Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (13): 2120-2125.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1851
Previous Articles Next Articles
Insight into white matter changes in Alzheimer’s disease: a focus on myelin and oligodendrocyte
Zhao Hong, Wang Suping, Lian Jianwen
- Department of Neurology, Dalian Municipal Central Hospital, Dalian 116033, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2019-04-20Revised:2019-05-05Accepted:2019-06-29Online:2020-05-08Published:2020-03-11 -
Contact:Lian Jianwen, Master, Chief physician, Department of Neurology, Dalian Municipal Central Hospital, Dalian 116033, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zhao Hong, MD, Chief physician, Department of Neurology, Dalian Municipal Central Hospital, Dalian 116033, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Hong, Wang Suping, Lian Jianwen. Insight into white matter changes in Alzheimer’s disease: a focus on myelin and oligodendrocyte[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2120-2125.
share this article
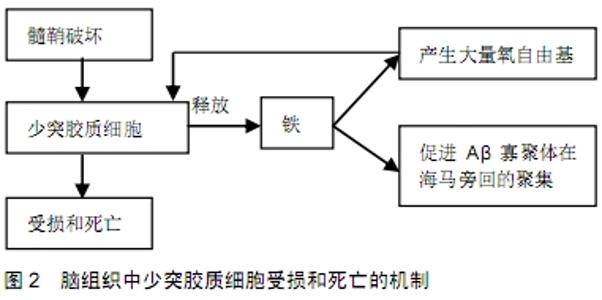
2.1 阿尔茨海默病存在广泛的白质损害 脑白质主要由少突胶质细胞及其形成的髓鞘构成,主要负责联系各个皮质及皮质下的结构。脑白质病变又称脑白质疏松或脑白质高信号(white matter hyperintensities,WMHs),这一概念是由加拿大神经病学家Hachinski等在1986年提出的一个影像学诊断术语,其诊断主要基于头CT及MRI技术,指在头CT中双侧对称的脑室旁及半卵圆中心白质呈现的弥漫性低密度病灶或在MRI T2加权相上出现的高信号病灶。随着年龄的增长,脑白质病变的发病率逐渐增加,其发展为阿尔茨海默病的风险也增高。阿尔茨海默病患者死后脑组织尸检发现,髓鞘蛋白如碱性髓鞘蛋白、髓鞘蛋白脂蛋白、环核苷酸磷酸水解酶和胆固醇的水平与没有痴呆的患者相比明显降低,且白质脂肪酸的比例也发生变化,提示阿尔茨海默病患者存在广泛的白质退行性变或因严重少突细胞丧失导致的白质疏松[2]。有趣的是,神经影像研究发现在阿尔茨海默病的临床前阶段即存在白质网络缺陷,而此时神经元的退行性变如皮质萎缩,皮质葡萄糖低代谢的改变尚未出现[3]。神经电生理研究证实阿尔茨海默病患者视觉和脑干听觉诱发电位的潜伏期延迟,提示阿尔茨海默病患者脑内存在髓鞘功能的紊乱[4]。阿尔茨海默病白质损伤在核磁影像学检查已得到证实,且白质损伤的严重程度与认知功能密切相关[5]。有研究发现,阿尔茨海默病患者脑白质病变的总体积升高,这种改变在阿尔茨海默病临床症状出现前的20年就已存在,提示白质病变是阿尔茨海默病的核心特征之一。另有研究发现阿尔茨海默病患者白质病变与脑脊液中Aβ和tau蛋白异常及认知功能损害存在一定关系[6],白质病变的严重程度可用于预测阿尔茨海默病的进展。 阿尔茨海默病白质病理改变包括少突胶质细胞的死亡、髓鞘破坏和轴索的缺失。阿尔茨海默病动物模型研究也证实少突胶质细胞的变化。PS-1敲除的小鼠模型,由于Aβ和谷氨酸的毒性作用及钙调节失衡,少突胶质细胞对于损伤极为敏感,死亡数增加,同时发现少突胶质细胞的异常变化是在Aβ和tau蛋白出现前的早期病理事件[7]。在6月龄的三重转基因小鼠模型(3xTg-AD)中发现成髓鞘少突胶质细胞数量明显减少[8];除此之外,少突胶质前体细胞亦发生变化。APP/PS1小鼠转基因老年痴呆模型显示少突胶质前体细胞数量增加[9]。Aβ-42是阿尔茨海默病相关老年斑的主要组分,研究者将NG2细胞暴露在Aβ-42中,NG2细胞形态发生变化,数量减少。阿尔茨海默病患者死后脑组织尸检发现Olig2阳性细胞数明显减少,NG2阳性前体细胞胞体肿胀,突起减少,进入激活状态[10]。然而,随着年龄增长自我修复能力的减弱和病理因子Aβ和tau蛋白的作用,这些细胞并不能分化为成熟少突胶质细胞参与新髓鞘的形成,提示阿尔茨海默病患者髓鞘修复受限。有趣的是临床确诊阿尔茨海默病患者脑脊液中NG2含量与非痴呆患者相比明显减少,脑脊液中NG2水平与阿尔茨海默病核心标记物Aβ-42,T-tau和P-tau密切相关,提示阿尔茨海默病患者脑内存在少突胶质细胞的丧失,因此进入脑脊液的部分减少,且其减少的程度与病情严重程度有关[11]。综上,阿尔茨海默病患者的影像学和阿尔茨海默病动物模型均发现广泛的白质病变,因此目前脑白质病变的研究越来越得到重视。 2.2 脑白质病变的发病机制 目前认为脑白质病变的发病机制可能包括Aβ毒性和tau蛋白、兴奋性毒性作用、铁过量等,但脑白质病变的确切发生机制仍有待于进一步阐明。 