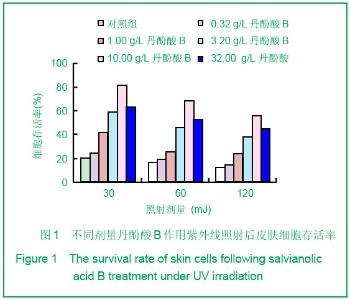
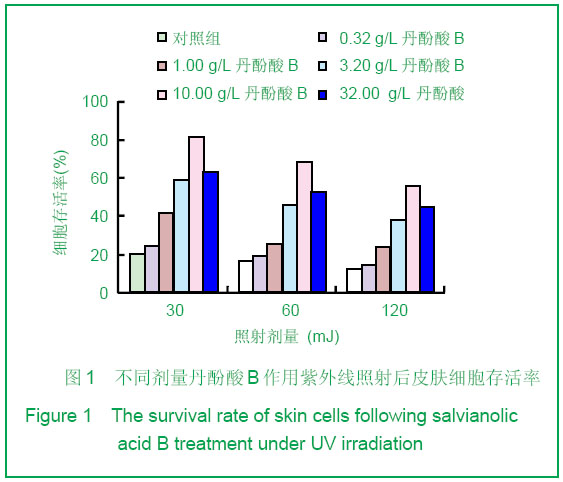
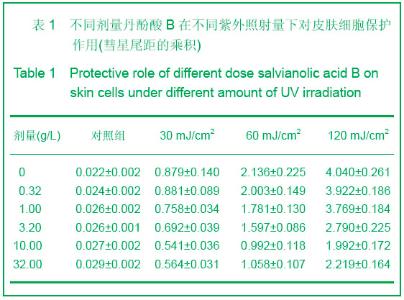
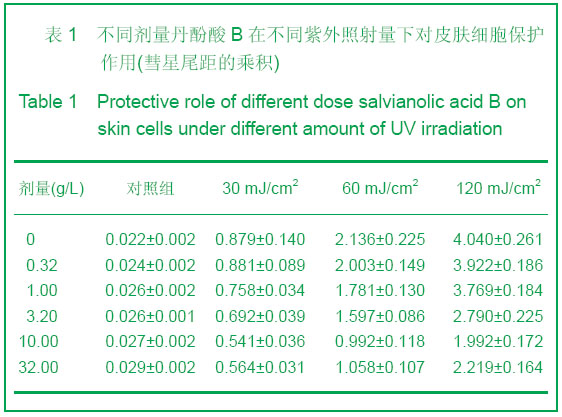
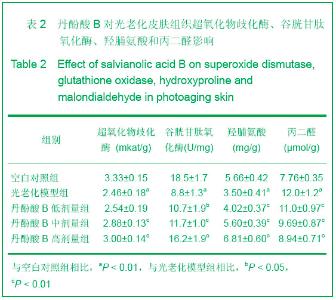
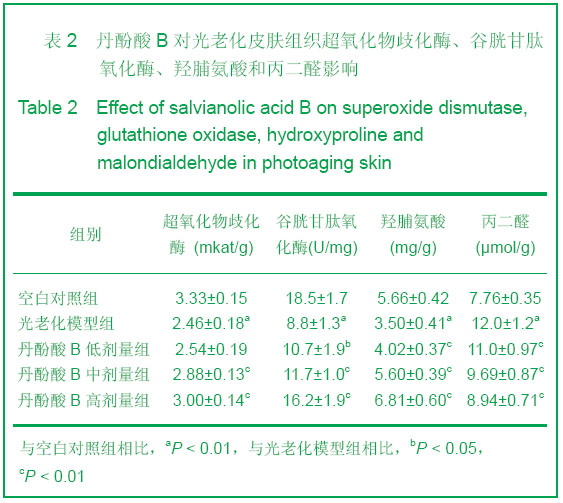
| [1] Alcaraz MV,Pathak MA,Rius F,et al. An extract of Polypodium leucotomos appears to minimize certain photoaging changes in a hairless albino mouse animal model.Photodermatol Photoim-munol Photomed.1999;15:120-126.[2] Moon HI,Kim EJ,Lee J,et al.The efect of sativan fromViola verecunda A. Gray on the expressions of matrix metalloproteinase-1caused by ultraviolet irradiated cultured primary human skin fibroblasts.J Ethnopharmacol.2006; 104: 12-17.[3] Moon HI,Lee J,Kwak JH,et al.Isoflavonoid from Viola hondoensis,regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in human skin fibroblasts.Biol Pharm Bull.2005;28:925-928.[4] Cheng JY,Liu GH,Huang JC,et al.Shizhen Guoyi Guoyao. 2006; 17(9):1672-1673.程基焱,刘国红,黄吉春,等.人参皂苷Rbl与芳维甲酸乙酯对光老化皮肤真皮成纤维细胞基质金属蛋白酶影响的比较研究[J].时珍国医国药,2006,17(9):1672-1673.[5] Wang SH.Zhongyiyao Xuekan.2006;24(4):718-719.王诗晗.黄芪提取液对光老化无毛小鼠皮肤组织HYP MDA含量及SOD活力的影响[J].中医药学刊,2006,24(4):718-719.[6] Min W,Luo D,Lin XF.Xuzhou Yixueyuan Xuebao.2004;24(2): 167-171.闵玮,骆丹,林向飞.黄芩对皮肤细胞紫外线辐射损伤的保护作用[J].徐州医学院学报,2004,24(2):167-171.[7] Du GH,Zhang JT.Yiyao Daobao. 2004,23(6):355.杜冠华,张均田.丹参现代研究概况与进展(续一)[J] 医药导报, 2004,23(6):355.[8] Du GH,Zhang JT.Jichuyixue Yu Linchuang.2000;20(5):210.杜冠华.张均田.丹参水溶性有效成分一丹酚酸研究进展[J].基础医学与临床,2000,20(5):210.[9] Peng ZG,Chen HS.Zhongguo Yaoxue Zazhi.2003;38(10): 744.彭宗根.陈鸿珊.紫草酸B的药理作用研究进展[J].中国药学杂志, 2003,38(10):744.[10] He YY,Huang JL,Gentry JB,et al.Epidermal growth factor receptor down-regulation induced by UVA inhuman keratinocytesdoes not require the receptor kinaseactivity.J Biol Chem.2003;278(43):42457-42465.[11] Maziere C,Floret S,Santus R,et al.Impairment of the EGF sign aling pathway by the oxidative stress generated with UVA. Free Radic Biol Med.2003;34(6):629-636.[12] Yaar M ,Gilchrest B A. Photoageing: mechanism,prevention and therapy.Br J Dermatol.2007;157:874-887.[13] Kosmadaki MG,Gilchrest BA.The role of telomeres in skin aging/photoaging.Micron.2004;35:155-159.[14] Liu Y, Wang BX . Review of mechanism of carcinoma by ultrabiolet. Chin J Public Health.2000;18:183-185.[15] Du H. Diyi Junyi Daxue. 2003.杜华.紫外辐射对人角质形成细胞的细胞周期调控的影响[D]. 第一军医大学,2003.[16] He Z,Cho YY,Liu G,et al. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase regulation of JB6 Cl41 cell transformation promoted by epidermal growth factor.J Biol Chem.2003;278(29): 26435- 26442. |