Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (20): 3261-3267.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1195
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of total shoulder arthroplasty with stemmed prosthesis versus stemless prosthesis for treating shoulder osteoarthritis
Wang Wei1, Zhou Haonan1, Zhang Yu1, Wang Chenglong1, Xie Chengxin1, Yin Dong2
- 1Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2the People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2019-07-18Published:2019-07-18 -
Contact:Yin Dong, MD, Professor, Chief physician, the People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wang Wei, Master candidate, Attending physician, Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Wei, Zhou Haonan, Zhang Yu, Wang Chenglong, Xie Chengxin, Yin Dong. Meta-analysis of total shoulder arthroplasty with stemmed prosthesis versus stemless prosthesis for treating shoulder osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(20): 3261-3267.
share this article

2.1 文献检索结果及质量评价 根据检索策略,共检索到相关文献417篇,采用EndnoteX7排除重复文献后剩余332篇,然后经过读文题和摘要,排除重复、非临床研究及非治疗性文献308篇,初步筛选得到的24篇经过阅读全文,再次排除不符合纳入标准的文献19篇,最终获得纳入文献5篇[12-16],其中3篇随机对照研究,2篇非随机对照试验,共计182例患者190肩。纳入研究的基本特征见表1,纳入文献质量评价及风险评价结果见图2。 2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 术后Constant肩关节评分 共有5篇文献报道了术后Constant评分[12-16],共计190肩,其中无柄假体94肩,有柄假体96肩,异质性检验各研究间无明显异质性(I2=1%,P=0.40),故采用固定效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,无柄假体组与有柄假体组的术后Constant评分比较差异有显著性意义[MD=-4.80,95%CI(-8.02,-1.58),P=0.003],无柄假体组术后Constant评分低于有柄假体组,见图3。敏感性分析结果显示,剔除1篇质量较低的文献[16],结果发生改变[MD=-2.07,95%CI(-6.39,2.25),P=0.35],提示Meta分析稳定性比较差,尚不能认为2组术后Constant评分差异有显著性意义。 2.2.2 术后日常生活活动能力评分 共有4篇文献报道了术后日常生活活动能力评分[13-16],异质性检验提示,各研究间无明显异质性(I2=0%,P=0.56),故采用固定效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,2组术后日常生活活动能力评分比较差异无显著性意义[MD=0.57, 95%CI(-0.24,1.38),P= 0.17],见图4。 2.2.3 术后疼痛评分 共有4篇文献报道了术后疼痛评 分[13-16],异质性检验提示,各研究间存在明显异质性(I2=51%,P=0.10),故采用随机效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,2组术后疼痛评分比较差异无显著性意义[MD= -0.55,95%CI(-2.05,0.95),P=0.47],见图5。"
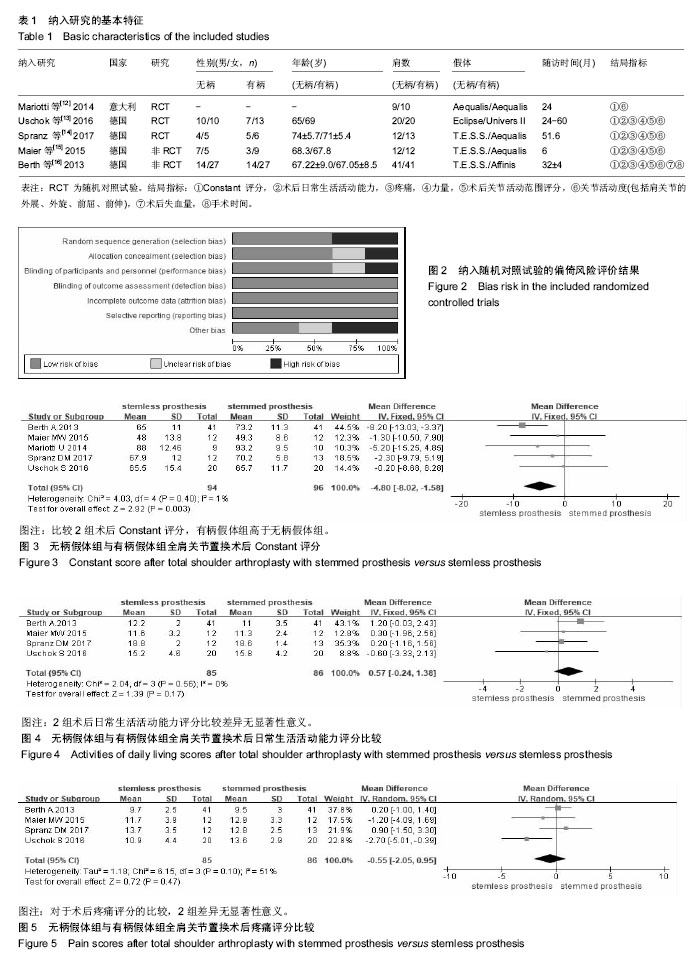
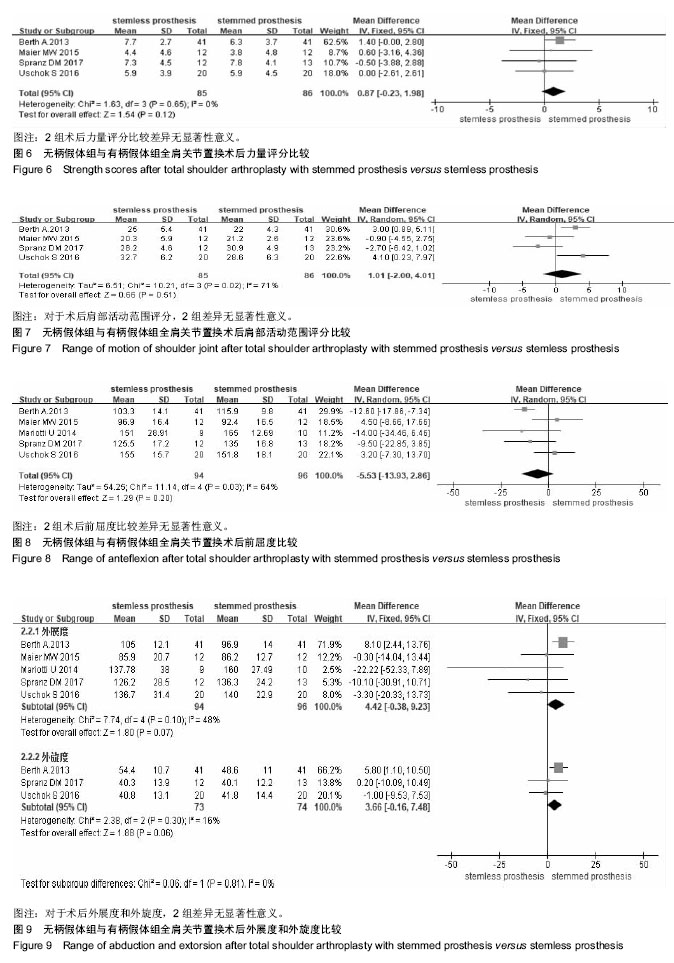
2.2.4 术后力量评分 共有4篇文献报道了术后力量评 分[13-16],异质性检验提示,各研究间无明显异质性(I2=0%,P=0.65),故采用固定效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,2组术后力量评分比较差异无显著性意义[MD=0.87,95%CI (-0.23,1.98),P=0.12],见图6。 2.2.5 术后肩部活动范围评分 共有4篇文献报道了术后肩部活动范围评分[13-16],异质性检验提示,各研究间存在明显异质性(I2=71%,P=0.02),故采用随机效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,2组术后肩部活动范围评分比较差异无显著性意义[MD=1.01,95%CI(-2.00,4.01),P=0.51],见图7。