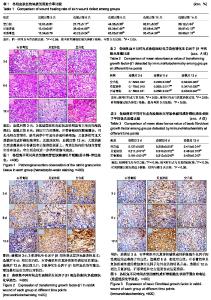
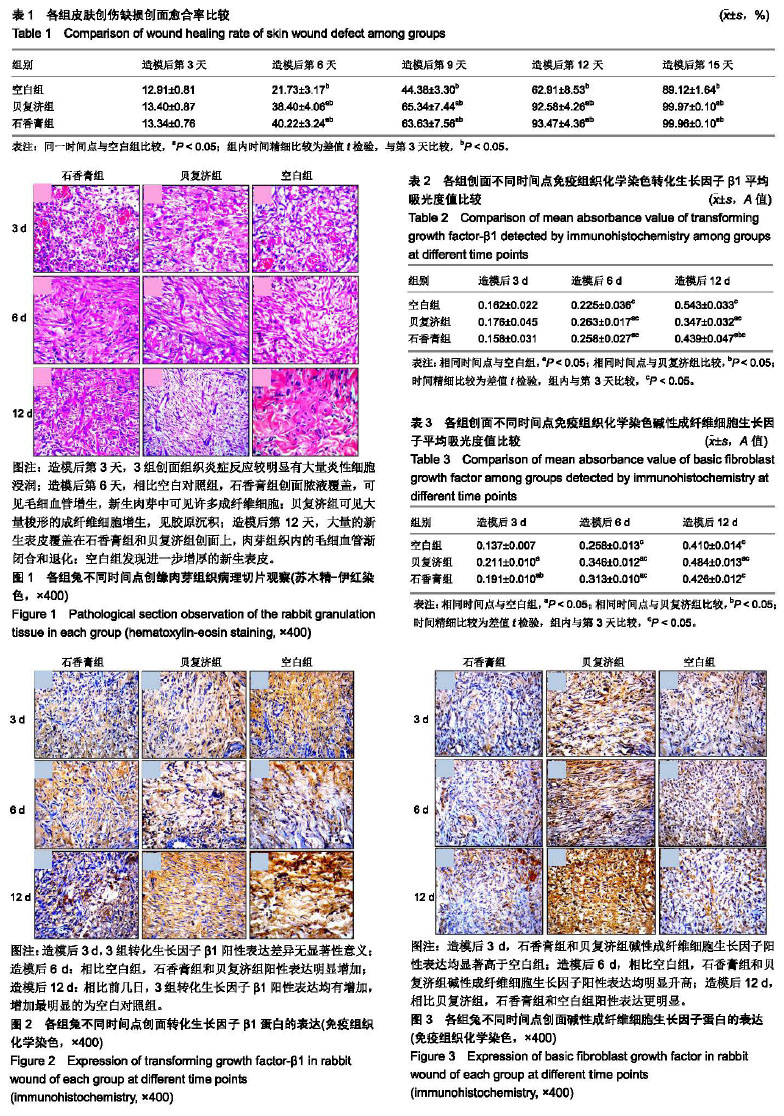
| [1]付小兵,程天民,陆树良,等.中国人体表难愈合创面发生新特征与防治的创新理论与关键措施研究[Z].中国人民解放军总医院第一附属医院,中国人民解放军第三军医大学,上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院,温州医科大学,深圳普门科技有限公司,无锡市第三人民医院,中国人民解放军第三零六医院,上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院,苏州大学,中国人民解放军总医院. 2015.[2]费冀,陈久毅,张开伟,等.中药石香膏促进慢性难愈合创面修复的随机对照临床研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2015,42(2):236-238.[3]朱旭,陈久毅,王勇.中药促进指端缺如再生修复临床初探[J],内蒙古中医药,2012,31(1):50-50.[4]费冀,陈久毅.中药“石香膏”促进糖尿病溃疡创面修复临床初探[J].亚太传统医药,2014,10(3):107-108.[5]van Solingen C, Araldi E, Chamorro-Jorganes A, et al. Improved repair of dermal wounds in mice lacking microRNA-155. J Cell Mol Med,2014,18(6):1104-1112.[6]邓步华.病理检验技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2005:77-81.[7]Rawat S,Singh R,Thakur P,et al.Wound healing Agents from Medicinal Plants: A Review. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine.2012;2(3):S1910-S1917.[8]朱梦茹,郭澍,刘洋,等.脂肪来源干细胞外泌体在组织修复和再生医学中的研究进展[J].中国美容整形外科杂志, 2018,29(12): 757-760. [9]高小月,张玉泉,杨晓清.人脐带间充质干细胞在组织损伤修复中的研究进展[J].生物医学工程与临床,2018, 22(2):208-213.[10]谢玉国,陈伟鹏,曾庆湖.旋髂浅动脉皮瓣修复手部皮肤软组织损伤中的治疗效[J].中国临床研究,2016,29(6):774-776.[11]Eming SA, Martin P ,Tomic-Canic M.Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling,and translation. Sci Transl Med. 2014 Dec 3;6(265):265sr6.[12]Reinke JM, Sorg H.Wound Repair and Regeneration. Eur Surg Res. 2012;49(1):35-43.[13]Velnar T , Ba T , Smrkolj V . The Wound Healing Process: An Overview of the Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms. J Int Med Res. 2009;37(5):1528-1542.[14]Buchanan PJ,Kung TA,Cederna PS.Evidence-based medicine: Wound closure.Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery. 2014;134(6):1391-1404.[15]Sonnemann KJ, Bement WM. Wound Repair: Toward Understanding and Integration of Single-Cell and Multicellular Wound Responses. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27: 237-263. [16]Thangapazham RL, Sharad S, Maheshwari RK. Phytochemicals in Wound Healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2016;5(5):230-241. [17]Barrientos S, Stojadinovic O , Golinko M S , et al. Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008;16(5):585-601.[18]Shi HX,Lin C,Lin BB,et al.The antiscar effects of basic fibroblast growth factor on the wound repair in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.2013;8(4):e59966.[19]武姗,刘洋,朱旅云,等. 转化生长因子β及其受体在糖尿病足创面愈合过程中作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志,2017, 25(6):569-572,[20]周思政.皮肤创伤愈合和增生性瘢痕动物模型的研究进展[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2018,14(1):48-52.[21]Yin H, Li XY,Hu SL,et al.IL-33 accelerates cutaneous wound healing involved in vedinupr upreguatlion ahernatively aivated macrophages.Molecular Immunology.2013; 56:347353. [22]刘公洪.湿性敷料治疗在烧伤创面的应用进展[J]. 西南军医, 2012,14(1):113-114.[23]武瑞仙,梁晨,王春晖,等.中医古籍中祛腐生肌方剂用药规律分析[J].辽宁中医杂志,2016,43(6):1146-1149.[24]张晓芬,孙桂芳,陈亚峰,等.活血化瘀中药促进创面愈合的研究进展[J].光明中医,2015,30(8):1816-1820.[25]聂元董,李刚.活血化瘀中药治疗足踝部软组织缺损皮瓣移植术后组织修复的临床研究[J].临床医药文献电子杂志, 2016,3(51): 10221. |