2.2.1 Aβ和tau的毒性损伤 Aβ的沉积是神经元变性的主要原因,Aβ对神经元和内皮细胞有毒性作用。越来越多的证据表明,在阿尔茨海默病发病过程中Aβ对少突胶质细胞亦有毒性作用。Aβ参与了少突胶质细胞的氧化应激过程,少突胶质细胞内谷胱甘肽含量下降和铁离子大量积聚,使少突胶质细胞清除自由基的能力受到了损伤,因而特别容易遭受损伤[12]。大鼠少突胶质细胞培养显示Aβ诱导的氧化应激使核染色体DNA断裂,线粒体功能失衡和细胞骨架崩解,从而导致少突胶质细胞死亡,同时揭示转录因子NF-Kb和AP-1的激活是Aβ所致少突胶质细胞死亡的可能机制[13]。除了Aβ1-42,Aβ的其他片段如Aβ1-40和Aβ25-35也可导致少突胶质细胞的死亡,且具有剂量依赖性。体外实验发现给予20 μmol/L Aβ片段导致75%的少突胶质细胞死亡[14-15]。此外,Aβ介导的氧化应激和年龄呈正相关。抗氧化剂N-乙酰半胱氨酸能够减少Aβ诱导的少突胶质细胞死亡。基于氧化应激假说,抗氧化剂如维生素E、司来吉兰等被用于阿尔茨海默病患者延缓病程进展的药物之一。 Aβ在阿尔茨海默病患者脑白质中的高表达已经被证实,Aβ对脑白质中少突胶质细胞有直接的细胞毒性作用。立体定向注射Aβ1-42到大鼠胼胝体导致广泛的白质损伤和少突胶质细胞死亡[16]。Aβ沉积于损伤白质的少突胶质细胞周围,激活少突胶质细胞、小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞,促使这些细胞合成炎症因子如iNOX和环氧化酶2等,此外,小胶质细胞亦能产生Aβ。Aβ可以与细胞膜直接作用或通过胶质细胞激活后释放的炎症因子增加富含胆固醇的膜结构的易损性,导致胶质细胞的死亡[17-18]。少突胶质细胞死亡后释放细胞内铁,又可以促进Aβ寡聚体的形成和增加Aβ的毒性作用。可见,胶质细胞作为潜在的炎症反应细胞加速Aβ的损伤。此外,Aβ还可以诱导少突胶质细胞的凋亡。体外实验发现Aβ1-42可以导致少突胶质前体细胞的凋亡,NG2阳性细胞数减少。Aβ诱导少突胶质细胞的凋亡可能是通过氧化机制激活nSMase-神经酰胺瀑布反应实现的[19]。 除了Aβ的毒性作用,tau蛋白对脑白质也有影响。tau是含磷蛋白质,是神经细胞中的微管相关蛋白,其主要生物学功能是促进微管组装并维持其稳定性,从而保证细胞骨架的完整性。当tau蛋白异常磷酸化时,微管稳定性丧失而失去正常的功能,神经元纤维缠结形成和神经变性。阿尔茨海默病中的tau蛋白发生了异常修饰和聚集,在诱导神经凋亡中发挥了重要作用。阿尔茨海默病脑中tau蛋白过度异常磷酸化主要发生在神经元,但在神经胶质细胞(星形胶质和少突胶质细胞)中也有tau蛋白磷酸化病变的发生[20-21]。转基因鼠的动物模型研究发现tau蛋白在少突胶质细胞内异常磷酸化并发生聚集,随后出现神经元的变性,提示异常的胶质细胞可能是神经变性病中是一个重要的致病因子[22-23]。另有研究发现,灰质中磷酸化的tau蛋白与白质的异常和髓鞘脱失密切相关。阿尔茨海默病白质中Calpain2(轴索损伤的标记物)的水平和皮质tau蛋白磷酸化水平呈正相关,提示磷酸化tau可以作为白质损害的指标[24]。在阿尔茨海默病脑中,异常磷酸化并发生聚集的tau蛋白对少突胶质细胞及阿尔茨海默病发病具体机制的影响仍不清楚,也未见报道,仍需进一步研究。 2.2.2 铁过量 铁广泛存在于脑组织中,在神经元、小胶质细胞、少突胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞中广泛存在,其中少突胶质细胞含铁量最多。在脑细胞内铁参与氧的运输,是众多酶的辅助因子。铁的摄取、吸收、储存和利用等环节正常协调运转才能维持机体的铁稳态,铁的过多沉积会引起中枢神经系统疾病:如阿尔茨海默病等。有研究发现阿尔茨海默病患者的大脑皮质和小脑等部位都均有铁的沉积,且阿尔茨海默病早期的轻度认知功能损害与脑内铁增高引起的自由基损伤和氧化应激有关[25-27]。使用MRI的磁敏感成像技术发现,阿尔茨海默病患者的壳核、尾状核、海马和齿状核存在铁沉积,并且铁沉积程度与反应患者的认知功能损害程度的简易智能状态量表(Mini-mental State Examination,MMSE)评分呈负相关[28]。少突胶质细胞富含铁蛋白和转铁蛋白,且随着年龄的增加尤其在阿尔茨海默病患者更为明显。有研究发现髓鞘破坏后铁从少突胶质细胞中释放,铁的释放一方面促进Aβ寡聚体在海马旁回的聚集,另一方面产生大量氧自由基,而少突胶质细胞对氧自由基高度敏感,在氧自由基的直接攻击下,引发脂质过氧化,导致少突胶质细胞的受损和死亡[29](示意图见图2)。 "
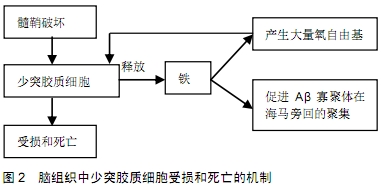

正常情况下还原型谷胱甘肽在氧自由基的清除中起关键作用;过氧化物则由谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶清除。与星形胶质细胞及神经元相比,少突胶质细胞内还原型谷胱甘肽过氧化酶的发育尚不完全,使其清除自由基的能力受到损伤,致使少突胶质细胞特别容易遭受损伤。除此之外,髓鞘形成阶段,少突胶质细胞合成膜结构需要的能量比其他细胞高二三倍,这使得他们对于重金属、氧自由基和兴奋性毒性等异常敏感,易于损伤。可见,阿尔茨海默病患者脑内与铁代谢相关的蛋白异常导致了铁的沉积,铁的沉积又可诱发自由基的产生、Aβ生成及神经元纤维缠结等,由此加速少突胶质细胞的死亡。多项研究表明病理状态下机体铁稳态失衡,过多的铁介导了一系列病理生理的变化。脑内铁沉积与中枢神经系统疾病的发生和发展有密切关系,对于脑铁代谢基础性研究的深入将更清楚认识铁代谢在神经系统疾病中的作用,为疾病防治奠定坚实的基础。 