重新检查这4篇研究,分析产生显著性异质性的可能原因是:①肩部活动范围评分带有主观性, 不同年代、地域、性别、年龄组的患者耐受能力和认识存在一定差异;②对于其评分的标准和所采用的具体方法没有详细说明,可能存在一定的差异;③手术方法的差别、术者经验的差别、假体类型的差别也可能造成研究间异质性。 2.2.6 术后前屈度 共有5篇文献报道了术后肩关节前屈度[12-16],异质性检验提示,各研究间存在明显异质性(I2=64%,P=0.03),故采用随机效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,2组术后前屈度比较差异无显著性意义[MD=-5.53,95%CI(-13.93,2.86),P=0.20],见图8。 2.2.7 术后外展度 共有5篇文献报道了术后外展 度[12-16],异质性检验提示,各研究间无明显异质性(I2=48%,P=0.10),故采用固定效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,2组术后外展度比较差异无显著性意义[MD=4.42,95%CI (-0.38,9.23),P=0.07],见图9。"
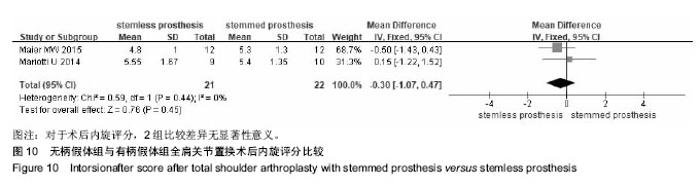
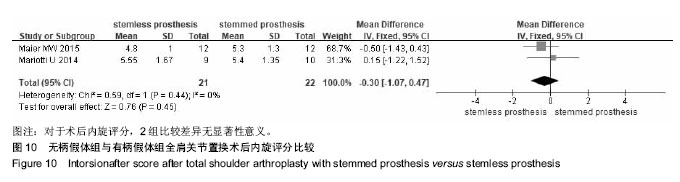
2.2.8 术后外旋度 共有3篇文献报道了术后外旋 度[13-14,16],异质性检验提示,各研究间无明显异质性(I2=16%,P=0.30),故采用固定效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,2组术后外旋度比较差异无显著性意义[MD=3.66,95%CI(-0.16,7.48),P=0.06],见图9。 2.2.9 术后内旋评分 共有2篇文献报道了术后内旋评 分[12,15],异质性检验提示,各研究间无明显异质性(I2=0%,P=0.44),故采用固定效应模型。Meta分析结果显示,2组术后内旋评分比较差异无显著性意义[MD=-0.30,95%CI (-1.07,0.47),P=0.45],见图10。 2.2.10 术后失血量及手术时间 1篇文献报道了术后失血量[16],其中无柄假体41例,有柄假体41例,有柄假体组术后估计失血量为(593.4±147.0)mL,无柄假体组术后估计失血量为(496.3±116.3)mL,2组比较差异有显著性意义(P=0.026),表明无柄假体组比有柄假体组的术后失血量少。该文献还报道了手术时间的比较,有柄假体组的手术时间为(106.2±23.3)min,无柄假体组的手术时间为(91.5± 14.5)min,2组比较差异有显著性意义(P=0.02),表明无柄假体组比有柄假体组的手术时间短。"
| [1] Mansat P, Mansat M, Bellumore Y, et al. Mid-term results of shoulder arthroplasty for primary osteoarthritis. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2002;88(6):544-552.[2] Huguet D, DeClercq G, Rio B, et al. Results of a new stemless shoulder prosthesis: radiologic proof of maintained fixation and stability after a minimum of three years' follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(6):847-852. [3] Bohsali KI, Bois AJ, Wirth MA. Complications of shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(3):256-269. [4] Chin PY, Sperling JW, Cofield RH, et al. Complications of total shoulder arthroplasty: are they fewer or different? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(1):19-22. [5] Farng E, Zingmond D, Krenek L, et al. Factors predicting complication rates after primary shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(4):557-563. [6] Pritchett JW. Long-term results and patient satisfaction after shoulder resurfacing. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(5): 771-777. [7] Jónsson E, Lidgren L, Mjöberg B, et al. Humeral cup fixation in rheumatoid shoulders. Roentgen stereophotogrammetry of 12 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1990;61(2):116-117.[8] Rydholm U, Sjögren J. Surface replacement of the humeral head in the rheumatoid shoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1993;2(6): 286-295. [9] Constant CR, Gerber C, Emery RJ, et al. A review of the Constant score: modifications and guidelines for its use. