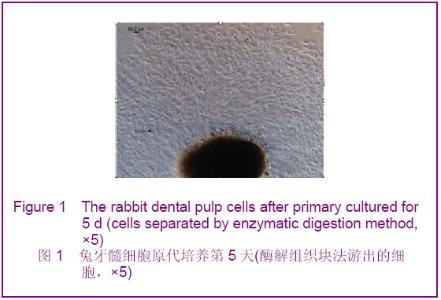
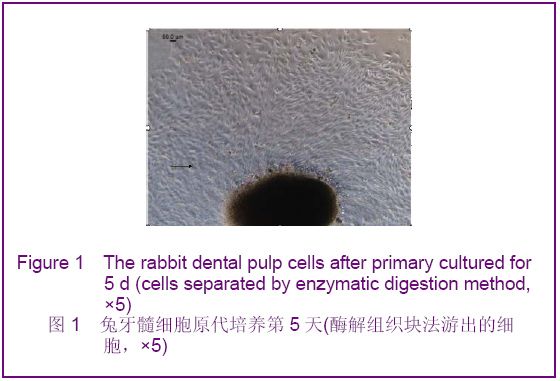
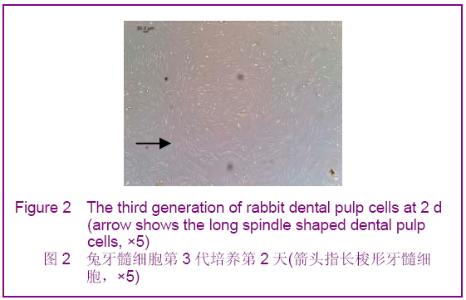
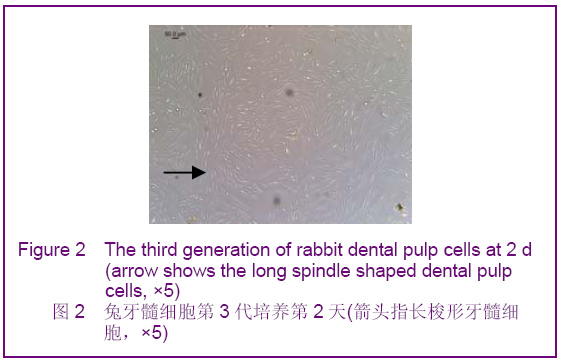
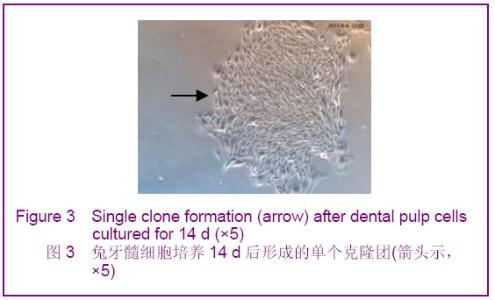
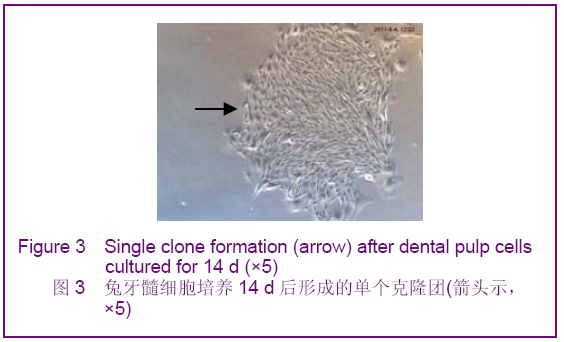
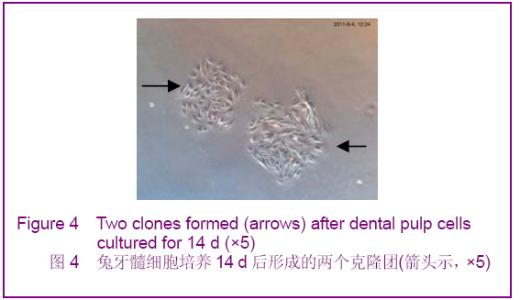
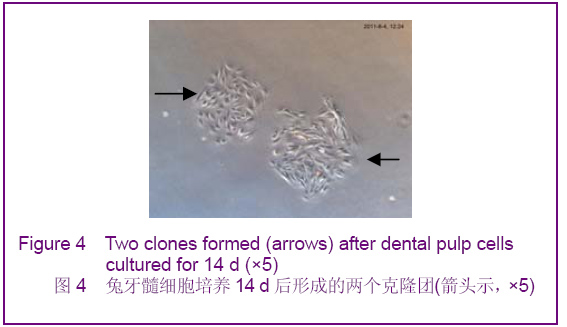
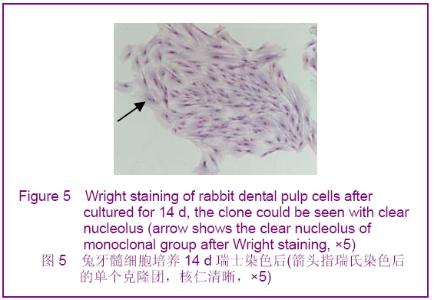
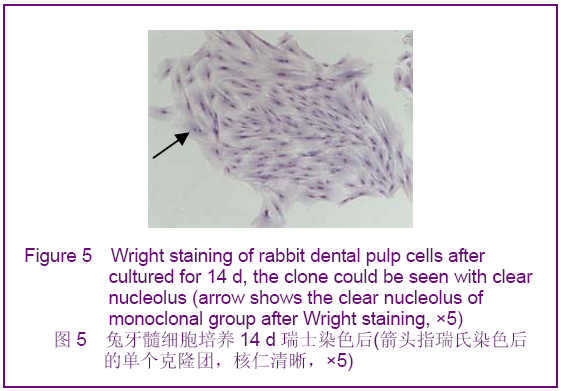
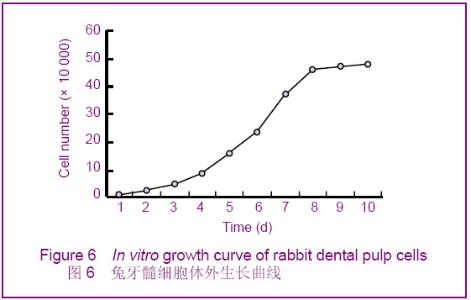
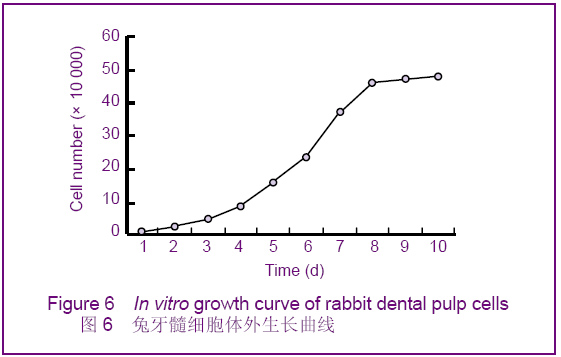
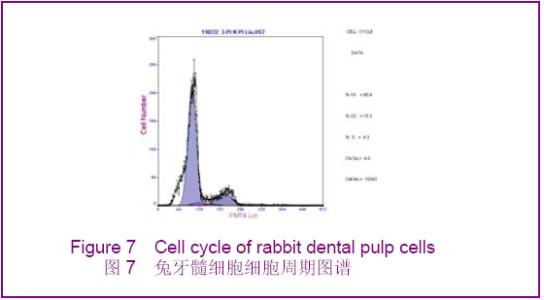
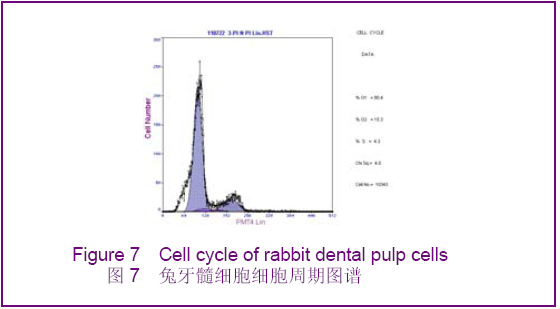
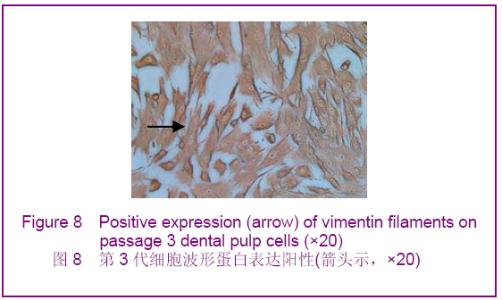
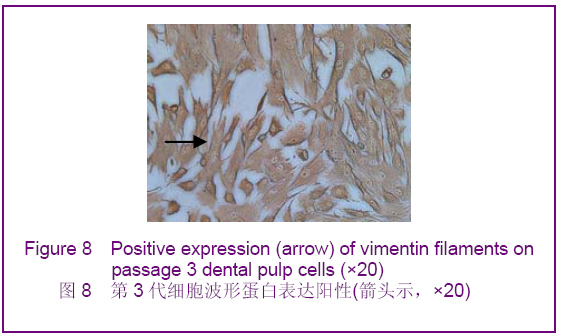
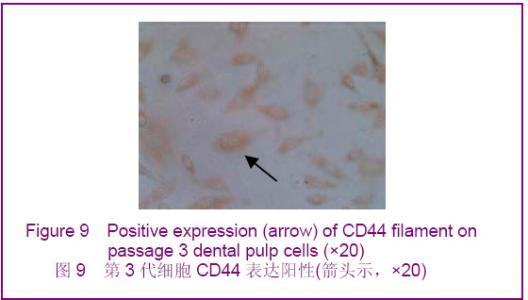
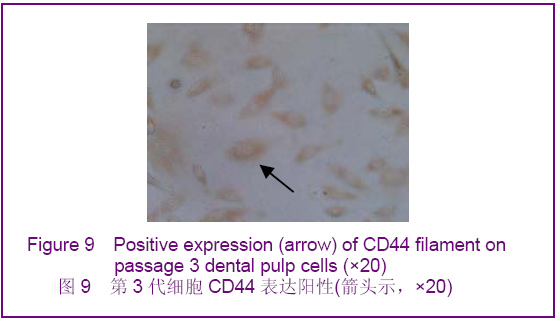
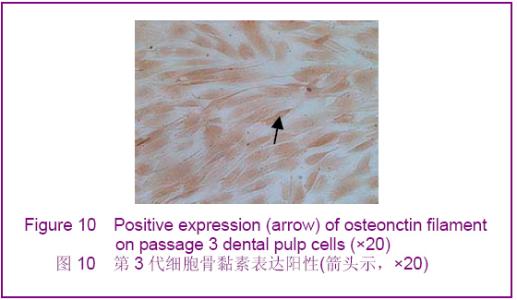
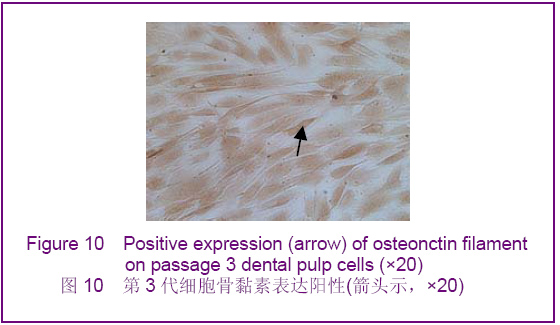
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2012, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (49): 9236-9240.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2012.49.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
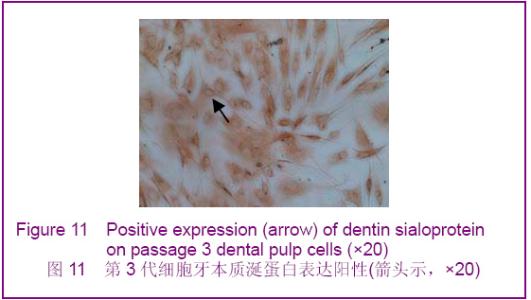
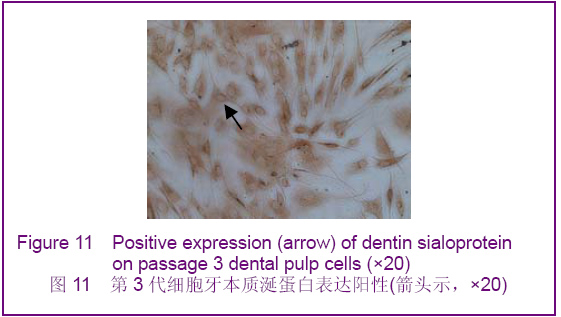
In vitro proliferation and identification of rabbit dental pulp cells
Ma Rong1, Wang Yan-mei2, Zhuang You-mei2, Muhetaer·Huojia2
- 1Department of Stomatology, People's Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830001, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, People's Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830001, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2012-04-13Revised:2012-05-16Online:2012-12-02Published:2013-01-16 -
