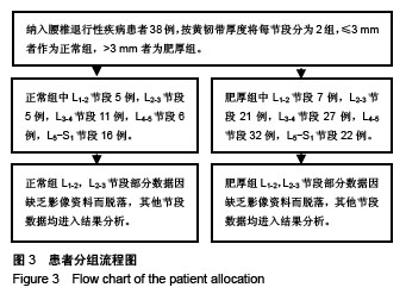
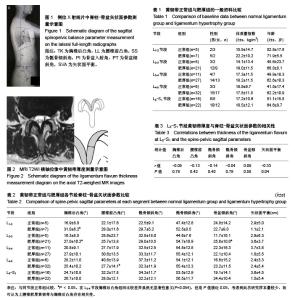
| [1] Reina MA, Lirk P, Puigdellivol-Sanchez A, et al. Human lumbar ligamentum flavum anatomy for epidural anesthesia: reviewing a 3D MR-based interactive model and postmortem samples. Anesth analg. 2016;122(3):903-907.[2] Abbas J, Hamoud K, Masharawi YM, et al. Ligamentum flavum thickness in normal and stenotic lumbar spines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(12):1225-1230.[3] Altun I, Yuksel KZ. Histopathological analysis of ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal stenosis and disc herniation. Asian Spine J. 2017;11(1):71-74.[4] Sairyo K, Biyani A, Goel V, et al. Pathomechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy: a multidisciplinary investigation based on clinical, biomechanical, histologic, and biologic assessments. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(23): 2649-2656.[5] Yoshiiwa T, Miyazaki M, Kawano M, et al. Analysis of the relationship between hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum and lumbar segmental motion with aging process. Asian Spine J. 2016;10(3):528-535.[6] Diebo BG, Varghese JJ, Lafage R, et al. Sagittal alignment of the spine: What do you need to know? Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;139:295-301.[7] 李庚午,杨长伟,陈凯,等. 腰椎间盘退变与脊柱骨盆矢状面参数的相关性[J].中国临床医学, 2017,24(2):194-198.[8] 李松,孙旭,陈曦,等. 高位腰椎间盘突出症患者脊柱-骨盆矢状面形态的影像学分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(6):532-538.[9] 吕昕,张斌,刘远,等.下腰椎小关节退变与脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡的相关性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(8):964-968.[10] 张奎渤,刘辉,王建儒,等. L5轻度峡部裂型滑脱患者脊柱-骨盆矢状面参数与椎间盘退变的关系[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015, 23(7):605-609.[11] Sakamaki T, Sairyo K, Sakai T, et al. Measurements of ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine using MRI[J]. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(10):1415-1419.[12] 吕兴隆,李淑华,高学功,等. 黄韧带肥厚的MRI诊断[J]. 中国医学影像技术,2002,8(10):1030-1032.[13] Yoshiiwa T, Miyazaki M, Notani N, et al. Analysis of the relationship between ligamentum flavum thickening and lumbar segmental instability, disc degeneration, and facet joint osteoarthritis in lumbar spinal stenosis. Asian Spine J. 2016;10(6):1132-1140.[14] Park JB, Chang H, Lee JK. Quantitative analysis of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in ligamentum flavum of lumbar spinal stenosis and disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(21):E492-E495.[15] Yabe Y, Hagiwara Y, Tsuchiya M, et al. Decreased elastic fibers and increased proteoglycans in the ligamentum flavum of patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(7):1241-1247.[16] Vialle R, Levassor N, Rillardon L, et al. Radiographic analysis of the sagittal alignment and balance of the spine in asymptomatic subjects. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(2): 260-267.[17] 李危石,孙卓然,陈仲强. 正常脊柱-骨盆矢状位参数的影像学研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2013,33(5):447-453.[18] 陈涛,黎观保,梁科友,等. 脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡及其在脊柱疾病治疗中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(13):2423-2430.[19] 任周梁,朱松青,梁卫东,等. 腰椎退变性后凸截骨矫形内固定后矢状面的平衡变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(4): 564-570.[20] Roussouly P, Pinheiro-Franco JL. Sagittal parameters of the spine: biomechanical approach. Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 5:578-585.[21] Vaz G, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, et al. Sagittal morphology and equilibrium of pelvis and spine. Eur Spine J. 2002;11(1):80-87. |