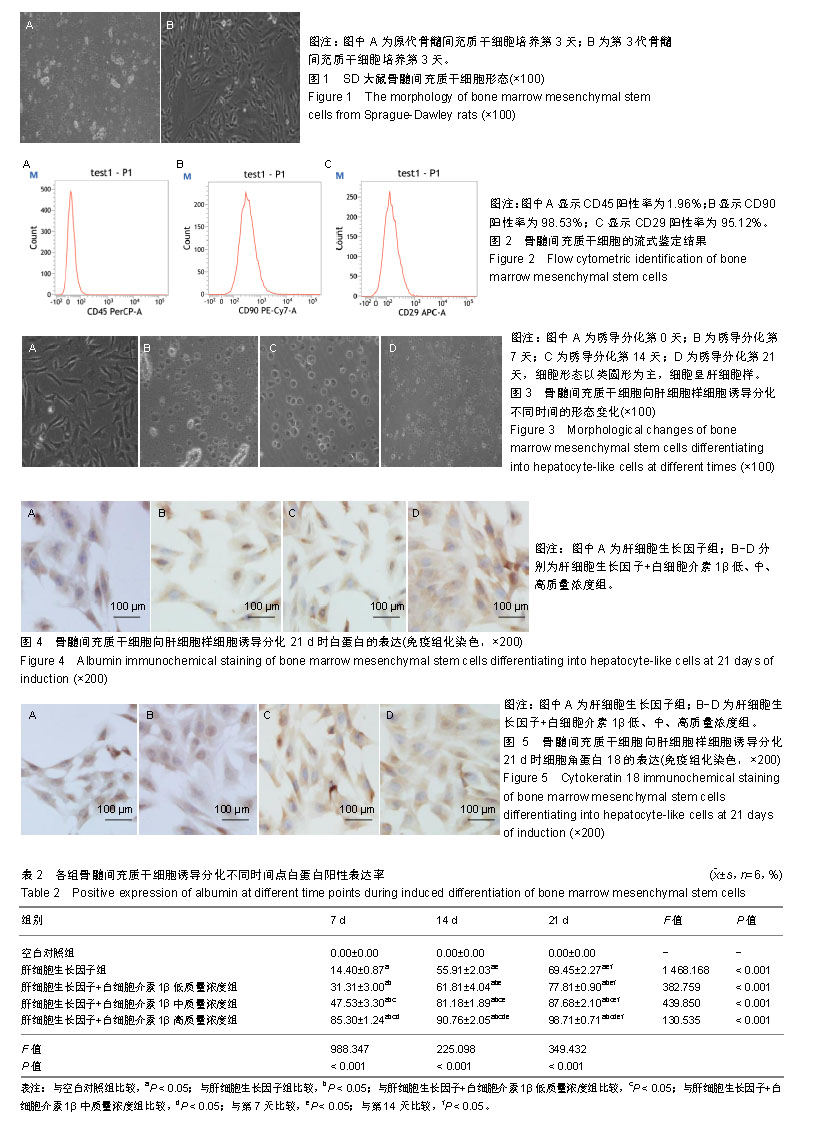
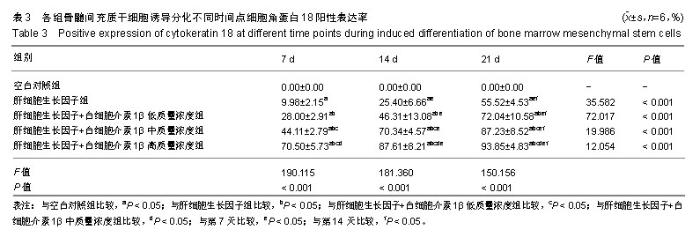
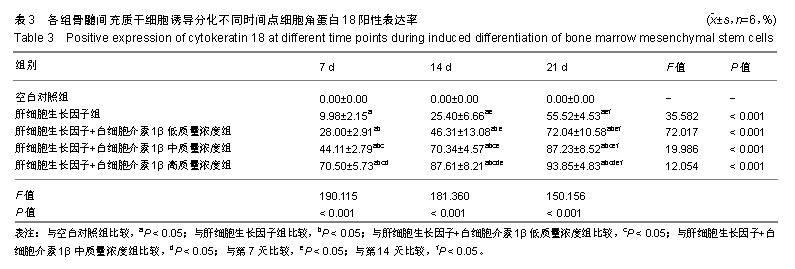
| [1]Sun L, Fan X, Zhang L, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell transplantation via four routes for the treatment of acute liver failure in rats. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(4):987-996.[2]Yuan S, Jiang T, Sun L, et al. The role of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of acute liver failure. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:251846.[3]Zhang H, Fang J, Wu Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells protect against neonatal rat hyperoxic lung injury. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013;13(6):817-829.[4]荣为为,韩明子,金世柱,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在组织工程研究中的应用新进展[J].现代生物医学进展, 2017,17(5):982-984.[5]He Q, He X, Wang Y, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) improves brain ischemia-induced pulmonary injury in rats associated to TNF-α expression. Behav Brain Funct. 2016; 12: 9.[6]Moore JK, Stutchfield BM, Forbes SJ. Systematic review: the effects of autologous stem cell therapy for patients with liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;39(7):673-685.[7]Levine P, McDaniel K, Francis H, et al. Molecular mechanisms of stem cell therapy in alcoholic liver disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2014; 46(5):391-397.[8]Salomone F, Barbagallo I, Puzzo L, et al. Efficacy of adipose tissue-mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in rats with acetaminophen liver injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(3):1037-1044.[9]Scott TR, Kronsten VT, Hughes RD, et al. Pathophysiology of cerebral oedema in acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(48):9240-9255.[10]郑盛,尤丽英.间充质干细胞分化为功能性肝细胞的研究进展[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2013,19(5):396-400.[11]Bernal W, Hyyrylainen A, Gera A, et al. Lessons from look-back in acute liver failure? A single centre experience of 3300 patients. J Hepatol. 2013;59(1):74-80.[12]Podoll AS, DeGolovine A, Finkel KW. Liver support systems--a review. ASAIO J. 2012;58(5):443-449.[13]谢树才,张剑权,蒋锡丽,等.骨髓间充质干细胞诱导分化为肝细胞的方法及机制研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(50): 7586-7593.[14]李伟,汪林,曾杰,等.瘀胆血清诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向肝细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(6):771-776.[15]孙红,李继尧,于吉人. IL-1β对离体培养的醋氨酚损伤的小鼠肝细胞的保护作用及其机制的初步探讨[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,1999, (1):13-15.