Contact:Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, People's Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830001, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China muhtarhoja@yahoo.com -
About author:Ma Rong★, Studying for master’s degree, Physician, Department of Stomatology, People's Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830001, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China pikamei@163.com -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30960423*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Rong, Wang Yan-mei, Zhuang You-mei, Muhetaer?Huojia. In vitro proliferation and identification of rabbit dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2012, 16(49): 9236-9240.
share this article
| [1] Gronthos S,Mankani M,Brahim J,et al.Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells(DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo Proc.Natl.Acad. Sci.USA.2000;97(25):13625-13630.[2] Miura M , Gronthos S, Zhao M, et al. SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100(10):5807-5812.[3] Lu Q.Xi’an:disi Junyi Daxue Boshi Xuewei Lunwen.2002.陆群.牙髓干细胞分离培养鉴定和体外诱导分化的研究[D].西安:第四军医大学博士学位论文,2002.[4] Guo HY.Xi’an:disi Junyi Daxue Boshi Xuewei Lunwen.2002.郭红延.大鼠牙髓干细胞的培养鉴定及生物学特性研究[D].第四军医大学博士学位论文.西安:2004.[5] Zheng Y,Wang XY,Zhang CM.Beijing Kouqiang Yixue. 2010; 18(3):125-128.郑颖,王晓颖,张春梅.小型猪乳牙牙髓干细胞体外分离培养及鉴定[J].北京口腔医学,2010,18(3):125-128.[6] Casagrande L, Cordeiro MM, Nör SA, et al.Dental pulp stem cells in regenerative dentistry.Odontology. Odontology. 