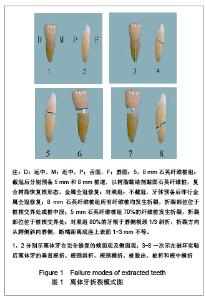
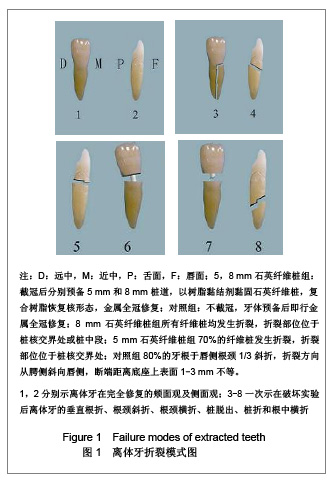
| [1] Zicari F,Van Meerbeek B,Scotti R,et al. Effect of fibre post length and adhesive strategy on fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth after fatigue loading. J Dent. 2012;40(4):312-321.[2] McLaren JD,McLaren CI,Yaman P,et al.The effect of post type and length on the fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth.J Prosthet Dent. 2009;101(3):174-182.[3] Schmitter M,Lippenberger S,Rues S,et al. Fracture resistance of incisor teeth restored using fibre-reinforced posts and threaded metal posts: effect of post length, location, pretreatment and cementation of the final restoration.Int Endod J.2010;43(5):436-442.[4] do Valle AL,Pereira JR,Shiratori FK,et al.Comparison of the fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth restored with prefabricated posts and composite resin cores with different post lengths.J Appl Oral Sci. 2007;15(1):29-32.[5] Nissan J,Barnea E,Carmon D,et al.Effect of reduced post length on the resistance to fracture of crowned, endodontically treated teeth.Quintessence Int. 2008;39(8): e179-182.[6] Costa RG,De Morais EC,Campos EA,et al. Customized fiber glass posts. Fatigue and fracture resistance.Am J Dent.2012; 25(1):35-38.[7] Heydecke G,Butz F,Hussein A,et al.Fracture strength after dynamic loading of endodontically treated teeth restored with different post-and-core systems. J Prosthet Dent. 2002;87(4): 438-445.[8] Abo El-Ela OA,Atta OA,El-Mowafy O.Fracture resistance of anterior teeth restored with a novel nonmetallic post.J Can Dent Assoc.2008;74(5):441.[9] Barjau-Escribano A,Sancho-Bru JL,Forner-Navarro L,et al.Influence of prefabricated post material on restored teeth: fracture strength and stress distribution. Oper Dent. 2006; 31(1):47-54.[10] Hayashi M,Takahashi Y,Imazato S,et al.Fracture resistance of pulpless teeth restored with post-cores and crowns. Dent Mater.2006;22(5):477-485.[11] Loney RW,Moulding MB,Ritsco RG. The effect of load angulation on fracture resistance of teeth restored with cast post and cores and crowns. Int J Prosthodont. 1995;8(3):247-251.[12] Guzy GE,Nichols JI.In vitro comparison of intact endodontically treated teeth with and without endo-post reinforcement. J Prosthet Dent. 1979;42(1):39-44.[13] Stockton LW.Factors affecting retention of post systems: a literature review. J Prosthet Dent. 1999;81(4):380-385.[14] Holms DC,Diaz-Arnold AM,Leary JM. Influence of post dimension on stress distribution in dentin. J Prosthet Dent. 1996; 75(2):140-147.[15] Zhang CY,Lu J,Chen XY,et al.Zhonghua Laonian Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2006;4(3):157-159. 张春元,鲁洁,陈霞云,等. 不同材料根管桩剪切粘结强度的比较[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2006,4(3):157-159.[16] Nergiz I,Schmage P,Ozcan M.Effect of length and diameter of tapered posts on the retention. J Oral Rehabil. 2002;29(1): 28-34.[17] Bitter K,Paris S,Martus P,et al.A confocal laser scanning microscope investigation of different dental adhesives bonded to root canal dentine. Int Endod J. 2004;37(12): 840-848.[18] Nissan J,Dmitry Y,Assif D.The use of reinforced composite resin cement as compensation for reduced post length. J Prosthet Dent. 2001;86(3):304-308.[19] [Ba?aran EG,Ayna E,Halifeo?lu M. Microleakage of endodontically treated teeth restored with 3 different adhesive systems and 4 different fiber-reinforced posts.J Prosthet Dent. 2012;107(4):239-251.[20] Mezzomo E,Massa F,Libera SD.Fracture resistance of teeth restored with two different post-and-core designs cemented with two different cements: an in vitro study. Part I. Quintessence Int. 2003; 34(4):301-306.[21] Nothdurft FP,Schmitt T,Rupf S,et al.Influence of fatigue testing and cementation mode on the load-bearing capability of bovine incisors restored with crowns and FRC posts.Dent Mater J.2011;30(1):109-114.[22] Juloski J,Radovic I,Goracci C,et al. Ferrule effect: a literature review. J Endod. 2012;38(1):11-9.[23] Nie EM,Chen XY,Qi LL,et al.Zhongshan Daxue Xuebao. 2009; 30(3):290-293. 聂二民,陈霞云,亓莉莉,等.不同牙体剩余量对石英纤维桩冠抗折性能的影响[J].中山大学学报,2009,30(3):290-293.[24] Sherfudhin H,Hobeich J,Carvalho CA,et al.Effect of different ferrule designs on the fracture resistance and failure pattern of endodontically treated teeth restored with fiber posts and all-ceramic crowns.J Appl Oral Sci. 2011; 19(1):28-33.[25] Mangold JT,Kern M.Influence of glass-fiber posts on the fracture resistance and failure pattern of endodontically treated premolars with varying substance loss: an in vitro study. J Prosthet Dent. 2011;105(6):387-393.[26] Dorriz H,Alikhasi M,Mirfazaelian A,et al. Effect of ferrule and bonding on the compressive fracture resistance of post and core restorations.J Contemp Dent Pract.2009;10(1):1-8.[27] Fu G,Deng F,Wang L,et al.The three-dimension finite element analysis of stress in posterior tooth residual root restored with postcore crown. Dent Traumatol. 2010;26(1):64-69.[28] Fu G,Du L,Ren AS,et al.The three-dimension finite element analysis of stress in posterior residual root restored with different designed post-core crown.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi.2009;27(1):24-28. |