2.2.3 缺血和兴奋性毒性作用 侧脑室旁的白质血供主要来自室管膜下动脉,这些分支血管与大脑表面的血管吻合稀疏甚至缺如。而脑室周围的深部白质恰好处于动脉供血分水岭区域。因此,当发生脑缺血时,脑白质很容易发生缺血性改变。有研究表明,脑血管病事件会促发阿尔茨海默病发病,脑卒中后老年人患阿尔茨海默病风险增加,且脑血管病的一些危险因素,如高血压、糖尿病、高血脂等,也增加阿尔茨海默病的患病风险。阿尔茨海默病的发生和脑血管病有一定的联系,有人认为,阿尔茨海默病本身就是血管性疾病,是由脑缺血所触发的神经变性病。 少突胶质细胞表达大量的受体和膜通道(如谷氨酸和ATP受体,电压门控钙通道和P2X7受体),对于过度的ATP和谷氨酸受体的激活异常敏感。谷氨酸受体(glutamate receptor,GluRs)过度活化导致少突胶质细胞死亡,是阿尔茨海默病发病机制中脑白质损伤的理论依据之一。少突胶质细胞表达的谷氨酸受体主要是AMPA受体,因为少突胶质细胞AMPA受体缺乏GluR2亚单位,与神经元相比,对Ca2+有更高的通透性。阿尔茨海默病脑内谷氨酸递质升高,AMPA受体过度激活,Ca2+通道开放,大量Ca2+内流,使得细胞内钙超载和一系列钙依赖的相关酶激活,少突胶质细胞发生变性和坏死。此外,由于兴奋性氨基酸毒性作用或高水平的ATP/ADP/AMP,少突胶质细胞的P2X7受体持续激活,引发细胞内钙超载和Caspase-3通路的激活,从而诱导细胞凋亡[30]。 2.3 脑白质改变与阿尔茨海默病认知功能的关系 Aβ沉积是阿尔茨海默病发病的主要原因,但Aβ沉积量和阿尔茨海默病临床症状之间并无相关性,甚至一些认知功能正常的老年人,脑内却又相当数量的Aβ沉积所形成的老年斑。清除阿尔茨海默病脑内的Aβ不能改善临床症状和减缓疾病的进展,针对Aβ蛋白的相关治疗药物在临床试验中也以失败告终[31-32]。这说明,虽然阿尔茨海默病发病机制大部分支持Aβ假说理论,然而还有其他的一些因素参与,白质损害位于其中。阿尔茨海默病患者存在白质结构的改变,且这种改变出现较早,可能是独立于灰质病变的阿尔茨海默病核心变化之一。阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型发现白质的破坏和髓鞘标记物表达的变化是最早出现的病理改变[33];早期阿尔茨海默病患者海马旁回少突胶质细胞核直径缩小,神经元细胞核平均直径没有改变[34]。有关阿尔茨海默病生物标记物的研究发现,Aβ水平的变化在临床症状(大脑的葡萄糖低代谢、脑萎缩、认知功能减退)出现前的15-20年出现,tau的病理改变在临床症状出现前的15年出现,脑白质病变是在Aβ和tau蛋白出现前的更早期的变化[35]。这一研究揭示阿尔茨海默病标志物的变化依赖于疾病自身进展的阶段,进一步研究除了Aβ和tau蛋白之外白质损伤的标记物及这些标记物随时间的变化趋势,可以更好检测疾病的进展。既往白质的变化被认为部分与皮质神经元退变有关,但阿尔茨海默病早期,少突胶质细胞功能失衡或深部白质血管的缺乏导致少突胶质细胞易损,不能对神经元和轴突起到保护性作用,提示白质的改变可能独立于皮质变化,且在皮质变化之前。究竟是白质改变在先还是白质的变化是继发于灰质的变化仍有待于进一步研究。Aβ的毒性作用、缺血、兴奋性毒性作用、氧化应激、铁过量及均可损伤少突胶质细胞,损伤的少突胶质细胞一方面导致髓鞘脱失和变性,使得与之关联的神经元功能丧失,另一方面释放铁,促进Aβ在皮质的聚集,进一步加重神经元的损伤。神经元功能失衡又可以加速髓鞘和轴突的变性,加重白质损害[36]。可见在阿尔茨海默病进展过程中,白质的变化影响灰质,灰质的改变反过来又加重白质的损害,两者间形成复杂的网络,互相影响。 脑白质病变与认知功能下降有着密切关系。白质异常即髓鞘和少突胶质细胞的损伤,可能通过皮质及皮质下结构间联系纤维的丢失或者通过减缓神经传导速度/损伤传导束的完整性[37],最终导致认知功能下降。有研究发现脑白质的病变部位而不是脑白质病变总体积对认知功能存在影响[38]。皮质下白质病变与记忆、执行功能以及信息处理速度下降有关。新近的研究发现白质微结构异常与阿尔茨海默病患者早期记忆力减退相关[39]。人和动物的阿尔茨海默病模型发现,脱髓鞘或轴索损伤可以改变轴索的传导速度,直接/间接影响认知功能。阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型发现,在2-6个月海马和内皮质出现白质破坏和髓鞘标记物表达的变化,这是最早出现的病理变化,这一期间,小鼠并没有显示学习和记忆的缺陷。在这3个月之后小鼠开始出现认知功能的减退[40]。可见,阿尔茨海默病早期阶段,患者不仅有白质结构的变化,还有认知功能的改变,且两者存在一定的相关性。 以往认为阿尔茨海默病主要是皮质性痴呆,近年来随着影像学的发展,越来越多的脑白质病变被发现,白质病变的研究越来越得到重视。针对脑白质的治疗可能是阿尔茨海默病预防和治疗的潜在靶点。新近的研究发现胆碱酯酶抑制剂多奈哌齐有促进少突胶质细胞分化的作用,而其他的胆碱酯酶抑制剂如石杉碱甲、卡巴拉丁没有此作用,提示多奈哌齐对阿尔茨海默病的治疗作用不仅在于提高突触间隙乙酰胆碱的含量,也同时促进少突胶质细胞的分化及髓鞘的再生,其在阿尔茨海默病治疗中具有双重作用[41]。修复损伤的白质从而对阿尔茨海默病患者起到治疗作用将是未来研究的方向之一。 "