2011;99(1):1-7. [7] Karaoz E,Dogan BN,Aksoy A, et al. Isolation and in vitro characterisation of dental pulp stem cells from natal teeth. Histochemistry and Cell Biology.2010;133:95-112.[8] Huang AH, Chen YK, Lin LM, et al. Isolation and characterization of dental pulp stem cells from a supernumerary tooth. Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine. 2008;37:571-574.[9] Shi S, Gronthos S. Perivascular niche of postnatal m esenchymal stem cells in human bone marrow and dental pulp J Bone Miner Res.2003;18(4):696-704.[10] Alliot -LichtB, Bluteau G, Magne D, et al.Dexamet- hasone stimulates differentiation of odontoblast like cells in human dental pulp cultures Cell Tissue Res.2005;321(3):391 400.[11] Woodbury D,Schwarz EJ,Prochop DJ,et al.Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons.J Neurosci Res.2000;61(4):364-370.[12] Gronthos S, Brahim J, Fisher LW, et al.Stem Cell Properties of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Dent Res.2002;81(8): 531-535.[13] Cui Q,Wang GJ,Balian C,Steroid-induced adipogenesis in a pluripotent cell line from bone marrow.J Bone Joint Surg. 1997;79;1054-1063.[14] Uchida N.The expected G0/G1 cell cycle status of mobilized hematopoietic stem cells from peripheral blood.Blood.1997; 89:465-451.[15] Situ Zhenqiang.Xi’an:Sijie Tushu Chuban Gongsi. 2007:68-77.司徒镇强.细胞培养[M]. 2版,西安:世界图书出版公司,2007: 68-77.[16] Fujimori Y,Izumi K,Feinberg SE,et al. Isolation of small-sized human epidermal progenitor/stem cells by Gravity Assisted Cell Sorting (GACS). J Dermatol Sci. 2009;56(3):181-187.[17] Dominici M,Le Blanc K,Mueller I,et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy.2006;8(4): 315-317.