[16]de Girolamo L, Lucarelli E, Alessandri G, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: a new ''cells as drugs'' paradigm. Efficacy and critical aspects in cell therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(13): 2459-2473.[17]Sun L, Fan X, Zhang L, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell transplantation via four routes for the treatment of acute liver failure in rats. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(4):987-996.[18]潘兴南,魏开鹏.肝细胞生长因子的浓度和诱导时间对人骨髓间充质干细胞向肝细胞分化的影响[J].肝脏,2013,18(6):382-385.[19]袁仙丽,李明才,李燕,等.白细胞介素-38及其相关细胞因子在炎症中的作用[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2013,35(8):1232-1237.[20]张东锋,王煜姝,滕军放.骨髓间充质干细胞对肝豆状核变性合并肝纤维化肝功能的临床研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2016,32(2):193-196.[21]罗显克,陆正峰,姜海行,等.肿瘤坏死因子-α刺激骨髓间充质干细胞后对肝星状细胞凋亡的促进作用[J].世界华人消化杂志,2012,20(19): 1713-1719.[22]霍大浪,刘代顺,宁家辉,等. SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞-肝细胞共培养上清液细胞因子分析[J].重庆医学,2014,43(28):3766-3768.[23]Lin L, Lin H, Bai S, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) improved functional recovery of spinal cord injury partly by promoting axonal regeneration. Neurochem Int. 2018;115: 80-84. [24]陈鹏飞,魏文斌,谭远忠,等.生长因子体外诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向肝样细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(49):9214-9220.[25]张美华,余卫,王巧瑜,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗大鼠白毒伞中毒致急性肝衰竭的效果[J].广东医学,2016,37(13):1917-1919.[26]荣为为,韩明子,金世柱,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在组织工程研究中的应用新进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2017,17(5):982-984.[27]王晓东,许烂漫,王丽萍,等.骨髓间充质干细胞免疫调节作用对急性肝功能衰竭大鼠肝再生的影响[J].中华传染病杂志,2016,34(2):97.[28]潘兴南,魏开鹏.肝细胞生长因子的浓度和诱导时间对人骨髓间充质干细胞向肝细胞分化的影响[J].肝脏,2013,18(6):382-385.[29]Xu TB, Li L, Luo XD, et al. BMSCs protect against liver injury via suppressing hepatocyte apoptosis and activating TGF-β1/Bax singling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;96:1395-1402.[30]徐土炳,李莉,罗兴迪,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在肝细胞损伤恢复中的作用[J].实用医学杂志,2017,33(5):687-692.[31]焦栓林,赵晓蕊,欧阳洪,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞联合促肝细胞生长素治疗失代偿期酒精性肝硬化疗效分析[J].实用肝脏病杂志, 2017,20(6):773-774.[32]符真,张剑权,李志,等. BMSCs对肝癌肝切除后肝细胞再生的作用[J].海南医学,2017,28(16):2665-2668.[33]徐土炳,李莉,罗兴迪,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在肝细胞损伤恢复中的作用[J].实用医学杂志,2017,33(5):687-692.[34]夏金华,夏建川,林万飞.骨髓源间充质干细胞注射疗法对肝硬化大鼠模型免疫系统的调节作用及其相关机制研究[J].免疫学杂志,2017, 33(7):623-628. |