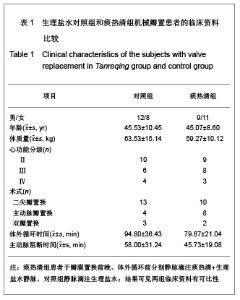
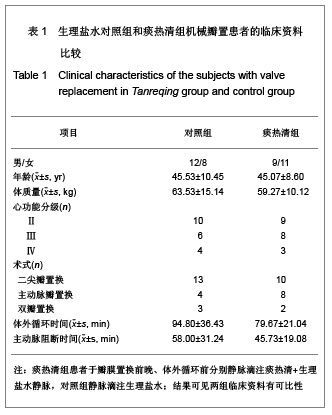
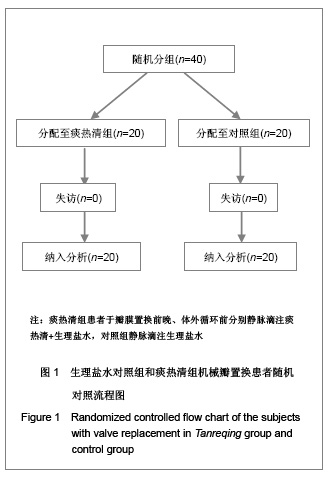
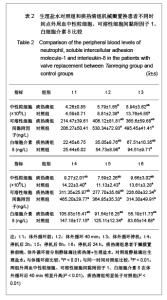
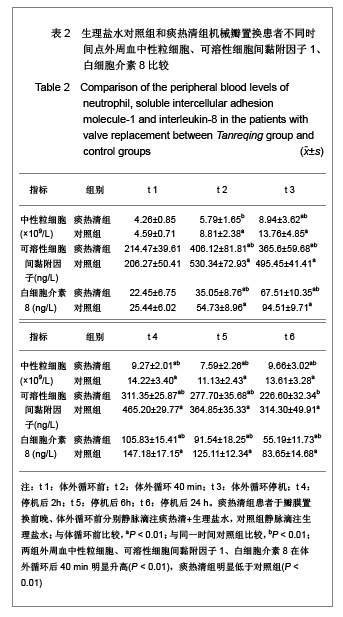
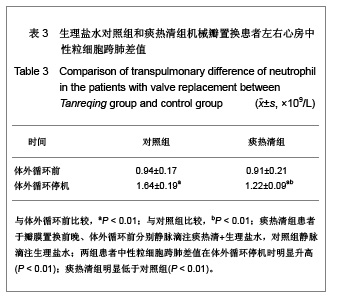
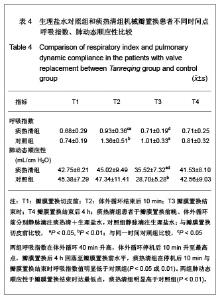
| [1] Woo CW, Cheung F, Chan VW, et al. Homocysteine stimulates inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in macrophages: antagonizing effect of ginkgolides and bilobalide. Mol Cell Biochem.2003;243:37-47.[2] Yeh CH, Lin YM, Wu YC, et al. Inhibition of NF -kappaB activation can attenuate ischemia/reperfusion-induced contractility impairment via decreasing cardiomyocytic proinflammatory gene up-regulation and matrix metalloproteinase expression. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2005;45:301-309.[3] Zhu HB, Gao CR, Liu WP, et al. Zhonghua Quanke Yixue. 2009;7(10): 1049-1050. 祝会斌,高从容,刘卫萍,等. 川芎嗪对体外循环患者血浆中性粒细胞弹性蛋白酶及ICAM-1的浓度影响[J]. 中华全科医学, 2009, 7(10): 1049-1050. [4] Chen JX, Su ZY, Zhan H. Linchuang Yixue Gongcheng. 2010; 17(7):22-24. 陈郡兴,苏志源,詹鸿.川芎嗪对体外循环心脏手术血浆神经元特异性烯醇化酶及术后认知功能障碍作用的初步探讨[J].临床医学工程,2010,17(7):22-24.[5] Wang G, Pan ZX, Wu C,et al.Shandong Yiyao. 2009;49(4): 29-31. 王刚,潘征夏,吴春,等.体外循环术对婴幼儿先心病术后肺的损伤及川芎嗪的保护作用[J].山东医药,2009,49(4):29-31. [6] Zhou LJ,Xiao MD.Zhongguo Tiwaixunhuan Zazhi. 2010;8(1): 61-64. 周黎瑾,肖明第.体外循环手术中性粒细胞致肺损伤的机制[J].中国体外循环杂志,2010,8(1):61-64.[7] Li X, Fan SZ, Li ZP, et al. Chongqing Yixue. 2005;34(8): 1167-1169. 李叙,范士志,李志平,等. 体外循环围手术期白细胞、中性粒细胞、细胞因子变化关系研究[J].重庆医学, 2005, 34(8): 1167-1169. [8] Zhu XH, Wu YQ, Chen SL, et al. Shandong Yiyao. 2010;50(2): 87-89. 朱晓红,吴延庆,陈受琳,等.体外循环下心内直视手术患者血浆中NE的表达变化及意义[J].山东医药,2010,50(2):87-89.[9] Chen XW, Fu J, Ruan XM, et al. Zhongguo Zhongxiyijiehe Zazhi. 2006; 26(9): 775-779. 陈晓伟,付鉴,阮新民,等.参附注射液对体外循环手术患者围术期机体免疫功能的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志, 2006, 26(9): 775-779. [10] Gao CR, Zhu HB, Liu WP, et al. Anhui Yixue. 2009;30(9): 1065-1067. 高从容,祝会斌,刘卫萍,等.体外循环对血管内皮细胞及中性粒细胞弹性蛋白酶影响[J].安徽医学,2009,30(9):1065-1067.[11] Xin XF, Zhao M, Zhang F, et al. Yixue Ynjiusheng Xuebao. 2008;21(8):831-835. 辛晓峰,赵明,张方,等.重度支气管哮喘患者诱导痰中白细胞介素-17水平及其与气道炎症和气流受限的关系[J].医学研究生学报, 2008,21(8):831-835. [12] Wu R, Zhou HY, Li N, et al. Zhongguo Xinshengerke Zazhi. 2012;27(3):201-204. 武荣,周海燕,李娜,等.比例辅助通气对重症胎粪吸入幼兔肺组织肿瘤坏死因子-α和白细胞介素-8水平的影响[J].