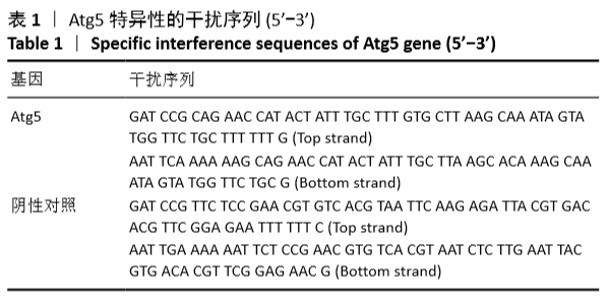
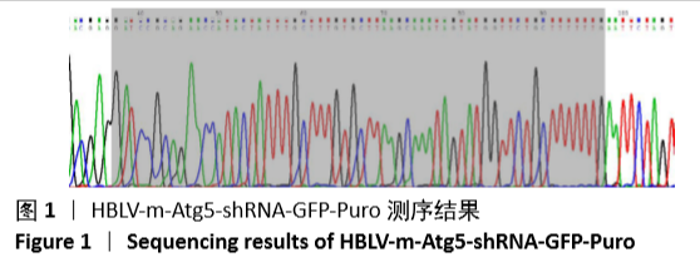
[1] MIZUSHIMA N. A brief history of autophagy from cell biology to physiology and disease. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(5):521-527.
[2] GALLUZZI L, BRAVO-SAN PEDRO JM, LEVINE B, et al. Pharmacological modulation of autophagy: therapeutic potential and persisting obstacles. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(7):487-511.
[3] YANG YP, HU LF, ZHENG HF, et al. Application and interpretation of current autophagy inhibitors and activators. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013; 34(5):625-635.
[4] YAMADA E, SINGH R. Mapping autophagy on to your metabolic radar. Diabetes. 2012;61(2):272-280.
[5] WANG Z, LIU N, LIU K, et al. Autophagy mediated CoCrMo particle-induced peri-implant osteolysis by promoting osteoblast apoptosis. Autophagy. 2015;11(12):2358-2369.
[6] WANG Z, DENG Z, GAN J, et al. TiAl6V4 particles promote osteoclast formation via autophagy-mediated downregulation of interferon-beta in osteocytes. Acta Biomater. 2017;48:489-498.
[7] DEVROE E, SILVER PA. Retrovirus-delivered siRNA. BMC Biotechnol. 2002;2:15.
[8] DREYER JL. Lentiviral vector-mediated gene transfer and RNA silencing technology in neuronal dysfunctions. Mol Biotechnol. 2011;47(2): 169-187.
[9] 李亚,付强,张俊波,等.巨噬细胞RAW264.7不同转染方法的比较[J].生物技术, 2014,24(2):44-48.
[10] CAI Y, MIKKELSEN JG. Lentiviral Delivery of Proteins for Genome Engineering. Curr Gene Ther. 2016;16(3):194-206.
[11] PICANCO-CASTRO V, DE SOUSA RUSSO-CARBOLANTE EM, TADEU COVAS D. Advances in lentiviral vectors: a patent review. Recent Pat DNA Gene Seq. 2012;6(2):82-90.
[12] ZHAO Z, QIAO L, DAI Z, et al. LncNONO-AS regulates AR expression by mediating NONO. Theriogenology. 2020;145:198-206.
[13] 郭宇丹,曾玉燕,姜心禅,等.PTEN shRNA慢病毒载体构建及转染人子宫腺肌病细胞的稳定细胞株筛选[J].中药新药与临床药理, 2019,30(8):990-995.
[14] LEVINE B, KROEMER G. Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 2008;132(1):27-42.
[15] DERETIC V, SAITOH T, AKIRA S. Autophagy in infection, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(10):722-737.
[16] YAO Z, DELORME-AXFORD E, BACKUES SK, et al. Atg41/Icy2 regulates autophagosome formation. Autophagy. 2015;11(12):2288-2299.
[17] YE X, ZHOU XJ, ZHANG H. Exploring the Role of Autophagy-Related Gene 5 (ATG5) Yields Important Insights Into Autophagy in Autoimmune/Autoinflammatory Diseases. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2334.
[18] CLARKE AJ, SIMON AK. Autophagy in the renewal, differentiation and homeostasis of immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(3):170-183.
[19] SHIBUTANI ST, SAITOH T, NOWAG H, et al. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in the immune system. Nat Immunol. 2015; 16(10): 1014-1024.
[20] NETEA-MAIER RT, PLANTINGA TS, VAN DE VEERDONK FL, et al. Modulation of inflammation by autophagy: Consequences for human disease. Autophagy. 2016;12(2):245-260.
[21] HUA Y, SHEN M, MCDONALD C, et al. Autophagy dysfunction in autoinflammatory diseases. J Autoimmun. 2018;88:11-20.
[22] WU MY, LU JH. Autophagy and Macrophage Functions: Inflammatory Response and Phagocytosis. Cells. 2019;9(1). pii: E70.
[23] MARTINEZ J, MALIREDDI RK, LU Q, et al. Molecular characterization of LC3-associated phagocytosis reveals distinct roles for Rubicon, NOX2 and autophagy proteins. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17(7):893-906.
[24] SANJUAN MA, DILLON CP, TAIT SW, et al. Toll-like receptor signalling in macrophages links the autophagy pathway to phagocytosis. Nature. 2007;450(7173):1253-1257.
[25] MOSSER DM, EDWARDS JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12):958-969.
[26] LIU K, ZHAO E, ILYAS G, et al. Impaired macrophage autophagy increases the immune response in obese mice by promoting proinflammatory macrophage polarization. Autophagy. 2015;11(2):271-284.
[27] INOMATA M, INTO T, NIIDA S, et al. Atg5 regulates formation of MyD88 condensed structures and MyD88-dependent signal transduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;437(4):509-514.
[28] PACCHIA AL, ADELSON ME, KAUL M, et al. An inducible packaging cell system for safe, efficient lentiviral vector production in the absence of HIV-1 accessory proteins. Virology. 2001;282(1):77-86.
[29] 江梦,夏中元,赵博,等.慢病毒转染稳定表达GFP融合自噬蛋白LC3大鼠H9c2心肌细胞系的建立[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2016, 15(2):101-104.
[30] 王成博,康巧珍,丁聪,等.利用CRISPR/Cas9系统构建稳定敲除4.1R基因的RAW264.7细胞株[J].南方医科大学学报, 2017,37(12): 1609-1614.
[31] 郭陈智,史桂英.流式分选仪FACSAriaⅡ分选GFP阳性乳腺癌MCF-7细胞株的条件优化研究[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2013,33(1):127-130.
[32] TILGNER K, ATKINSON SP, YUNG S, et al. Expression of GFP under the control of the RNA helicase VASA permits fluorescence-activated cell sorting isolation of human primordial germ cells. Stem Cells. 2010; 28(1):84-92.
[33] ZAGORE LL, AKESSON CC, LICATALOSI DD. Efficient GFP-labeling and analysis of spermatogenic cells using the IRG transgene and flow cytometry. Genesis. 2019;57(4):e23283. |