Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (15): 2421-2426.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0757
Previous Articles Next Articles
Animal models in periprosthetic osteolysis
Gong Dong1, 2, Wu Guo-tai1, 3, Zhen Ping2
- 1Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Lanzhou General Hospital of Lanzhou Military Command, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 3Key Laboratory of Pharmacology and Toxicology of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
-
Online:2018-05-28Published:2018-05-28 -
About author:Gong Dong, Master candidate, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; Department of Orthopedics, Lanzhou General Hospital of Lanzhou Military Command, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81371983
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gong Dong, Wu Guo-tai, Zhen Ping. Animal models in periprosthetic osteolysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(15): 2421-2426.
share this article
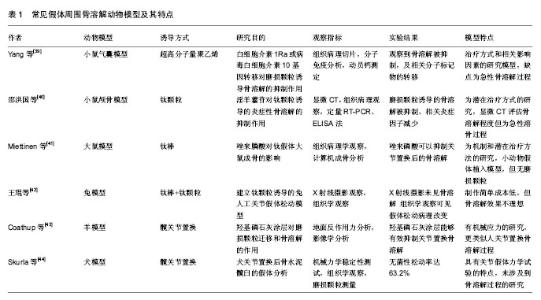
2.1 常见骨溶解动物模型的复制方法 建立PPOL的动物模型是研究PPOL发病机制、病理过程和治疗方法的重要途径。骨溶解动物模型的建立可以选择不同的动物通过多种因素诱导实现。按照实验动物的体积大小可将其分为小动物(大鼠、小鼠)模型和大动物(犬、羊、兔等)模型。根据是否植入假体而分为植入性和非植入性(病理)动物模型。 2.1.1 小鼠模型 (1)Air-pouch模型(气囊)模型:加拿大病理学家Selye最早建立此模型用于研究炎症反应,后Ren等[9]对气囊模型进行改良后用于研究磨损颗粒诱导的骨吸收和骨溶解,其方法是在小鼠背部注入无菌空气建立气囊,6 d后处死小鼠取其颅骨并修剪成骨片作为其他小鼠气囊植骨的供体。对气囊小鼠腹腔麻醉后在气囊上做切口将骨片植入,预防感染并缝合切口。最后把超高分子量聚乙烯颗粒悬浮液注入实验组小鼠气囊中,对照组小鼠气囊内注入无菌PBS,术后14 d CO2处死小鼠,收集小鼠的气囊和植入骨组织。Geng[10]、陈德胜[11]、耿德春等[12]也采用类似方法研究钛颗粒诱导气囊模型,先取部分小鼠麻醉脱颈处死后,取其颅骨作为2只小鼠的气囊植骨供体。再取小鼠做气囊形成术,植入处理好的颅骨,然后实验组气囊内注入钛颗粒,对照组注入无菌PBS。于术后14 d收集标本进行观察。 (2)颅骨模型:磨损颗粒诱导的小鼠骨溶解颅骨模型是由Merkel等[13]最先在小鼠颅骨正中矢状缝做一10 mm长的切口,然后向暴露出的骨外膜区域中直接注入干燥的聚乙烯颗粒,缝合伤口,14 d后CO2处死小鼠,观察小鼠颅骨。此模型证明聚乙烯颗粒对颅骨会造成严重的炎症反应,导致破骨细胞的形成和骨溶解[14]。Shang[15]、Córdova[16]、张雨笛等[17]用类似的方法证明金属或陶瓷颗粒也产生类似的骨溶解效果。 (3)植入物承重模型:Warme等[18]将小鼠双股骨关节切开后,插入10 mm克氏针,然后实验组注射钛颗粒悬浮液,对照组无钛颗粒,结果发现实验组骨质破坏,实现了有植入物承重条件下髓腔内磨损颗粒诱导的骨溶解模型。Yang等[19]研究了长期负重条件下磨损颗粒诱导的鼠骨溶解模型,将不锈钢钛合金钉置入胫骨髓腔,然后实验组关节内注射钛颗粒,对照组无颗粒,进一步进行拔拉实验,实验组拔拉力量小于0.4 N,对照组为 5 N,6个月后实验组提示承重条件下的骨溶解发生。Zhang等[20]用钛针制成鼠的膝关节假体模型,再向胫骨髓腔内注入PBS配置的钛颗粒,经过拔拉实验证实了膝关节假体骨溶解及无菌性松动的发生。Ren等[21]也用相似的模型在胫骨近端植入钛针,建造了负重膝关节假体的动物模型。另外,Pap等[22]想要通过增加关节机械负荷的方式加速骨溶解的出现而计了一个特殊的旋转装置,使得假体植入后的大鼠术每天能够运动2 h,每周运动运动5 d,但术后6个月并未发现明显的骨溶解。 2.1.2 大鼠模型 非植入性PPOL的大鼠模型首先由Howie等[23]建立,方法是切开股骨,从其远端注入丙烯酸和聚乙烯颗粒,重复注射并在聚乙烯颗粒周围发现骨溶解现象。Gelb等[24]建立大鼠的皮下Air-pouch模型定量证明了聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯颗粒的大小、形态和表面积与假体周围急性炎症反应的关系。Allen等[25]在雄性大鼠胫骨近端承重部位插入大钉,建立了大鼠植入性假体骨溶解模型,结果在假体周围组织发现慢性炎症反应和异形细胞。Ren等[26]先在SD大鼠右后肢胫骨平台置入钛针,然后在钛针周围注入超高分子量聚乙烯颗粒建立骨溶解导致无菌性松动的大鼠模型。在研究假体是否影响骨溶解及药物的干预效果时,Miettinen等[27]对大鼠股骨髓腔进行来磷酸冲洗后植入钛假体。 2.1.3 兔模型 新西兰大白兔术前麻醉,从膝关节前外侧入路暴露股骨关节面,沿股骨轴线方向钻孔,然后植入金属人工假体,缝合切口,术后不制动。第1-3天肌注青霉素,分别于术后第4,6,8,10,12,14周向实验组大白兔的膝关节腔注射磨损颗粒悬液1.5 mL,同时向对照组白兔膝关节腔注射等渗盐水,术后第16 周处死动物,收取标本[28]。Im等[29]采用类似的方法制作兔膝关节假体植入模型,不同的是将实验组放入多孔涂层金属棒(植入前在其表面喷涂磨损颗粒),对照组放入干燥纱布包裹的聚乙烯颗粒,预防感染。