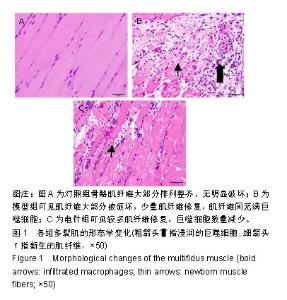
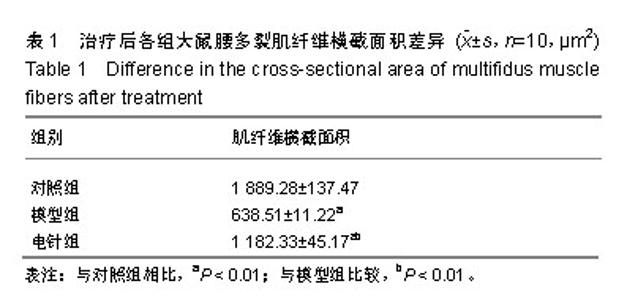
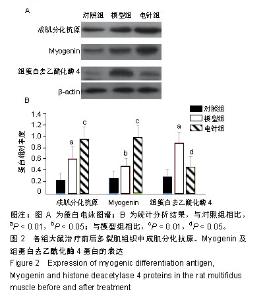
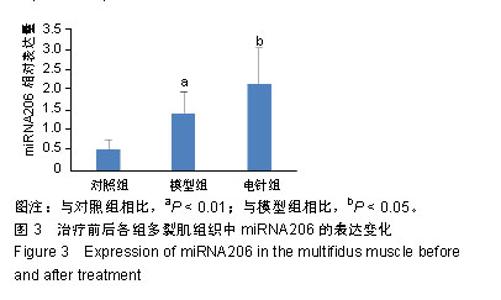
| [1]Snider RK.A prospective, randomized study of lumbar fusion: preliminary results.Spine.1994;19(1):109.[2]Aghion D,Chopra P,Oyelese AA.Failed back syndrome. Med Health R I. 2012;95(12):391-393.[3]刘通,于佳妮,邹德辉,等.电针血清对多裂肌卫星细胞增殖及Pax-7、成肌分化抗原、磷酸化蛋白激酶B表达的影响[J].针刺研究,2016,41(5):402-409.[4]刘通.电针“委中”穴对腰多裂肌卫星细胞增殖及PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路的影响[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学, 2016.[5]Wang YM,Ding XB,Dai Y,et al: Identification and bioinformatics analysis of miRNAs involved in bovine skeletal muscle satellite cell myogenic dif- ferentiation. Mol Cell Biochem.2015; 404: 113-122.[6]Hudson MB,Woodworth-Hobbs ME,Zheng B,et al.miR-23a is decreased dur- ing muscle atrophy by a mechanism that includes calcineurin signaling and exosome-mediated export.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014; 306: C551-558. ?[7]Huang QK,Qiao HY,Fu MH,et al.MiR-206 Attenuates Denervation- Induced Skeletal Muscle Atrophy in Rats Through Regulation of Satellite Cell Differentiation via TGF-β1, Smad3, and HDAC4 Signaling. Med SciMonit.2016;22:1161-1170.[8]Dai Y,Wang YM,Zhang WR,et al.The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-206 in the proliferation and differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2016;52(1):27-34. [9]Toru Taguchi, Ulrich Hoheisel, Siegfried Mense. Dorsal horn neurons having input from low back structures in rats. Pain. 2008;138(1):119-129.[10]陈玉佩,刘通,邹德辉,等.局部注射布比卡因建立大鼠骨骼肌损伤模型的组织形态学评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(18):2615-2621.[11]李忠仁. 实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社, 2003:316.[12]Hung CW,Wu MF,Hong RT,et al.Comparison of multifidus muscle atrophy afterposterior lumbar interbody fusion with conventional and cortical bone trajectory. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016;145:41-45.[13]Cha JR, Kim YC,Jang C,et al.Pedicle screw fixation and posterior fusion for lumbar degenerative diseases: effects on individual paraspinal muscles and lower back pain; a single-center, prospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:63.[14]Gilbert F,Heintel TM,Jakubietz MG,et al.Quantitative MRI comparison of multifidus muscle degeneration in thoracolumbar fractures treated with open and minimally invasive approach. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):75. [15]Yarjanian JA,Fetzer A,Yamakawa KS,et al.Correlation of Paraspinal Atrophy and Denervation in Back Pain and Spinal Stenosis Relative to Asymptomatic Controls.PM&R.2013;5(1):39-44. [16]Waschke A,Hartmann C , Walter J ,et al.Denervation and atrophy of paraspinal muscles after open lumbar interbody fusion is associated with clinical outcome-electromyographic and CT-volumetric investigation of 30 patients. ActaNeurochirurgica.2014;156(2):235-244.[17]GilleO ,Jolivet E , Dousset V , et al. Erector Spinae Muscle Changes on Magnetic Resonance Imaging Following Lumbar Surgery Through a Posterior Approach. Spine.2007;32(11):1236-1241.[18]季传婷,徐平,谢龙.电针对Cardiotoxin肌肉损伤小鼠MyoD表达的影响[J].南京中医药大学学报, 2012, 28(2):136-138.[19]Watanabe K, Matsumoto M,Ikegami T, et al.Reduced postoperative wound pain after lumbar spinous process–splitting laminectomy for lumbar canal stenosis: a randomized controlled study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;14(1):51-58.[20]Sebaaly A,Lahoud MJ, Rizkallah M,et al.Etiology, Evaluation, and Treatment of Failed Back Surgery Syndrome. Asian Spine J. 2018;12(3): 574-585. [21]Scalone L,Zucco F, Lavano A, et al. Benefits in pain perception, ability function and health-related quality of life in patients with failed back surgery syndrome undergoing spinal cord stimulation in a clinical practice setting. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2018;16(1):68. [22]Tuijp SJ,Van Zundert J,De Vooght P, et al. Does the use of epiduroscopic lysis of adhesions reduce the need for spinal cord stimulation in failed back surgery syndrome: a short term pilot study?.Pain Pract. 2018;18(7): 839-844.[23]刘通,刘悦,邝伟川,王小寅,文希,于佳妮.刺骨调筋针法治疗腰椎术后失败综合征临床疗效[J].中华中医药学刊, 2018,36(12):2914-2917.[24]刘宇,肖卫华,罗贝贝,等.急性骨骼肌钝挫伤修复过程及MyoD、Myogenin变化的实验研究[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2016,35(2):152-158.[25]Joung H, Kwon S, Kim K H, et al. Sumoylation of histone deacetylase 1 regulates MyoD signaling during myogenesis. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(1): e427.[26]Testa S, D'Addabbo P, Fornetti E, et al.Myoblast Myogenic Differentiation but Not Fusion Process Is Inhibited via MyoDTetraplexInteraction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:7640272.[27]Yamamoto M,Legendre NP,Biswas AA, et al. Loss of MyoD and Myf5 in Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells Results in Altered Myogenic Programming and Failed Regeneration. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;10(3):956-969. [28]Van Rooij E,Sutherland LB,Qi X,et al.Control of stress- dependent cardiac growth and gene expression by a microRNA. Science.2007;316: 575-579. [29]Sempere LF, Freemantle S, Pitha-Rowe I, et al. Expression profiling of mammalian microRNAs uncovers a subset of brain- expressed microRNAs with possible roles in murine and human neuronal differentiation. Genome Biol. 2004;5(3):R13. Epub 2004 Feb 16. [30]陈彩珍,李德深,邱守涛,等.肌组织特异性microRNA介导的骨骼肌衰减机制及运动的干预研究[J].西安体育学院学报, 2017,34(6):70-78.[31]Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, et al. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation.Nat Genet.2006;38(2): 228-233.[32]NakasaT,Ishikawa M, Shi M, et al. Acceleration of muscle regeneration by local injection of muscle-specific microRNAs in rat skeletal muscle injury model. J Cell Mol Med. 2010; 14(10):2495-2505.[33]Liu N, Williams AH, Maxeiner JM, et al. microRNA-206 promotes skeletal muscle regeneration and delays progression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in mice. J Clin Invest.2012;122(6):2054-2065.[34]Chen J F, Tao Y, Li J, et al. microRNA-1 and microRNA-206 regulate skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by repressing Pax7. J Cell Biol.2010;190(5): 867-879.[35]Dey BK,Gagan J,Dutta A.miR-206 and miR-486 induce myoblast differentiation by downregulating Pax7. Mol Cell Biol. 2011 ;31(1):203-214. [36]Kim HK,Lee YS,Sivaprasad U,et al.Muscle-specific microRNA miR-206 promotes muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol.2006;174(5):677-687. [37]余涛,王平,周翔,等.失神经支配大鼠腓肠肌的演变及其miR-206和MyoD表达的变化[J].中华显微外科杂志, 2017, 40(2):150.[38]Williams AH,Valdez G,Moresi V,et al.MicroRNA-206 delays ALS progression and promotes regeneration of neuromuscular synapses in mice. Science.2009; 326(5959): 1549-1554.[39]Yoshihara T,Machida S,Kurosaka Y,et al.Immobilization induces nuclear accumulation of HDAC4 in rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol Sci. 2016;66(4): 337-343.[40]Parra M.Class IIa HDACs-new insights into their func?tions in physiology and pathology.FEBS J.2015;282(9):1736-1744.?[41]张鑫愉,牛燕媚,傅力. HDAC4/5在运动改善骨骼肌代谢中的作用研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2018, 37(9):67-70.[42]McKinsey TA, Zhang CL, Lu J, et al.Signal-dependent nuclear export of a histone deacetylase regulates muscle differentiation.Nature.2000; 408 (6808):106-111.[43]Kirby TJ, McCarthy JJ. MicroRNAs in skeletal muscle biology and exercise adaptation. Free RadicBiol Med.2013;64:95-105.[44]Pan Y, Liu L, Li S, et al. Activation of AMPK inhibits TGF-β1-induced airway smooth muscle cells proliferation and its potential mechanisms. Sci Rep.2018;8(1):3624. |