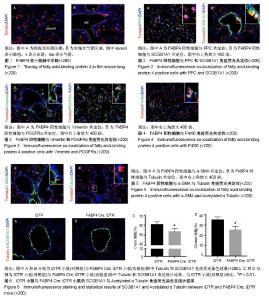
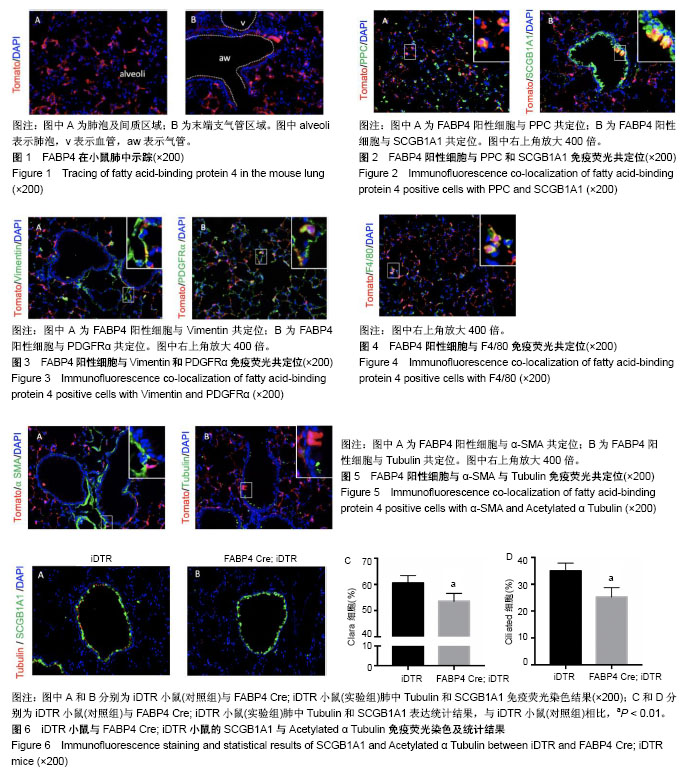
| [1] Furuhashi M, Hotamisligil GS. Fatty acid-binding proteins: role in metabolic diseases and potential as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(6):489-503.[2] Storch J, McDermott L. Structural and functional analysis of fatty acid-binding proteins. J Lipid Res. 2009;50 Suppl: S126-131.[3] Mullassery D, Smith NP. Lung development. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2015; 24(4):152-155.[4] Demircik F, Buch T, Waisman A. Efficient B cell depletion via diphtheria toxin in CD19-Cre/iDTR mice. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60643.[5] Barkauskas CE, Cronce MJ, Rackley CR, et al. Type 2 alveolar cells are stem cells in adult lung. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(7):3025-3036.[6] Zhang L, Whitsett JA, Stripp BR. Regulation of Clara cell secretory protein gene transcription by thyroid transcription factor-1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1350(3):359-367.[7] Zepp JA, Zacharias WJ, Frank DB, et al. Distinct Mesenchymal Lineages and Niches Promote Epithelial Self-Renewal and Myofibrogenesis in the Lung. Cell. 2017;170(6):1134-1148.[8] Hostettler KE, Gazdhar A, Khan P, et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells in lung fibrosis. PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0181946.[9] Austyn JM, Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981;11(10):805-815.[10] Mitchell J, Woodcock-Mitchell J, Reynolds S, et al. Alpha-smooth muscle actin in parenchymal cells of bleomycin-injured rat lung. Lab Invest. 1989; 60(5):643-650.[11] Lee D, Wada K, Taniguchi Y, et al. Expression of fatty acid binding protein 4 is involved in the cell growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2014;31(3):1116-1120.[12] Uysal KT, Scheja L, Wiesbrock SM, et al. Improved glucose and lipid metabolism in genetically obese mice lacking aP2. Endocrinology. 2000;141(9):3388-3396.[13] Agardh HE, Folkersen L, Ekstrand J, et al. Expression of fatty acid-binding protein 4/aP2 is correlated with plaque instability in carotid atherosclerosis. J Intern Med. 2011;269(2):200-210.[14] Shum BO, Mackay CR, Gorgun CZ, et al. The adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein aP2 is required in allergic airway inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(8):2183-2192.[15] von Eynatten M, Breitling LP, Roos M, et al. Circulating adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein levels and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with coronary heart disease: a 10-year prospective study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32(9):2327-2335.[16] Wynn TA, Chawla A, Pollard JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013;496(7446):445-455.[17] Lambrecht BN. Alveolar macrophage in the driver's seat. Immunity. 2006;24(4):366-368.[18] Srikanth L, Venkatesh K, Sunitha MM, et al. In vitro generation of type-II pneumocytes can be initiated in human CD34(+) stem cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2016;38(2):237-242.[19] Jiang Y, Ma S, Zhang H, et al. FABP4-mediated homocysteine-induced cholesterol accumulation in THP-1 monocyte-derived macrophages and the potential epigenetic mechanism. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(1):969-976.[20] Kuppe C, Kramann R. Role of mesenchymal stem cells in kidney injury and fibrosis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016;25(4):372-377.[21] Stone JS, Wisner SR, Bucks SA, et al. Characterization of Adult Vestibular Organs in 11 CreER Mouse Lines. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2018;19(4):381-399.[22] El Agha E, Kramann R, Schneider RK, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Fibrotic Disease. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21(2):166-177.[23] Dave JM, Bayless KJ. Vimentin as an integral regulator of cell adhesion and endothelial sprouting. Microcirculation. 2014;21(4):333-344.[24] Li LF, Kao KC, Liu YY, et al. Nintedanib reduces ventilation-augmented bleomycin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lung fibrosis through suppression of the Src pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(11): 2937-2949.[25] Hamilton TG, Klinghoffer RA, Corrin PD, et al. Evolutionary divergence of platelet-derived growth factor alpha receptor signaling mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(11):4013-4025.[26] Elizur A, Adair-Kirk TL, Kelley DG, et al. Clara cells impact the pulmonary innate immune response to LPS. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007;293(2):L383-392.[27] Nkadi PO, Merritt TA, Pillers DA. An overview of pulmonary surfactant in the neonate: genetics, metabolism, and the role of surfactant in health and disease. Mol Genet Metab. 2009;97(2):95-101.[28] Miyachi H, Reinhardt JW, Otsuru S, et al. Bone marrow-derived mononuclear cell seeded bioresorbable vascular graft improves acute graft patency by inhibiting thrombus formation via platelet adhesion. Int J Cardiol. 2018;266:61-66.[29] Overholt KM, Otsuru S, Olson TS, et al. Identification of a murine CD45-F4/80lo HSC-derived marrow endosteal cell associated with donor stem cell engraftment. Blood Adv. 2017;1(27):2667-2678.[30] Dyer EL. The lung: scientific foundations.Chest. 1992;101(2):24. |