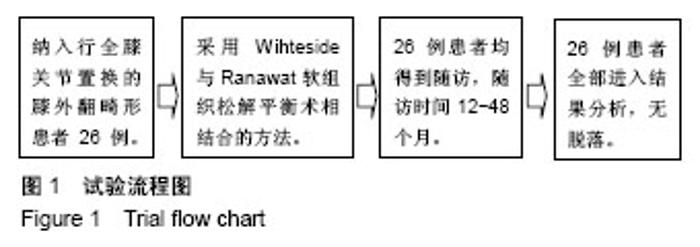
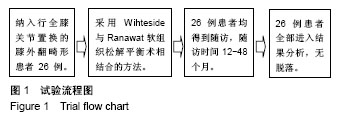
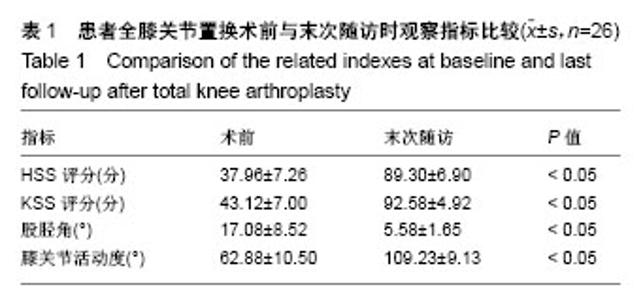
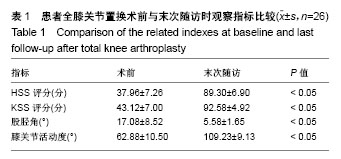
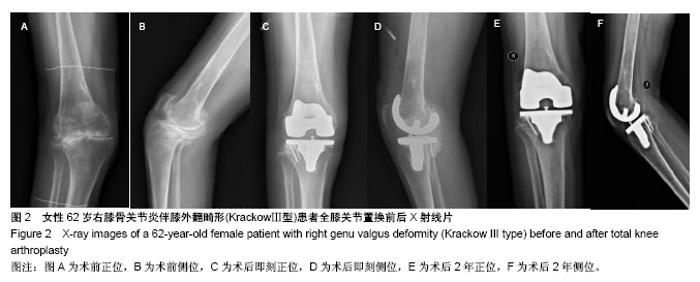
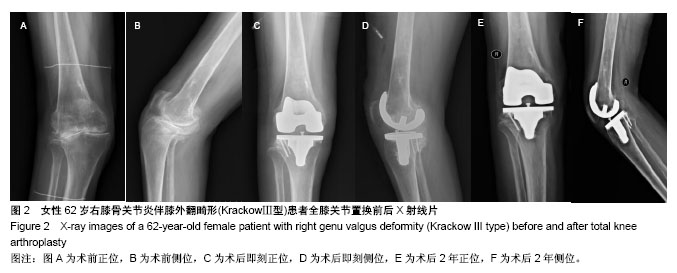
| [1] Koskinen E, Remes V, Paavolainen P, et al. Results of total knee replacement with a cruciate-retaining model for severe valgus deformity-a study of 48 patients followed for an average of 9 years. Knee. 2011;18(3):145-150.[2] 王兴山,翁习生,林进,等. 人工全膝关节置换术治疗终末期膝关节病变合并膝外翻畸形的手术技巧及临床疗效评价[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2012,26(5):513-517.[3] 张锐,柳海平,谢兴文,等.全膝关节置换治疗膝关节外翻畸形[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(9):1343-1349.[4] 王宏伟,周殿阁. 髂胫束松解在外翻膝全膝关节置换术中的作用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015,30(8):812-814.[5] Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS, Elkus M, et al. Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87 Suppl 1(Pt 2):271-284.[6] Whiteside LA. Selective ligament release in total knee arthroplasty of the knee in valgus.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1999; 367:130-140.[7] 冯宗权,陈坚锋,潘耀成. 全膝关节置换术治疗膝外翻畸形的手术探讨[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(17):1563-1567.[8] Miyasaka KC, Ranawat CS, Mullaji A. 10- to 20-year follow up of total knee arthroplasty for valgus deformities. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1997;345):29-37.[9] Whiteside LA. Soft tissue balancing: The knee. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(4 Suppl 1):23-27.[10] 史法见,张锦洪,王芳,等. 全膝关节置换术治疗膝外翻畸形疗效观察[J].实用骨科杂志, 2011,17(8):701-703.[11] Peters CL, Jimenez C, Erickson J, et al. Lessons learned from selective soft-tissue release for gap balancing in primary total knee arthroplasty: An analysis of 1216 consecutive total knee arthroplasties: Aaos exhibit selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013; 95(20):e152.[12] 刘志远,李宝军,柴志勇,等. 人工膝关节置换治疗膝外翻畸形的疗效[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2014,20(3):220-223.[13] 徐美涛,查振刚,刘宁,等. 人工全膝关节置换术在外翻膝的临床应用[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2011,19(2):109-112.[14] Strauch M, von Eisenhart Rothe R, Graichen H. A new navigation- based technique for lateral distalizing condylar osteotomy in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty with fixed valgus deformity. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10): 2263-2270.[15] Buechel FF. A sequential three-step lateral release for correcting fixed valgus knee deformities during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;260):170-175.[16] Clarke HD, Fuchs R, Scuderi GR, et al. Clinical results in valgus total knee arthroplasty with the "pie crust" technique of lateral soft tissue releases. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(8):1010-1014.[17] Aglietti P, Lup D, Cuomo P, et al. Total knee arthroplasty using a pie-crusting technique for valgus deformity . Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;464:73-77.[18] Politi J, Scott R. Balancing severe valgus deformity in total knee arthroplasty using a lateral cruciform retinacular release. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(5):553-557.[19] Insall J. A midline approach to the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971;53(8):1584-1586.[20] Krackow KA, Jones MM, Teeny SM, et al. Primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with fixed valgus deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;273:9-18.[21] Healy WL, Iorio R, Lemos DW. Medial reconstruction during total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;356:161-169.[22] Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, et al. Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(12):2143-2149.[23] Thompson NW, McAlinden MG, Breslin E, et al. Periprosthetic tibial fractures after cementless low contact stress total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16(8):984-990.[24] 唐成,严俊伟,王黎明,等.选择性软组织松解技术在重度膝外翻畸形全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014,29(6): 547-549.[25] Smith JL Jr, Tullos HS, Davidson JP. Alignment of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1989;4 Suppl:S55-61.[26] Anderson JA, Baldini A, MacDonald JH, et al. Primary constrained condylar knee arthroplasty without stem extensions for the valgus knee. Clin Orthop Relat Rese.2006;442:199-203.[27] Bonner TJ, Eardley WG, Patterson P, et al. The effect of post-operative mechanical axis alignment on the survival of primary total knee replacements after a follow-up of 15 years . J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(9):1217-1222.[28] Mullaji A, Kanna R, Marawar S, et al. Comparison of limb and component alignment using computer-assisted navigation versus image intensifier-guided conventional total knee arthroplasty: A prospective, randomized, single-surgeon study of 467 knees . J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(7):953-959.[29] Pagoti R, O'Brien S, Doran E, et al. Unconstrained total knee arthroplasty in significant valgus deformity: A modified surgical technique to balance the knee and avoid instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(9):2825-2834. [30] Krackow KA, Holtgrewe JL. Experience with a new technique for managing severely overcorrected valgus high tibial osteotomy at total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1990;258:213-224.[31] 甄平,李慎松,李旭升,等.晚期类风湿性关节炎合并屈膝位强直的人工全膝关节置换术[J]. 中国骨伤, 2015,28(3):272-275.[32] Matsushita T, Kuroda R, Kubo S, et al. Total knee arthroplasty combined with medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for osteoarthritic knee with preoperative valgus deformity and chronic patellar dislocation. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(3):505 e517-520. |