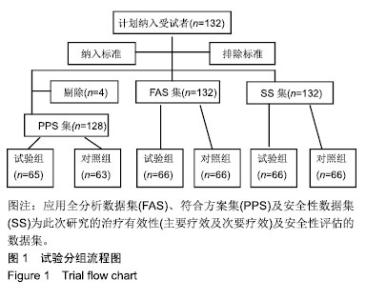
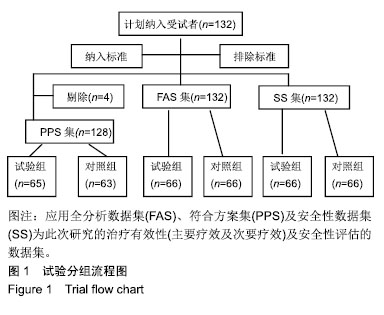
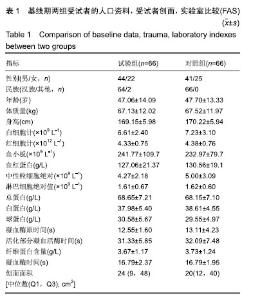
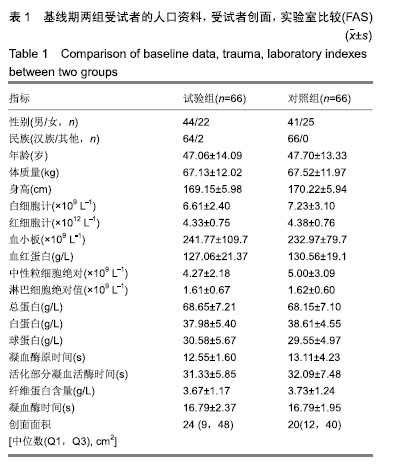
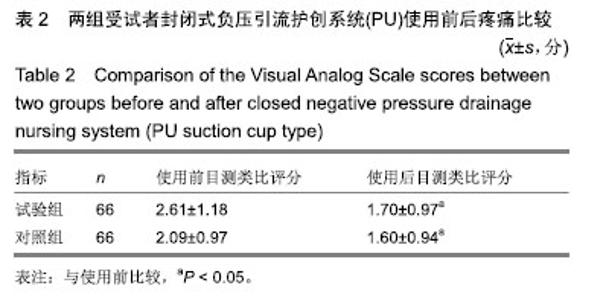
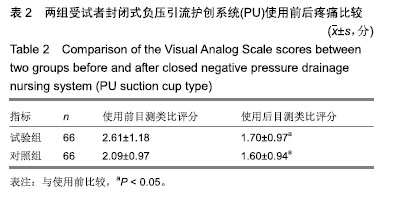
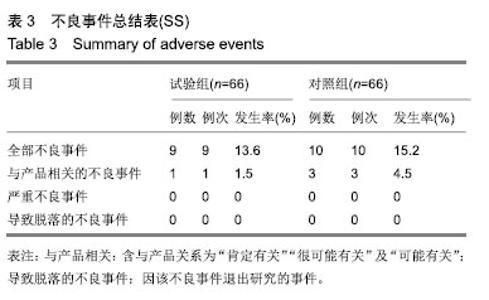
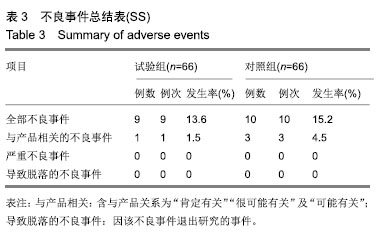
| [1]Fleischmann W, Strecker W, Bombelli M, et al. Vacuum sealing as treatment of soft tissue damage in open fractures. Unfallchirurg. 1993;96(9):488-492.[2]裘华德,宋九宏.负压封闭吸引技术[M].2版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2008:3-34.[3]胡建武,任继魁,姜娟,等.封闭负压技术治疗各种创面的临床应用体会[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2007,2(5):305-306.[4]李志强,刘树江,吴文杰.负压封闭引流技术的研究进展及在骨科的应用[J].牡丹江医学院学报,2015,36(6):93-95.[5]王志勇,施耘,阮建春,等.持续封闭负压引流技术在深度烧伤创面修复中的应用[J].广东医学,2011,32(7):852-854.[6]袁有义.封闭负压吸引技术在小腿创面中应用意义及机理探讨[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(10):32-33. [7]Armstrong DG, Lavery LA. Negative pressure wound therapy after partial diabetic foot amputation: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;366(9498): 1704-1710.[8]刘琳娜,李学拥,吴晓春,等.银离子抗菌敷料用于Ⅱ度烧伤创面的疗效和安全性[J].实用药物与临床,2013,16(10):922-924.[9]张俊成,谢有富,梁达荣,等.封闭式负压引流在30例烧伤植皮区和供皮创面的应用[J].广东医学,2009,30(12):1949-1949.[10]严广斌.视觉模拟评分法[J].中华关节外科杂志,2014,8(2):34.[11]Zhang C, Liu D, Liang Z, et al. Repair of refractory wounds through grafting of artificial dermis and autologous epidermis aided by vacuum-assisted closure. Aesthet Plast Surg. 2014; 38(4):727-732.[12]Ruran W, Yanhua F, Bo D. Comparisons of negative pressure wound therapy and ultrasonic debridement for diabetic foot ulcers: a network meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8(8):12548.[13]Wojciech W, Arkadiusz J, Wojciech W, et al. Initial multi-centre observations upon the effect of a new topical negative pressure device upon patient and clinician experience and the treatment of wounds. Int Wound J. 2010; 6(2):167-174.[14]Scherer LA, Stephen S, Michael C, et al. The vacuum assisted closure device: a method of securing skin grafts and improving graft survival. Arch of Surg. 2002;137(8):930.