Fornasier等[30]在研究假体植入的稳定性和磨损颗粒与骨溶解之间的关系时,将年龄6-12个月、体质量3.5-4.5 kg的新西兰兔全麻后行正中髌骨关节切开,分别移除交叉韧带和胫骨软骨,然后用锥形锉在胫骨平台中心钻出一个能够植入假体的导孔,手动旋转使得假体变得不稳定,再把这些关节置换后的兔分成注入超高分子量聚乙烯颗粒组、聚乙烯颗粒和钛颗粒混合液组及不注入磨损颗粒组,术后6个月处死动物并收集材料。也有先通过向兔股骨远端骨髓腔内局部注射内毒素阴性的钛颗粒悬液,再植入钛合金假体,于第1,3,5周再次注射钛颗粒悬液,术后第6周处死动物,收集标本[31-32]。 2.1.4 犬模型 犬模型在1987年由Lennox等[33]首先报道,后经Jones等[34]改良,取纯种犬经膝关节在近端胫骨缺损处植入聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯颗粒涂层的聚乙烯棒,另一端固定于股骨远端。膝关节的屈伸可创造植入物的相对活动。Lind等[35]通过暴露犬肱骨近端, 生理盐水清洗后植入表面涂以陶瓷涂层的圆柱型钛假体,然后压配垫圈固定。每头犬仅在一侧肱骨植入假体,另取犬作空白对照组。6周后收获犬的肱骨近端。严孟宁等[36]对成年雄性Beagle犬常规麻醉消毒,用环钻于双侧股骨外髁造成直径10 mm,深度为11 mm的骨缺损,植入带垫片假体后,保持假体周围3 mm骨缺损区,模型组一左侧骨缺损区植入吸附1 mL颗粒混悬液的明胶海棉,右侧植入吸附1 mL PBS的明胶海绵,颗粒组双侧骨缺损区均植入吸附1 mL颗粒混悬液的明胶海绵,2个月后可观察到典型的骨溶解松动界面形成。 2.1.5 羊模型 Kalia等[37]利用山羊模型对山羊进行髋关节置换研究术后髋臼周围骨溶解,选取12只体质量60-70 kg骨骼成熟的雌性Saanan山羊,实验组臼杯用生物型表面并喷涂骨髓间充质细胞,对照组喷涂纤维蛋白胶,两组均使用抛光钴铬合金股骨头,麻醉后经后外侧入路切除股骨头,置入假体并用骨水泥固定,闭合伤口并预防感染,术后6周和12周摄片,并进行地面反作用力的测量,实验结果显示喷涂骨髓间充质细胞的髋臼周围骨溶解被抑制,新生骨增加。El-Warrak等[38]对绵羊随机选取一侧肢体行全髋关节置换,对照组用骨水泥覆盖大小适当的股骨假体,选择合适的前倾角,维持假体稳定,而实验组在股骨干外侧造出骨水泥缺陷并扩大到假体全长,术后对2个月处死组在狭小空间制动,8.5个月处死组不制动,实验结束后处死绵羊,收集材料进行下一步研究。 2.2 常见PPOL动物模型的特点 建立骨溶解动物模型的目的是研究其发病机制,治疗和预防的方法,然而目前并没有一种理想的模型能够适用于研究的每一阶段或每一类型。每个实验方法都有自己的优点和局限,了解他们有助于正确合理的选择,从而做出更科学的研究结果。常见PPOL动物模型的研究方法和特点见表1。 2.3 新型PPOL模型研究 除了以上经典的常用骨溶解动物模型建立方法和其所具有的特点外,有些学者开发和研究了具有创新见解的新模型,或者通过对既往骨溶解模型的改良,从而使其更加简单、经济、具有更高的可行性和准确性。 在研究巨噬细胞在假体磨损颗粒诱导骨溶解中的作用的实验中,Ren等[45]在小鼠颅骨气囊骨片植入前对小鼠腹腔麻醉下行氯磷酸卵磷脂处理诱导巨噬细胞凋亡,建立了巨噬细胞衰竭的小鼠骨溶解模型,实验表明氯膦酸卵磷脂处理对超高分子量聚乙烯颗粒诱导的炎性骨溶解起到了抑制作用,然而该模型也是急性溶骨的病理模型,没有假体的植入。 Zhang等[46]为研究RANKL/RANK/OPG系统在伴随感染的PPOL中的作用时,将12只健康成年杂种犬随机分为对照组和实验组,并均行右侧股骨头置换,假体股骨头为钴铬钼材料,股骨柄为全羟基磷灰石涂层钛合金,实验组接受关节腔内注射细菌液的同时对照组注射生理盐水,然而该模型只通过ELISA证实了RANKL/ RANK/OPG系统失衡与伴随感染的PPOL相关,并未用更多方法如micro-CT等对骨溶解更进一步验证。 Ma等[47]发明了一种可以连续向小鼠髓腔内输送磨损颗粒的渗透泵,这虽然这解决了其他小鼠模型的急性溶骨问题,然而并没有观察到明确的骨溶解现象。有学者将符合骨溶解诱导调节的磨损颗粒和盐水混合,自然蒸发后获得其结晶体混合物,然后把这种混合物置入部分去除小鼠颅骨外膜的颅顶处,这种方法建立骨溶解模型不会出现磨损颗粒向周围蔓延的现象,并能抑制细菌生长[48]。 另外,万睿等[49]发现纱布纤维有类似于磨损颗粒的作用,可在小鼠气囊植骨模型中诱发炎性骨溶解。 "
| [1] Francesca V,Matilde T,Milena F,et al.Gene expression in osteolysis: review on the identification of altered molecular pathways in preclinical and clinical studies. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):499.[2] Drynda A,Singh G,Buchhorn G,et al.Metallic wear debris may regulate CXCR4 expression in vitro and in vivo.Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103:1940-1948.[3] Saad S,Dharmapatni A,Crotti T,et al.Semaphorin-3a, neuropilin-1 and plexin-A1 in prosthetic-particle induced bone loss Acta Biomater.2016;30:311-318.[4] Zhao YP, Wei JL, Tian QY,et al.Progranulin suppresses titanium particle induced inflammatory osteolysis by targeting TNFα signaling.Sci Rep.2016;6:20909.[5] Cordova LA,Stresing V,Gobin B,et al.Orthopaedic implant failure:Aseptic implant loosening-The contribution and future challenges of mouse models in translational research.Clin Sci. 2014;127:277-293.