| [1] WANG SS, ZHANG Z, ZHU TB, et al. Myelin injury in the central nervous system and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res Bull. 2018;140:162-168. [2] ROHER AE, WEISS N, KOKJOHN TA, et al.Increased a beta peptides and reduced cholesterol and myelin proteins characterize white matter degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Biochemistry.2002;41(37):11080-11090. [3] FISCHER FU, WOLF D, SCHEURICH A, et al.Altered whole-brain white matter networks in preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2015;8:660-666. [4] TANAKA F ,KACHI T, YAMADA T, et al.Auditory and visual event-related potentials and flash visual evoked potentialsin Alzheimer’s disease: correlations with Mini-Mental State Examinationand Raven’s Coloured Progressive Matrices.J Neurol Sci.1998;156(1):83-88. [5] KAO YH, CHOU MC, CHEN CH, et al.White Matter Changes in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease and Associated Factors. J Clin Med. 2019;8(2):pii: E167. [6] TOSTO G, ZIMMERMAN ME, HAMILTON JL, et al.The effect of white matter hyperintensities on neurodegeneration in mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimers Dement.2015;11(12): 1510-1519. [7] PAK K, CHAN SL, MATTSON MP. Presenilin-1 mutation sensitizes oligodendrocytes to glutamate and amyloid toxicities, and exacerbates white matter damage and memory impairment in mice.Neuro Molecular Med.2003;3(1):53-64. [8] DESAI MK, MASTRANGELO MA, RYAN DA, et al. Early oligodendrocyte/myelin pathology in Alzheimer's disease mice constitutes a novel therapeutic target.Am J Pathol. 2010; 177(3):1422-1435. [9] BEHRENDT G, BAER K, BUFFO A, et al. Dynamic changes in myelin aberrations and oligodendrocyte generation in chronic amyloidosis in mice and men.Glia.2013;61(2): 273-286. [10] DONG YX, ZHANG HY, LI HY, et al .Association between Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and early demyelination and oligodendrocyte dysfunction. Neural Regen Res.2018; 13(5):908-914. [11] NIELSEN HM, EK D, AVDIC U, et al.NG2 cells, a new trail for Alzheimer's disease mechanisms? Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2013;1:7. [12] HIGGINS GC, BEART PM, SHIN YS, et al. Oxidative stress: emerging mitochondrial and cellular themes and variations in neuronal injury.J Alzheimer’s Dis.2010;20(Suppl 2): S453-S473. [13] DEYTS C, CLUTTER M, PIERCE N, et al. APP-Mediated Signaling Prevents Memory Decline in Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Model.Cell Rep.2019;27(5):1345-1355. [14] CAI Z, XIAO M.Oligodendrocytes and Alzheimer’s disease.Int J Neurosci.2016;126(2):97-104. [15] HORIUCHI M, MAEZAWA I, ITOH A, et al. Amyloid beta1-42 oligomer inhibits myelin sheet formation in vitro.Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33(3):499-509. [16] JANTARATNOTAI N, RYU JK, KIM SU, et al.Amyloid beta peptide-induced corpus callosum damage and glial activation in vivo. Neuroreport.2003;14(11):1429-1433. [17] ZHU S, WANG J, ZHANG Y, et al.The role of neuroinflammation and amyloid in cognitive impairment in an APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurosci Ther.2017;23(4):310-320. [18] FAKHOURY M.Microglia and Astrocytes in Alzheimer's Disease: Implications for Therapy. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(5): 508-518. [19] DE S, WIRTHENSOHN DC, FLAGMEIER P, et al.Different soluble aggregates of Aβ42 can give rise to cellular toxicity through different mechanisms. Nat Commun.2019;10(1): 1541. [20] MCALEESE KE, FIRBANK M, DEY M, et al.Cortical tau load is associated with white matter hyperintensities. Acta Neuropathol Commun.2015;3:60. [21] REDDY PH, OLIVER DM.Amyloid Beta and Phosphorylated Tau-Induced Defective Autophagy and Mitophagy in Alzheimer's Disease. Cells.2019;8(5).pii: E488. [22] VELDE C, PANAYI F, LOUIS C, et al. Tau accumulation in the retina promotes early neuronal dysfunction and precedes brain pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener.2017;12(1):58. [23] LIAO D, MILLER EC, TERAVSKIS PJ. Tau acts as a mediator for Alzheimer's disease-related synaptic deficits.Eur J Neurosci. 2014;39(7):1202-1213. [24] MCALEESE KE, WALKER L, GRAHAM S, et al. Parietal white matter lesions in Alzheimer's disease are associated with cortical neurodegenerative pathology, but not with small vessel disease. Acta neuropathologica.2017;134(3):459-473. [25] LIU JL,FAN YG,YANG ZS, et al. Iron and Alzheimer's Disease: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications.Front Neurosci. 2018;12:632. [26] LANE DJR, AYTON S, BUSH AI. Iron and Alzheimer's Disease: An Update on Emerging Mechanisms.J Alzheimers Dis.2018; 64(s1):S379-S395. [27] CAROCCI A, CATALANO A, SINICROPI MS, et al. Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: the involvement of iron. Biometals.2018;31(5):715-735. [28] VAN DUIJN S, BULK M, VAN DUINEN SG, et al. Cortical Iron Reflects Severity of Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;60(4):1533-1545. [29] HUANG XT, LIU X, YE CY, et al. Iron-induced energy supply deficiency and mitochondrial fragmentation in neurons.J Neurochem.2018;147(6):816-830. [30] KRASNOW AM, ATTWELL D.NMDA Receptors: Power Switches for Oligodendrocytes. Neuron.2016;91(1):3-5. [31] KELLEHER RJ 3RD, SHEN J.Presenilin-1 mutations and Alzheimer’s disease.ProcNatlAcadSci U S A. 2017;114(4): 629-631. [32] BARTZOKIS G. Alzheimer's disease as homeostatic responses to age-related myelin breakdown. Neurobiol Aging. 