[18] Engelhardt M.Telomerse regulation,cell cycle,and telomere stability in primitive hematopoietic cells.Blood.1997;90:182.[19] He HX. Xi’an:disi Junyi Daxue Boshi Xuewei Lunwen. 2005.贺慧霞.牙髓干细胞分离鉴定及其制备组织工程化牙本质牙髓复合体的实验研究[D].第四军医大学博士学位论文,西安:2005.[20] He F,Tan YH,Zhang G.Huaxi Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2005; 23(1): 75-78.何飞,谭颖徽,张纲.人牙髓干细胞的体外培养和鉴定[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2005. |
| [1] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [2] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [3] | Liu Xun, Ouyang Hougan, Pan Rongbin, Wang Zi, Yang Fen, Tian Jiaxuan . Optimal parameters for physical interventions in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6727-6732. |
| [4] | Lin Meiyu, Zhao Xilong, Gao Jing, Zhao Jing, Ruan Guangping. Action mechanism and progress of stem cells against ovarian granulosa cell senescence [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5414-5421. |
| [5] | Hu Enxi, He Wenying, Tao Xiang, Du Peijing, Wang Libin. Regulation of THZ1, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 7, on stemness of glioma stem cells and its mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5374-5381. |
| [6] | Tian Zhenli, Zhang Xiaoxu, Fang Xingyan, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on lipid metabolism in human hepatocytes and regulatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4956-4964. |
| [7] | Han Fang, Shu Qing, Jia Shaohui, Tian Jun. Electrotactic migration and mechanisms of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4984-4992. |