[6] Kurtz S,Ong K,Lau E,et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:780 -785.[7] Inacio MC,Ake CF,Paxton EW,et al.Sex and risk of hip implant failure:assessing total hip arthroplasty outcomes in the United States. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173(6):435-441.[8] Marshall A, Ries MD, Paprosky W,et al.How prevalent are implant wear and osteolysis, and how has the scope of osteolysis changed since 2000?. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16 (Suppl 1): S1-S6.[9] Ren W,Yang SY,Wooley PH,et al.A novel murine model of orthopaedic wear debris associated osteolysis.Scand J Rheumatol. 2004;33(5):349-357.[10] Geng D,Xu Y,Yang H,et al.Protection against titanium particle induced osteolysis by cannabinoid receptor 2 selective antagonist.Biomaterials. 2010;31(8):1996-2000.[11] 陈德胜,李燕,郭凤英,等.钛颗粒诱导小鼠植骨气囊骨溶解模型的构建[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2016,38(11):1228-1231.[12] 耿德春,徐耀增,朱雪松,等.钛颗粒诱导小鼠骨溶解模型的评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2009,13(22):4223-4226.[13] Merkel KD,Erdmann JM,Mchugh KP,et al.Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates orthopedic implant osteolysis.Am J Pathol. 1999;154(2):203-210.[14] Wedemeyer C,Neuerburg C,Pfeiffer A,et al.Polyethylene particle-induced bone resorption in substance P-deficient mice.Calcif Tissue Int. 2007;80(4):268-274.[15] Shang JY,Zhan P,Jiang C,et al.Inhibitory effects of lanthanum chloride on wear particle-induced osteolysis in a mouse calvarial model.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016;169(2):303-309.[16] Córdova LA,Trichet V,Escriou V,et al.Inhibition of osteolysis and increase of bone formation after local administration of siRNA-targeting RANK in a polyethylene particle-induced osteolysis mode.Acta Biomater.2015;13:150-158.[17] 张雨笛,严明,俞立虹,等.PI3K/Akt信号通路在磷酸三钙磨损颗粒诱导小鼠颅骨溶解中的作用[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2017,36(3): 212-217.[18] Warme B,Epstein N,Trindade M,et al.Proinflammatory mediator expression in a novel murine model of titanium particle induced intramedullary inflammation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004;71:360-366.[19] Yang S,Yu H,Gong W,et al.Murine model of prosthesis failure for the long-term study of aseptic loosening.J Orthop Res. 2007;25:603 -611.[20] Zhang T,Yu H,Gong W,et al.The effect of osteoprotegerin gene modification on wear debris induced osteolysis in a murine model of knee prosthesis failure. Biomaterials. 2009; 30(30):6102-6108.[21] Ren W,Zhang R,Hawkins M,et al. Efficacy of periprosthetic erythromycin delivery for wear debris-induced inflammation and osteolysis.Inflamm Res. 2010;59(12):1091-1097.[22] Pap G, Machner A, Rinnert T, et al. Development and characteristics of a synovial-like interface membrane around cemented tibial hemiarthroplasties in a novel rat model of aseptic prosthesis loosening. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(4): 956-963.[23] Howie DW,Vernon-Roberts B,Oakeshott R, et al. A rat model of resorption of bone at the cement-bone interface in the presence of polyethylene wear particles.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988;7:257-263.[24] Gelb H,Schumacher H,Cuckler J,et al.In vivo inflammatory response to polymethylmethacrylate particulate debris:effect of size,morphology,and surface area.J Orthop Res.1994;12: 83-92.[25] Allen M,Brett F,Millett P,et al.The effects of particulate polyethylene at a weight-bearing bone-implant interface:a study in rats.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78: 32-37.[26] Ren W,Muzik O,Jackson N,et al.Differentiation of septic and aseptic loosening by PET with both 11C-PK11195 and 18F-FDG in rat models.Nucl Med Commun. 2012;33(7): 747-756.[27] Miettinen SS,Jaatinen J,Pelttari A,et al.Effect of locally administered zoledronic acid on injury-induced intramembranous bone regeneration and osseointegration of a titanium implant in rats.J Orthop Sci. 2009;14:431-436.[28] 丁悦,黄健斌,秦础强.人工关节无菌性松动动物模型的建立[J].实用骨科杂志,2010,16(7):510-515.[29] Im GI, Kwon BC, Lee KB. The effect of COX-2 inhibitors on periprosthetic osteolysis. Biomaterials.2004;25(2):269-275.[30] Fornasier VL, Goodman SB, Protzner K, et al. The role of implant alignment on stability and particles on periprosthetic osteolysis--A rabbit model of implant failure. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004;70(2):179-186.[31] Zhao X, Cai XZ, Shi ZL,et al,Low intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) may prevent polyethylene induced periprosthetic osteolysis in vivo.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012;38:238-246.[32] Hu B,Cai XZ,Shi ZL,et al.Microbubble injection enhances inhibition of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on debris-induced periprosthetic osteolysis in rabbit model.Ultrasound Med Biol.2015;41(1):177-186.[33] Lennox DW,Lewis CG,Jones LC,et al.Tissue response to motion at the bone/cement interface: a histological study in a canine model.Trans Soc Biomaterials.1987;10:133.[34] Jones LC,Frondoza C,Hungerford DS.Effect of PMMA particles and movement on an implant interface in a canine model.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2001;83(3):448-458.[35] Lind M,Overgaard S,Bunger C,et al. Improved bone anchorage of hydroxypatite coated implants compared with tricalcium-phosphate coated implants in trabecular bone in dogs.Biomaterials. 1999;20(8):803-808.[36] 严孟宁,戴尅戎,汤亭亭.假体周围骨溶解性骨缺损的转骨形态发生蛋白-2基因治疗[J].中华实验外科杂志,2008,25(6):702-704.[37] Kalia P,Coathup MJ,Oussedik S,et al.Augmentation of bone growth onto the acetabular cup surface using bonemarrow stromal cells in total hip replacement surgery. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15:3689-3696.[38] El-Warrak AO,Olmstead M,Apelt D,et al.An animal model for interface tissue formation in cemented hip replacements.Vet Surg. 2004;33:495-504.