Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (16): 4021-4029.doi: 10.12307/2026.703
BTN3A2 is a key target for the development or prevention of new drugs for knee osteoarthritis: a randomization study based on drug targeting
Wei Bingqi1, 2, Sun Jiahui1, 2, Chen Liu1, 2, Li Yijing1, 2, Wan Hejia1, 2, Qi Yifan1, 2, Wang Shangzeng1, 2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Henan Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine (The Second Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine), Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China; 2School of Orthopedics, Henan University of Chinese medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-01Accepted:2025-08-20Online:2026-06-08Published:2025-11-25 -
Contact:Wang Shangzeng, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Henan Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine (The Second Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine), Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China; School of Orthopedics, Henan University of Chinese medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
About author:Wei Bingqi, MS candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Henan Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine (The Second Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine), Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China; School of Orthopedics, Henan University of Chinese medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82374490 (to WSZ); Henan Provincial Natural Science Foundation Project, No. 222300420486 (to WSZ); Henan University Science and Technology Innovation Team, No. 24IRTSTHN040 (to WSZ); Henan Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Projects, Nos. 2023ZYZD06, 2021ZY2010, and 2019ZY2035 (all to WSZ); Zhengzhou Science and Technology Benefit People Plan Project, No. 2023KJHM0009 (to WSZ); Henan College Students’ Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program, No. 202410471006 (to QYF); Henan Province Key Research and Development Project, No. 241111311700 (to WSZ); Henan Province Middle-aged and Young Leading Talent for Health and Wellness Science and Technology Innovation, No. LJRC2024020 (to WSZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Bingqi, Sun Jiahui, Chen Liu, Li Yijing, Wan Hejia, Qi Yifan, Wang Shangzeng. BTN3A2 is a key target for the development or prevention of new drugs for knee osteoarthritis: a randomization study based on drug targeting[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4021-4029.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
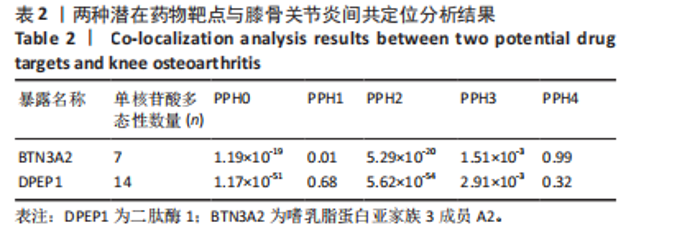
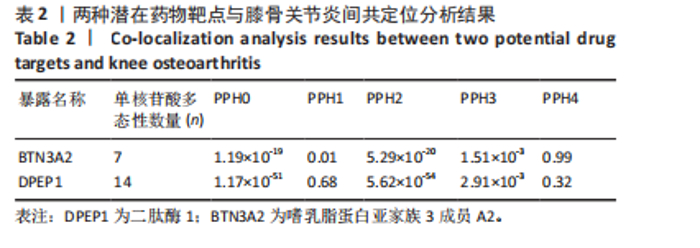
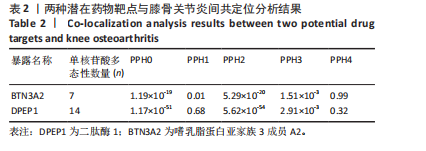
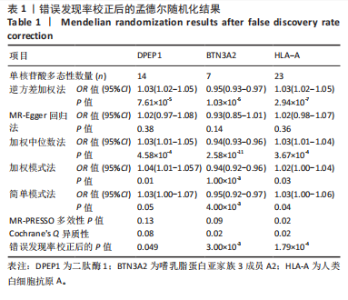
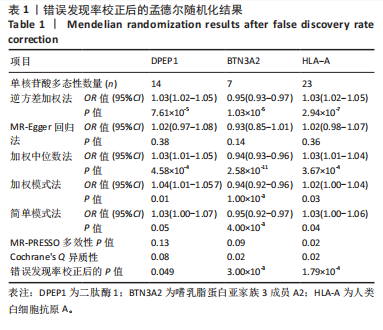
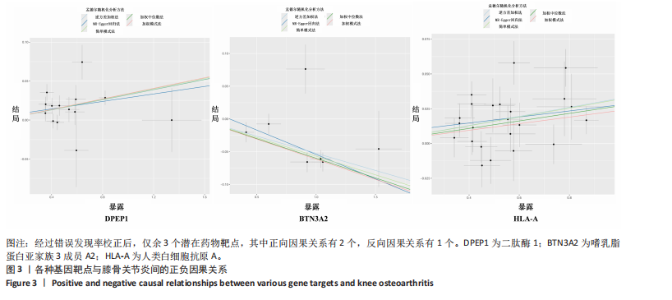
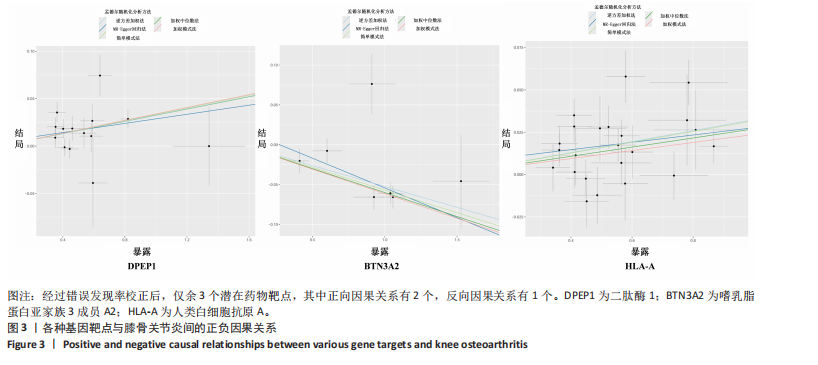
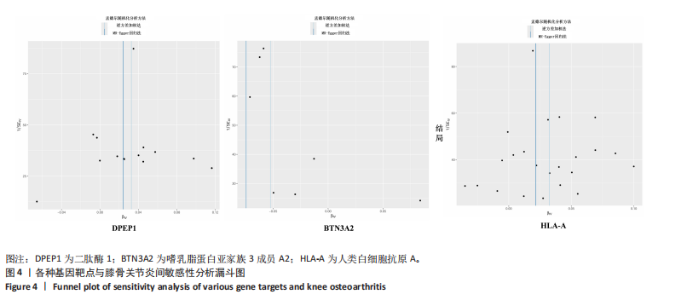
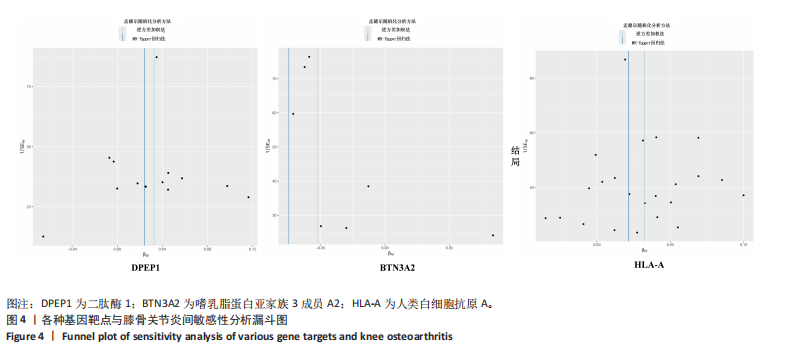
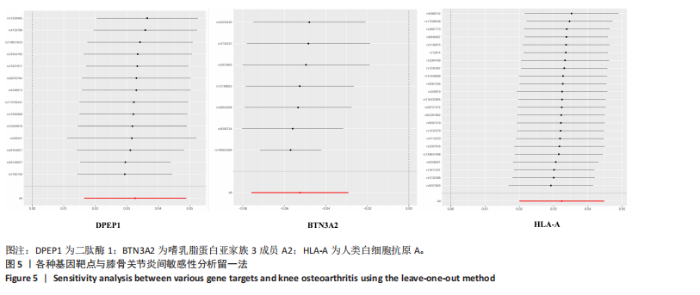
