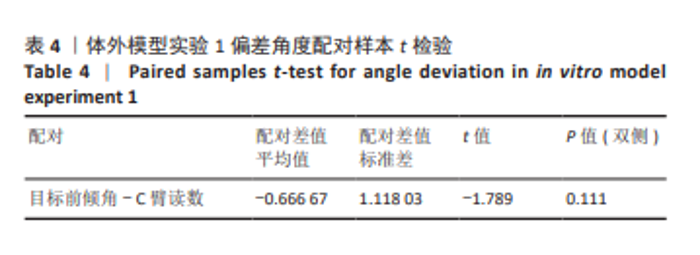
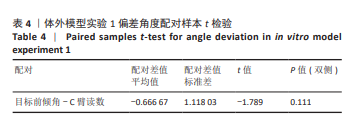
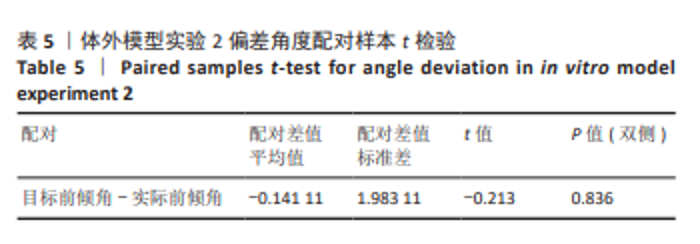
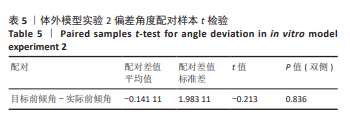
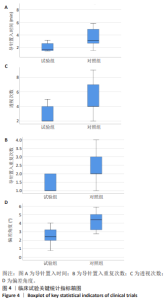
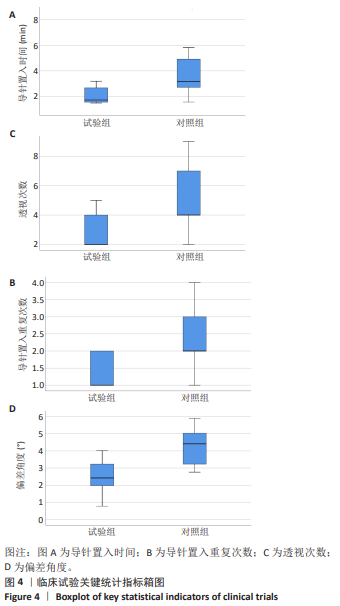
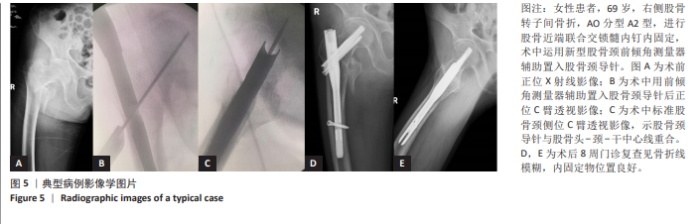
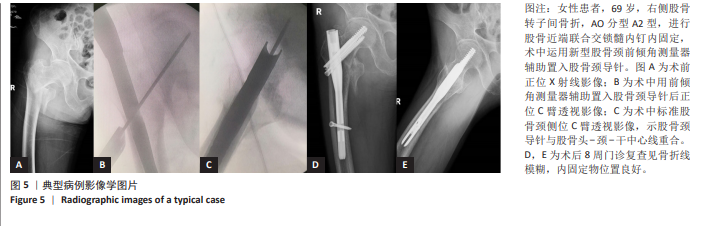
[1] 国家统计局. 第七次全国人口普查公报[Z]. 2021.
[2] 高超,王淑君,于普林. 人口老龄化的现状及发展趋势[J].中华老年医学杂志,2014,33(8):924-926.
[3] ZHANG C, FENG J, WANG S, et al. Incidence of and trends in hip fracture among adults in urban China: a nationwide retrospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020;17(8):e1003180.
[4] 居家宝,张培训.髋部骨折流行病学特点:单中心1397例分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(7):592-595.
[5] 姬晨妮,陈伟,朱燕宾,等.京津唐地区1583例老年股骨转子间骨折流行病学特征分析[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2015, 1(1):45-49.
[6] SEYHAN M, TURKMEN I, UNAY K, et al. Do PFNA devices and Intertan nails both have the same effects in the treatment of trochanteric fractures? A prospective clinical study. J Orthop Sci. 2015;20(6): 1053-1061.
[7] 洪石,吴征杰,李灿辉.机器人辅助下股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定治疗股骨粗隆间骨折8例[J].实用医学杂志,2019,35(2):335-336.
[8] 刘明军,万先亮,李洪波,等.骨科创伤机器人辅助PFNA内固定治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的效果[J].实用老年医学,2023,37(5): 491-494+499.
[9] BRUNNER A, EICHINGER M, HENGG C, et al. A Simple Method for Measurement of Femoral Anteversion-Validation and Assessment of Reproducibility. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30(8):e273-e278.
[10] 高血压精准化诊疗专家共识组成员,老年心脑血管病教育部重点实验室.高血压精准化诊疗中国专家共识(2024)[J].中华高血压杂志(中英文),2024,32(6):505-519.
[11] 蔡群斌.HbAlc对合并糖尿病老年髋部骨折围手术期的影响[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2012.