| [8] | Hu Chen, Jiang Ying, Chen Jia, Qiao Guangwei, Dong Wen, Ma Jian. Preparation and characterization of alendronate/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel films [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(22): 4720-4730. |
| [9] | Yang Chao, Luo Zongping. Small molecule drug TD-198946 enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2648-2654. |
| [10] | Li Xiaofeng, Zhao Duo, Ouyang Qin, Pang Zixiang, Li Yuquan, Chen Qianfen. Protective effect of mangiferin on oxidative stress injury in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2669-2674. |
| [11] | Hu Zezun, Yang Fanlei, Xu Hao, Luo Zongping. Effect of surface roughness of polydimethylsiloxane on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under stretching conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1981-1989. |
| [12] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [13] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [14] | Liu Haowen, Qiao Weiping, Meng Zhicheng, Li Kaijie, Han Xuan, Shi Pengbo. Regulation of osteogenic effects by bone morphogenetic protein/Wnt signaling pathway: revealing molecular mechanisms of bone formation and remodeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 563-571. |
| [15] | Zhou Shijie, Li Muzhe, Yun Li, Zhang Tianchi, Niu Yuanyuan, Zhu Yihua, Zhou Qinfeng, Guo Yang, Ma Yong, Wang Lining. Effect of Wenshen Tongluo Zhitong formula on mouse H-type bone microvascular endothelial cell/bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 8-15. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||