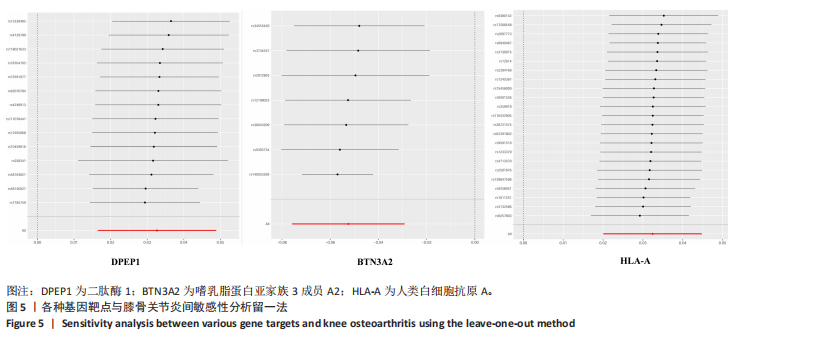
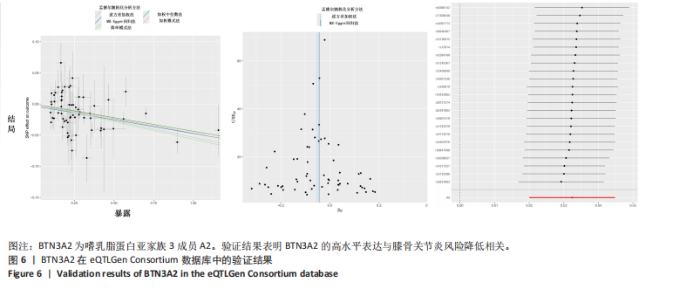
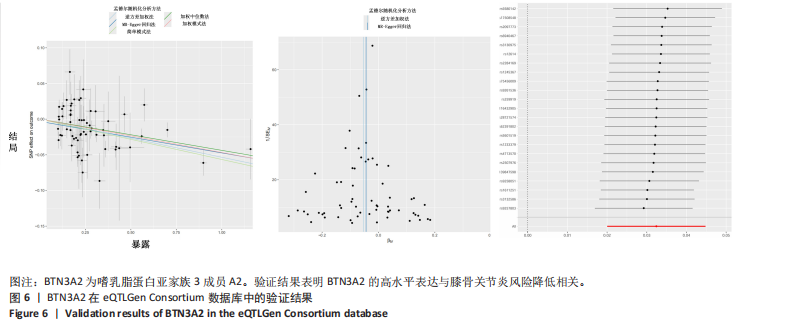
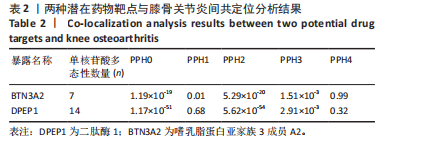
进行校正,校正后的显著性阈值设定为0.05。结果提示经过错误发现率校正后,仅余3个潜在药物靶点,其中正向因果关系有2个,反向因果关系有1个,分别为二肽酶1(Dipeptidase 1,DPEP1)(OR=1.03,95%CI:1.02-1.05)、嗜乳脂蛋白亚家族3成员A2 (Butyrophilin Subfamily 3 Member A2,BTN3A2)(OR=0.95,95%CI:0.93-0.97)、人类白细胞抗原A (Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I-A,HLA-A) (OR=0.95,95%CI:0.93-0.97),见图3。 2.3 敏感性分析 对以上经过错误发现率校正后的孟德尔随机化结果进行多效性检验,结果发现其中HLA-A的MR-PRESSO多效性P < 0.05,提示存在多效性,需排除该潜在药物靶点;DPEP1和BTN3A2与膝骨关节炎间不存在多效性。采用Cochrane’s Q 检验余下2个潜在药物靶点与膝骨关节炎间是否存在异质性。结果提示DPEP1不存在异质性,但BTN3A2与膝骨关节炎间存在一定的异质性,但其逆方差加权法结果提示BTN3A2与膝骨关节炎间具有显著的因果关系,故可认为结果的可靠性不受影响。最终,经敏感性分析可知,仅余DPEP1和BTN3A2可作为膝骨关节炎的潜在药物靶点。见图4,5。 2.4 共定位分析 将DPEP1和BTN3A2这2种潜在药物靶点与膝骨关节炎进行共定位分析,以共享因果变异的概率,见表2。结果提示仅BTN3A2的PPH4值大于0.80,以上表明膝骨关节炎和BTN3A2共享一个因果变异。因此,基于共定位分析,BTN3A2被确定为膝骨关节炎新型药物研发或防治的关键药物靶点。"
| [1] URITANI D, KODA H, YASUURA Y, et al. Factors associated with subjective knee joint stiffness in people with knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Int J Rheum Dis. 2023;26(3):425-436. [2] LONG H, LIU Q, YIN H, et al. Prevalence trends of site-specific osteoarthritis from 1990 to 2019: Findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74(7):1172-1183. [3] DI JK, BAI J, ZHANG JR, et al. Regional disparities, age-related changes and sex-related differences in knee osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):66. [4] SHAO W, HOU H, HAN Q, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional survey in Nanjing, China. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1441408. [5] BIJLSMA JW, BERENBAUM F, LAFEBER FP. Osteoarthritis: an update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet. 2011;377(9783):2115-2126. [6] WANG ST, NI GX. Depression in Osteoarthritis: Current Understanding. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022;18:375-389. [7] GBD 2021 OSTEOARTHRITIS COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national burden of osteoarthritis, 1990-2020 and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5(9):e508-e522. [8] ZENG C, DOHERTY M, PERSSON MSM, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of acetaminophen, topical and oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for knee osteoarthritis: evidence from a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and real-world data. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(9):1242-1251. [9] ZENG F, WANG K, DUAN H, et al. Diacerein versus non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):308. [10] STACEY SK, MCELENEY M. Topical corticosteroids: choice and application. Am Fam Physician. 2021;103(6):337-343. [11] RABADE A, VISWANATHA GL, NANDAKUMAR K, et al. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of glucosamine sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, and their combination regimen in the management of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflammopharmacology. 