2011;32(8):1341-1371. [33] DESAI MK, SUDOL KL, JANELSINS MC, et al. Triple-transgenic Alzheimer's disease mice exhibit region-specific abnormalities in brain myelination patterns prior to appearance of amyloid and tau pathology.Glia.2009; 57(1):54-65. [34] GAGYI E, KORMOS B, CASTELLANOS KJ, et al. Decreased oligodendrocyte nuclear diameter in Alzheimer's disease and Lewy body dementia. Brain Pathol.2012; 22(6):803-810. [35] BATEMAN RJ, XIONG C, BENZINGER TL, et al. Clinical and biomarker changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer's disease.N Engl J Med.2012;367(9):795-804. [36] RIZVI B, NARKHEDE A, LAST BS, et al.The effect of white matter hyperintensities on cognition is mediated by cortical atrophy. Neurobiol Aging.2018;64:25-32. [37] NASRABADY SE, RIZVI B, GOLDMAN JE, et al.White matter changes in Alzheimer’s disease: a focus on myelin and oligodendrocytes. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018;6(1):22. [38] KASAHARA H, IKEDA M, NAGASHIMA K, et al. Deep White Matter Lesions Are Associated with Early Recognition of Dementia in Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019; 68(2):797-808. [39] JI F, PASTERNAK O, NG KK, et al. White matter microstructural abnormalities and default network degeneration are associated with early memory deficit in Alzheimer's disease continuum. Sci Rep.2019;9(1):4749. [40] LEE S, VIQAR F, ZIMMERMAN ME, et al. White matter hyperintensities are a core feature of Alzheimer's disease: evidence from the dominantly inherited Alzheimer network. Ann Neurol.2016;79(6):929–939. [41] CUI X,GUO YE,FANG JH,et al. Donepezil, a drug for Alzheimer's disease, promotes oligodendrocyte generation and remyelination. Acta Pharmacol Sin.2019; [Epub ahead of print]. |
| [1] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [2] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [3] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [4] | Luo Anyu, Liu Hanlin, Xie Xiaofei, Huang Chen. Effect of antioxidant mixture on structural degeneration of an osteoarthritis rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3625-3629. |
| [5] | Cong Renyuan, Yuan Jing, Xia Jinchan, Sun Ying . Effects of baicalin on oxidative stress in BEAS-2B cells stimulated by lipopolysaccharide combined with adenosine triphosphate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 286-291. |