中国新生儿科杂志,2012,27(3):201-204.[13] Matilla M, Garcia Yuste M, Sanchez Crespo M, et al. Interleukin-8 expression in lung tissue during ischemia/ reperfusion. Arch Bronconeumol.2007;43(10): 542-548.[14] Jia WK, Zhang EY, Wei SL, et al. Zhongguo Xiongxinxueguan Waike Linchuang Zazhi. 2010;17(4):279-282. 贾维坤,张尔永,魏蜀亮,等.体外循环围术期细胞黏附分子CD11/CD18,P-选择素的表达及其意义[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2010,17(4):279-282. [15] Yang XL, Wang GY. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2010; 30(8):1108-1110. 杨学良,王广义.重症急性胰腺炎肺损伤大鼠s-ICAM-1和LEA-1变化及丹参注射液的干预作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2010, 30(8): 1108-1110.[16] Fan LL, Yu XY. Zhonghua Shiyongzhenduanyuzhiliao Zazhi. 2009;24(2):136-139. 范丽丽,于湘友.乌司他丁对体外循环患者细胞黏附分子浓度影响及对肺损伤保护作用[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2009, 24(2):136-139.[17] Zhao X, Dib M, Andersson E, et al. Alterations of adhesion molecule expression and inflammatory mediators in acute lung injury induced by septic and non-septic challenges. Lung.2005;183(2):87-100. [18] Ye J, Han GQ, Nan XZ, et al. Zhongguo Jijiu Yixue. 2007; 27(2):178-180. 叶璟,韩国强,南向珍,等.不同病因致急性肺损伤患儿可溶性细胞间黏附分子-1的变化和临床意义[J].中国急救医学, 2007,27(2): 178-180.[19] Kira S, Daa T, Kashima K, et al. Mild hypothermia reduces expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and the accumulation of neutrophils after acid-induced lung injury in the rat. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand.2005;49(3): 351-359.[20] Li X, Yan YJ, Deng JT, et al. Zhongguo Dangdai Yiyao. 2011; 18(7):37-38. 李曦,严永俊,邓继廷,等.呼吸指数对重症创伤患者预后评估的临床研究[J].中国当代医药,2011,18(7):37-38.[21] Li XY, Yu L. Huabei Meitanyixueyuan Xuebao. 2011;13(3): 334-335. 李秀勇,于兰.胸肺顺应性监测在心脏外科的临床意义[J].华北煤炭医学院学报,2011,13(3):334-335.[22] Liu HJ, Zhang Y, Xin JB, et al. Zhongguo Yiyuanyaoxue Zazhi. 2009;29(19):1607-1670. 刘红菊,张玉,辛建保,等.痰热清的抗氧化作用及对急性肺损伤的抑制作用研究[J].中国医院药学杂志,2009,29(19):1607-1670.[23] Lei LM. Yiyao Daobao. 2008;27(4):420-421. 雷李美.痰热清注射液对急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者细胞因子的影响[J].医药导报,2008,27(4):420-421.[24] Li PT, Zhang N, Zhu XL, et al. Zhongguo Yaoxue Zazhi. 2005; 40(7):518-521. 李彭涛,张娜,朱晓磊,等.痰热清注射液抗内毒素所致急性肺损伤的实验研究[J].中国药学杂志,2005,40(7):518-521.[25] Liu WC, Zheng J. Shanxi Yikedaxue Xuebao. 2006;37(5): 489-492. 刘文操,郑军.痰热清对抗内毒素诱导致大鼠急性肺损伤的实验研究[J].山西医科大学学报,2006,37(5):489-492. |