2024;32(3):1759-1775. [12] DAVIES NM, HOLMES MV, DAVEY SMITH GD. Reading mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ. 2018;362(12):k601. [13] BURGESS S, SCOTT RA, TIMPSON NJ, et al. Using published data in Mendelian randomization: a blueprint for efficient identification of causal risk factors. Eur J Epidemiol. 2015;30(7):543-552. [14] SANDERSON E, GLYMOUR MM, HOLMES MV, et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat Rev Method Prim. 2022;2(1):6. [15] ZOU MR, SHAO ZX. Proteome-wide Mendelian randomization and colocalization analysis identify therapeutic targets for knee and hip osteoarthritis. Biomolecules. 2024;14(3):355. [16] WANG YZ, SHEN HB. Challenges and factors that influencing causal inference and interpretation, based on Mendelian randomization studies. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41(8):1231-1236. [17] LEVIN MG, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization as a tool for cardiovascular research: A review. JAMA Cardiol. 2024;9(1):79-89. [18] LIU CY, YANG YS, PEI MQ, et al. Mendelian randomization analysis reveals causal association of anthropometric measures on sepsis risk and mortality. PLoS One. 2024;19(9):e0310898. [19] LIN LJ, WEI YY, ZHANG RY, et al. Application of Mendelian randomization methods in causal inference of observational study. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019;53(6):619-624. [20] LIU HH, JIANG X, DENG GH, et al. Mendelian randomization analysis of the causal relationship between asthma, allergic rhinitis, and chronic sinusitis. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024; 59(8):820-827. [21] MINELLI C, DEL GRECO MF, VAN DER PLAAT DA, et al. The use of two-sample methods for Mendelian randomization analyses on single large datasets. Int J Epidemiol. 2021;50(5):1651-1659. [22] JIANG X, ALFREDSSON L. Modifiable environmental exposure and risk of rheumatoid arthritis-current evidence from genetic studies. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;22(1):154. [23] KURKI MI, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. Author correction: FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature. 2023;615(7952):e19. [24] KURKI MI, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature. 2023; 613(7944):508-518. [25] TACHMAZIDOU I, HATZIKOTOULAS K, SOUTHAM L, et al. Identification of new therapeutic targets for osteoarthritis through genome-wide analyses of UK Biobank data. Nat Genet. 2019;51(2):230-236. [26] CEREZO M, SOLLIS E, JI Y, et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog: standards for reusability, sustainability and diversity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024;2024.10.23.619767 [27] VÕSA U, CLARINGBOULD A, WESTRA HJ, et al. Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression. Nat Genet. 2021;53(9):1300-1310. [28] KINTU C, SOREMEKUN O, KAMIZA AB, et al. The causal effects of lipid traits on kidney function in Africans: bidirectional and multivariable Mendelian-randomization study. EBioMedicine. 