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008; 17:355-361. [10] Constant CR. Assessment of shoulder function. Orthopade. 1991; 20(5):289-294.[11] Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0[EB].2011. Available from www.Cochrane-Handbook.org.[12] Mariotti U, Motta P, Stucchi A, et al. Stemmed versus stemless total shoulder arthroplasty: a preliminary report and short-term results. Musculoskelet Surg. 2014;98(3):195-200. [13] Uschok S, Magosch P, Moe M,et al. Is the stemless humeral head replacement clinically and radiographically a secure equivalent to standard stem humeral head replacement in the long-term follow-up? A prospective randomized trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(2): 225-232. [14] Spranz DM, Bruttel H, Wolf SI, et al. Functional midterm follow-up comparison of stemless total shoulder prostheses versus conventional stemmed anatomic shoulder prostheses using a 3D-motion-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):478. [15] Maier MW, Lauer S, Klotz MC, et al. Are there differences between stemless and conventional stemmed shoulder prostheses in the treatment of glenohumeral osteoarthritis? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:275. [16] Berth A, Pap G. Stemless shoulder prosthesis versus conventional anatomic shoulder prosthesis in patients with osteoarthritis: a comparison of the functional outcome after a minimum of two years follow-up. J Orthop Traumatol. 2013;14(1):31-37. [17] Habermeyer P, Lichtenberg S, Tauber M,et al. Midterm results of stemless shoulder arthroplasty: a prospective study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(9):1463-1472. [18] Churchill RS, Athwal GS. Stemless shoulder arthroplasty-current results and designs. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2016;9(1):10-16. [19] Razmjou H, Holtby R, Christakis M,et al. Impact of prosthetic design on clinical and radiologic outcomes of total shoulder arthroplasty: a prospective study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013; 22(2):206-214. [20] Routman HD, Becks L, Roche CP. Stemless and Short Stem Humeral Components in Shoulder Arthroplasty. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2015;73(1): 145-147.[21] Bohsali KI , Wirth MA , Rockwood CA. Complications of Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2006; 88(10):2279-2292.[22] Gonzalez JF, Alami GB, Baque F, et al. Complications of unconstrained shoulder prostheses. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011; 20(4):666-682.[23] Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications of total shoulder- replacement arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(4):603-616.[24] Cofield RH, Edgerton BC. Total shoulder arthroplasty: complications and revision surgery. Instr Course Lect. 1990;39:449-462.[25] Anglin C, Wyss UP, Pichora DR. Mechanical testing of shoulder prostheses and recommendations for glenoid design. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2000;9(4):323-331. [26] Hawi N, Tauber M, Messina MJ, et al. Anatomic stemless shoulder arthroplasty and related outcomes: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17(1):376. [27] Ballas R, Teissier P, Teissier J. Stemless shoulder prosthesis for treatment of proximal humeral malunion does not require tuberosity osteotomy. Int Orthop.2016; 40(7):1473-1479.[28] Copeland S. The continuing development of shoulder replacement: “reaching the surface”. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(4):900-905. [29] Levy O, Copeland SA. Cementless surface replacement arthroplasty (Copeland CSRA) for osteoarthritis of the shoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2004;13(3):266-271.[30] Boileau P, Sinnerton RJ, Chuinard C, et al. Arthroplasty of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88:562-575.[31] Irlenbusch U, Berth A, Blatter G, et al. Variability of medial and posterior offset in patients with fourth-generation stemmed shoulder arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2012;36:587-593. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [4] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [5] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [6] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [7] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [8] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [9] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [10] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [11] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [12] | Zhang Lei, Ma Li, Fu Shijie, Zhou Xin, Yu Lin, Guo Xiaoguang. Arthroscopic treatment of greater tuberosity avulsion fractures with anterior shoulder dislocation using the double-row suture anchor technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 895-900. |
| [13] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [14] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [15] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||