[15]Swanson EW, Susarla SM, Lough DM, et al. Incisional negative pressure wound therapy following ventral hernia repair reduces wound complications and hernia recurrence: a meta-analysis. Plast Rec Surg. 2015;136(4 Suppl):12.[16]Fischer JE. A cautionary note: the use of vacuum-assisted closure systems in the treatment of gastrointestinal cutaneous fistula may be associated with higher mortality from subsequent fistula development. Am Jour of Surg. 2008;196(1):1-2.[17]马虹,孙强,田卓民.负压封闭引流技术在42例难治性压疮患者中的应用[J].中华护理杂志,2010,45(8):696-697.[18]朱家伟,谭谦.封闭负压引流技术对创面愈合影响的Meta分析[J].东南大学学报(医学版),2015,34(2):253-260.[19]Anesäter E, Borgquist O, Hedström E, et al. The influence of different sizes and types of wound fillers on wound contraction and tissue pressure during negative pressure wound therapy. Int Wound J. 2011;8(4):336-342.[20]Fox A, Tadros A, Perks AGB. An unusual complication of Vacuum Assisted Closure in the treatment of a pressure ulcer. J Wound Care. 2004;13(8):344-345.[21]李宇飞,赵建宁,张文俊.含纳米银聚氨酯敷料的持续封闭负压引流在创面治疗中的应用[J].中国美容医学,2014,23(5):353-356.[22]罗伟东,黄枫,何才勇,等.游离植皮联合负压封闭引流治疗骨科创面的临床研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2011,11(2):269-273.[23]李晨阳,马兵.负压引流技术在临床应用中的研究进展[J].华西医学,2011,26(10):1461-1465.[24]邓件良,刘宝恒,陈先礼,等.持续封闭负压引流治疗复杂创伤性皮肤软组织缺损的临床疗效观察[J].实用手外科杂志,2010,24(4): 272-273.[25]李靖,陈绍宗,李学拥,等.封闭负压引流对创面微循环超微结构影响的实验研究[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2006,17(1):75-77.[26]张丽华,刘佳佳, 徐淑娟,等.负压封闭引流技术治疗骨科创伤及感染创面的护理对策[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2012,22(7): 1384-1385.[27]阙云端,王东明.负压封闭引流技术在四肢复杂创面治疗中的应用18例分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2011,11(9):2238-2239.[28]郝剑,刘宾,陶谏,等.封闭负压引流技术中不同材质敷料治疗慢性创面效果的实验研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2014,43(10):1287-1289.[29]Heit YI, Dastouri P, Helm DL, et al. Foam pore size is a critical interface parameter of suction-based wound healing devices. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129(3):589-597.[30]Huang C, Leavitt T, Bayer LR, et al. Effect of negative pressure wound therapy on wound healing. Curr Probl Surg. 2014;51(7):301-331.[31]CCTS工作组,陈平艳(执笔).临床试验中样本量确定的统计学考虑[J].中国卫生统计,2015,32(4):727-733. |