2023;90:104537. [29] BULL CJ, HAZELWOOD E, LEGGE DN, et al. Impact of weight loss on cancer-related proteins in serum: results from a cluster randomised controlled trial of individuals with type 2 diabetes. EBioMedicine. 2024;100:104977. [30] BURGESS S, DUDBRIDGE F, THOMPSON SG. Combining information on multiple instrumental variables in Mendelian randomization: comparison of allele score and summarized data methods. Stat Med. 2016;35(11):1880-1906. [31] HEMANI G, BOWDEN J, SMITH GD. Evaluating the potential role of pleiotropy in Mendelian randomization studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27(R2): R195-R208. [32] GIAMBARTOLOMEI C, VUKCEVIC D, SCHADT EE, et al. Bayesian test for colocalisation between pairs of genetic association studies using summary statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(5):e1004383. [33] CHEN SH, LI ZY, HUANG WY, et al. Prognostic and Therapeutic Significance of BTN3A Proteins in Tumors. J Cancer. 2021;12(15):4505-4512. [34] RHODES DA, CHEN HC, PRICE AJ, et al. Activation of human γδ T cells by cytosolic interactions of BTN3A1 with soluble phosphoantigens and the cytoskeletal adaptor periplakin. J Immunol. 2015;194(5):2390-2398. [35] YU HL, MI CH, WANG Q, et al. Long noncoding RNA profiling reveals that LncRNA BTN3A2 inhibits the host inflammatory response to Eimeria tenella infection in chickens. Front Immunol. 2022;13:891001. [36] GALLO J, RASKA M, KRIEGOVA E, et al. Inflammation and its resolution and the musculoskeletal system. J Orthop Transl. 2017;10:52-67. [37] REN H, LI SL, LIU X, et al. Multi-omics analysis of the expression and prognostic value of the butyrophilins in breast cancer. J Leukoc Biol. 2021;110(6):1181-1195. [38] LIU BH, WANG XY, YANG ZR, et al. A genetic study to identify pathogenic mechanisms and drug targets for benign prostatic hyperplasia: a multi-omics Mendelian randomization study. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):23120. [39] DIKIY S, RUDENSKY AY. Principles of regulatory T cell function. Immunity. 2023;56(2):240-255. [40] HAN S. Osteoarthritis year in review 2022: biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(12):1575-1582. [41] CAI PA, LU ZH, WU JJ, et al. BTN3A2 serves as a prognostic marker and favors immune infiltration in triple-negative breast cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(3):2643-2654. [42] YANG K, XU JJ, FAN M, et al. Lactate suppresses macrophage pro-inflammatory response to LPS stimulation by inhibition of YAP and NF-κB activation via GPR81-mediated signaling. Front Immunol. 2020;11: 587913. [43] YE QY, XU HK, LIU SY, et al. Apoptotic extracellular vesicles alleviate Pg-LPS induced inflammatory responses of macrophages via AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB pathway and inhibit osteoclast formation. J Periodont. 2022;93(11):1738-1751. [44] LIN YS, ZHOU H, LI SJ. BTN3A2 expression Is connected with favorable prognosis and high infiltrating immune in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Genet. 