidence of instability and noise. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(2): 437-442.[23] Affatato S, Modena E, Toni A, et al. Retrieval analysis of three generations of Biolox(®) femoral heads: Spectroscopic and SEM characterisation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;13: 118-128.[24] Esposito CI, Walter WL, Roques A, et al. Wear in alumina-on-alumina ceramic total hip replacements: a retrieval analysis of edge loading. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012; 94(7):901-907.[25] Haidukewych GJ, Petrie J. Bearing surface considerations for total hip arthroplasty in young patients. Orthop Clin North Am. 2012;43(3):395-402.[26] Williams SR, Wu JJ, Unsworth A,et al. Wear and surface analysis of 38 mm ceramic-on-metal total hip replacements under standard and severe wear testing conditions.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2011;225(8):783-796.[27] Gaga?a J, Mazurkiewicz T, Dajewski Z. Large diameter femoral heads in primary alumina/alumina and XSPE/alumina total hip arthroplasty. A follow-up study of 50 hips after average 40 months and review of literature. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2011;76(1):14-20.[28] Amanatullah DF, Landa J, Strauss EJ,et al. Comparison of surgical outcomes and implant wear between ceramic-ceramic and ceramic-polyethylene articulations in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(6 Suppl): 72-77.[29] Patel D, Parvizi J, Sharkey PF. Alternative bearing surface options for revision total hip arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2011;60:257-267.[30] Sedel L. Evolution of alumina-on-alumina implants: a review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(379):48-54.[31] Firkins PJ, Tipper JL, Ingham E, et al. A novel low wearing differential hardness, ceramic-on-metal hip joint prosthesis. J Biomech. 2001;34(10):1291-1298.[32] Chang WR.The effect of surface roughness and contaminant on the dynamic friction of porcelain tile. Appl Ergon. 2001; 32(2): 173-184.[33] Nevelos JE, Prudhommeaux F, Hamadouche M,et al. Comparative analysis of two different types of alumina-alumina hip prosthesis retrieved for aseptic loosening. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(4):598-603.[34] Williams SR, Wu JJ, Unsworth A,et al. Wear and surface analysis of 38 mm ceramic-on-metal total hip replacements under standard and severe wear testing conditions. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2011;225(8):783-796.[35] Gaga?a J, Mazurkiewicz T, Dajewski Z. Large diameter femoral heads in primary alumina/alumina and XSPE/alumina total hip arthroplasty. A follow-up study of 50 hips after average 40 months and review of literature. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2011;76(1):14-20.[36] Chevillotte C, Trousdale RT, An KN,et al. Retrieval analysis of squeaking ceramic implants: are there related specific features. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(3):281-287.[37] Whittingham-Jones P, Mann B, Coward P,et al. Fracture of a ceramic component in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(4):570-573.[38] Buttaro MA, Zanotti G, Comba FM, et al. Squeaking in a Delta ceramic-on-ceramic uncemented total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(6):1257-1259.[39] Hohman DW, Affonso J, Anders M. Ceramic-on-ceramic failure secondary to head-neck taper mismatch. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2011;40(11):571-573.[40] Chotai PN, Su EP. Fracture of a titanium sleeve-encased third-generation ceramic liner in a modern THA. Orthopedics. 2011;34(10):e682-e684.[41] Zywiel MG, Sayeed SA, Johnson AJ,et al. State of the art in hard-on-hard bearings: how did we get here and what have we achieved. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2011;8(2):187-207.[42] Butt U, Knowles D. A fractured and immovable ceramic liner in a screw-fixed acetabular shell during total hip arthroplasty: a case report. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2012;20(3): 395-397.[43] Whittingham-Jones P, Mann B, Coward P, et al. Fracture of a ceramic component in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(4):570-573. [44] Taheriazam A, Mohajer MA, Aboulghasemian M, et al. Fracture of the alumina-bearing couple delta ceramic liner. Orthopedics. 2012;35(1):e91-e93.[45] Bal BS, Garino J, Ries M, et al. A review of ceramic bearing materials in total joint arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2007;17(1):21-30.[46] Koo KH, Ha YC, Jung WH, et al. Isolated fracture of the ceramic head after third-generation alumina-on-alumina total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(2):329-336.[47] Cogan A, Nizard R, Sedel L. Occurrence of noise in alumina-on-alumina total hip arthroplasty. A survey on 284 consecutive hips. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011; 97(2): 206-210.[48] Chevillotte C, Pibarot V, Carret JP,et al. Hip squeaking: a 10-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(6): 1008-1013.[49] Chang JD, Kamdar R, Yoo JH,et al. Third-generation ceramic-on-ceramic bearing surfaces in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(8):1231-1235. |
| [1] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [3] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [4] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [5] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [6] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [7] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [8] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [9] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [10] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [11] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [12] | Zhang Nianjun, Chen Ru. Analgesic effect of cocktail therapy combined with femoral nerve block on total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 866-872. |
| [13] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [14] | Liu Lihua, Sun Wei, Wang Yunting, Gao Fuqiang, Cheng Liming, Li Zirong, Wang Jiangning. Type L1 steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through femoral head and neck junction decompression by fenestration: a single-center prospective clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 906-911. |
| [15] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||