[39] Yang SY,Wu B,Mayton L,et al.Protective effects of IL-1Ra or vIL-10 gene transfer on a murine model of wear debris-induced osteolysis.Gene Therapy.2004;11(5):483-491.[40] 邵洪国,崔京福,朱世军,等.淫羊藿苷对钛颗粒诱导的炎症性骨溶解的抑制作用[J].中华创伤杂志,2015,31(9):850-855.[41] Miettinen SSA,Jaatinen J,Pelttari A,et al.Effect of locally administered zoledronic acid on injury-induced intramembranous bone regeneration and osseointegration of a titanium implant in rats.J Orthop Sci. 2009;14(4):431-436.[42] 王琨,王英振,夏长所,等.钛颗粒诱导的兔人工关节假体松动模型制备[J].青岛大学医学院学报,2013,49(5):399-402.[43] Coathup MJ,Blackburn J,Goodship AE,et al.Role of hydroxyapatite coating in resisting wear particle migration and osteolysis around acetabular components.Biomaterials. 2005; 26(26):4161-4169.[44] Skurla CP,James SP.Assessing the dog as a model for human total hip replacement:analysis of 38 postmortem- retrieved canine cemented acetabular components.J Bone Joint Surg. 2005;87(1):120-127.[45] Ren W,Markel DC,Schwendener R,et al. Macrophage depletion diminishes implant-wear-induced inflammatory osteolysis in a mouse model. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008; 85(4):1043-1051.[46] Zhang HW,Peng L,Li WB,et al.The role of RANKL/RANK/OPG system in the canine model of hip periprosthetic infection osteolysis. Int J Artif Organs. 2016; 39(12): 619-624.[47] Ma T,Ortiz S,Huang Z,et al.In vivo murine model of continuous intramedullary infusion of particles-A preliminary study.Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009;88(1): 250-253.[48] 刘铭,张健,魏小兰,等.改良型磨损颗粒诱导小鼠颅骨溶解模型的构建[J].中国老年学,2013,33(23):5927-5930.[49] 万睿,李平,周园东,等.纱布纤维可否在小鼠气囊植骨模型中诱发炎性骨溶解的研究[J].中国全科医学,2013,16(7):648-652.[50] Mcgonigle P,Ruggeri B.Animal models of human disease: Challenges in enabling translation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014; 87(1):162-171. |
| [1] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [3] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [4] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [5] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [6] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [7] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [8] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [9] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [10] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [11] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [12] | Tan Jingyu, Liu Haiwen. Genome-wide identification, classification and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciclin gene family for osteoblast specific factor 2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1243-1248. |
| [13] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [14] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [15] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||