2022;13:848476. [45] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440. [46] ZHAO K, RUAN JQ, NIE LY, et al. Effects of synovial macrophages in osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1164137. [47] MEHANA ESE, KHAFAGA AF, EL-BLEHI SS. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: An updated review. Life Sci. 2019;234:116786. [48] RAMSEWAK RS, DEWITT DL, NAIR MG. Cytotoxicity, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of curcumins I-III from curcuma longa. Phytomedicine. 2000;7(4):303-308. [49] SI SC, LIU HY, XU L, et al. Identification of novel therapeutic targets for chronic kidney disease and kidney function by integrating multi-omics proteome with transcriptome. Genome Med. 2024;16(1):84. [50] ZENG C, WEI J, PERSSON MSM, et al. Relative efficacy and safety of topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials and observational studies. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(10):642-650. [51] AFRACHE H, PONTAROTTI P, ABI-RACHED L, et al. Evolutionary and polymorphism analyses reveal the central role of BTN3A2 in the concerted evolution of the BTN3 gene family. Immunogenetics. 2017; 69(6):379-390. [52] CAO JX, WANG YL, WANG ZX. Advances in precise regulation of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology. Yi Chuan. 2020;42(12):1168-1177. |
| [1] | Chen Qiuhan, Yang Long, Yuan Daizhu, Wu Zhanyu, Zou Zihao, Ye Chuan. Peri-knee osteotomy for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: optimization of treatment strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2303-2312. |
| [2] | Li Linzhen, Jiao Hongzhuo, Chen Weinan, Zhang Mingzhe, Wang Jianlong, Zhang Juntao. Effect of icariin-containing serum on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory damage in human chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [4] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [5] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [6] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [7] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [8] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| [9] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [10] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [11] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [12] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [13] | Gu Fucheng, Yang Meixin, Wu Weixin, Cai Weijun, Qin Yangyi, Sun Mingyi, Sun Jian, Geng Qiudong, Li Nan. Effects of Guilu Erxian Glue on gut microbiota in rats with knee osteoarthritis: machine learning and 16S rDNA analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1058-1072. |
| [14] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [15] | Liu Chu, Qiu Boyuan, Tong Siwen, He Linyuwei, Chen Haobo, Ou Zhixue. A genetic perspective reveals the relationship between blood metabolites and osteonecrosis: an analysis of information from the FinnGen database in Finland [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 785-794. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||