| [6] | Zhou Yi, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun, Lai Yu, Liao Jianzhao, Li Shibin. An exploration on mechanism of Shengyu Decoction in treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2687-2696. |
| [7] | Zhang Xiang, Zhang Yeting. Exercise improves progression of Alzheimer’s disease in mice: a dose-effect relationship [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2761-2766. |
| [8] | Yuan Baohong, Zhao Weishan, Wang Ruotian, Guan Aoran, Wang Yu, Li Ruhong. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from pigs inhibit inflammatory response induced by lipopolysaccharide and improve islet cell dysfunction in pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1969-1975. |
| [9] | Zhao Ning, Yu Hongdan, Feng Zhen, Ding Jiayuan, Liu Xuezheng. Salidroside inhibits apoptosis of retinal Müller cells induced by high glucose in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1664-1669. |
| [10] | Cao Haixin, Wang Xiaomei . Aerobic exercise protects the rat brain against senile dementia induced by amyloid beta protein 1-42 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1675-1681. |
| [11] | Ye Dou, , Ma Xuexia , Guan Qian, , Luan Zuo , Yang Yinxiang , Wang Zhaoyan , Wang Qian , He Ying , Yao Ruiqin. Proportion and morphological characteristics of human oligodendrocyte precursor cells in different cell culture vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 44-49. |
| [12] | Zang Jing, Luan Zuo, Wang Qian, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wu Youjia, Guo Aisong. Two kinds of stem cell nasal transplantation for treating white matter injury in premature rat infants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 101-107. |
| [13] | Wan Huazhe, Chai Guangxin, Xiao Xiaoling, Huang Wenying. Effects of phellinus igniarius crude polysaccharides on sporting ability and free radical metabolism of skeletal muscle in mice suffering passive smoking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 689-693. |
| [14] | Yu Hui, Zhao Yang, Fei Jiayue, Zhang Wenli, Zhao Luosha. Isoliquiritigenin inhibits SETD7 expression against oxidative damage in cardiomyocytes induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5613-5618. |
| [15] | Lin Yicai, Wu Zhengyuan, Luo Yingli, Yao Jun. Effect of pterostilbene on oxidative stress induced apoptosis in chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5092-5096. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||