[12] 柳达,马瑞雪,吉士俊.股骨颈前倾角的测量及其临床意义[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2002(4):78-80.
[13] 李凤春,石福明,时国富,等.股骨颈前倾角与扭转角的区别[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2000(1):92.
[14] 李鸿恩,曾益辉,王伟,等.磁共振与CT在测量股骨颈前倾角中的应用及对比分析[J].罕少疾病杂志,2021,28(5):95-97.
[15] 曹进,胡珊珊,郑华江,等.3D打印技术测量儿童发育性髋关节脱位股骨颈前倾角[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(8):741-744.
[16] 刘建友,贾中伟,牛佳伟,等.构建股骨3D数字化模型提出一种新的股骨颈前倾角测量方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(24): 3779-3783.
[17] 陈佳晖,马剑雄,张士雄,等.基于三维模型标准化股骨前倾角的测量方法[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(S1):300.
[18] 蔡志浩,谢召勇.股骨颈前倾角测量评估:如何建立统一的方法和标准[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(9):1448-1454.
[19] 王礼跃,冯世波,张力,等.C臂X线机辅助下自制导向针测量前倾角在股骨颈内固定术中的应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(6):698-699.
[20] 白皓,屈新平,唐亮,等.一种新型股骨头髓钉倾斜角测量器的设计[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2022,19(4):91-93.
[21] 马台,党瑞山,丁任,等.股骨近端髓内钉三维导航器的研制与测试[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2014,11(4):73-75+84.
[22] 王振奎,高杰,孙泰安,等.股骨颈前倾角导向器的研制及临床应用[J].中国骨伤,2008,21(9):705-706.
[23] 汪心毅,张落舟,王忍,等.股骨颈前倾角导向器的研制与应用[J].骨科,2011,2(3):145-146.
[24] 汤世斌,骆志权,胡耀华,等.体外股骨颈前倾角导向器的研制及其临床应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(3):240-243.
[25] 张德光,韩桂全,张秀玲,等.自制仪器术中股骨颈前倾角测量的临床应用[J].中国实验诊断学,2003,7(4):328-329.
[26] 万超,廉伟,董圣杰,等. 基于CT测量的旋顶角、旋顶距在全髋关节置换术前股骨假体个体化选择中的应用[J]. 中华解剖与临床杂志,2024,29(5):322-330.
[27] 陆清达,刘趁心,王欢,等. 儿童单侧发育性髋关节发育不良股骨近端截骨术后肢体过度生长的临床特点[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2025, 45(10):613-620.
[28] 沈永辉,周健,章小君,等.自动角度测量仪用于测量全髋关节置换术中前倾角的效果[J].临床骨科杂志,2015,18(4):429-432.
[29] 刘和风,李业海,唐浩然,等.自动角度测量仪应用于全髋关节置换术对患者远期效果及预后的影响[J].局解手术学杂志,2018, 27(10):742-745.
[30] 朱求亮,许斌,沈良华,等.激光投射法测量股骨颈扭转角及前倾角[J].解剖学报,2014,45(5):694-697.
[31] VAVOURAKIS M, ZACHARIOU D, GALANIS A, et al. Incidence of Rotational Malalignment after Intertrochanteric Fracture Intramedullary Nailing: A CT-Based Prospective Study. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania). 2024;60(9):1535-1535.
[32] GOETHALS J, CAVAZOS DR, DENISIUK M, et al. Acute Correction of Femoral Malrotation After Intramedullary Nailing Using an Intraoperative Digital Protractor. Cureus. 2023;15(4):e37108.
[33] KINAMI Y, HASEI J, FUJIWARA K. Measurement of Lag-Screw Anteversion With an iPhone During Trochanteric Fracture Surgery. Cureus. 2022;14(12):e33110-e33110.
[34] GEBHARDT C, GÖTTLING L, BUCHBERGER L, et al. Femur reconstruction in 3D ultrasound for orthopedic surgery planning. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2023;18(6):1001-1008.
[35] MITSUTAKE R, TANINO H, NISHIDA Y, et al. A simple angle-measuring instrument for measuring cemented stem anteversion during total hip arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disorde. 2020;21(1):113.
[36] MATSUBAYASHI S, ISOBE Y, CHIBA K, et al. Measurement of Femoral Axial Offset. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(7):1383-1389.
[37] SONG KS, YON CJ, HEO YR, et al. Using the Axial Oblique View of Computed Tomography (CT) in Evaluating Femoral Anteversion: A Comparative Cadaveric Study. Diagnostics. 2022;12(8):1820.
[38] KINAMI Y, HORITA M, FUJIWARA K. Measurement Method of Femoral Anteversion During Surgery for Trochanteric Fractures. Cureus. 2024; 16(10):e72532.
[39] PONGKUNAKORN A, PHETPANGNGA N, KANANAI N. Accuracy of intraoperative estimation of femoral stem anteversion in cementless total hip arthroplasty by using a digital protractor and a spirit level. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):27.
[40] XIAO H, YIBULAYIMU S, ZHAO C, et al. Rethinking femoral neck anteversion assessment: a novel automated 3D CT method compared to traditional manual techniques. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025; 26(1):466.
[41] SANGEUX M, MAHY J, GRAHAM HK. Do physical examination and CT-scan measures of femoral neck anteversion and tibial torsion relate to each other? Gait Posture. 2014;39(1):12-16. |