Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (15): 3801-3809.doi: 10.12307/2026.684
Previous Articles Next Articles
Fully visualized foraminoscopy for treating lumbar intervertebral space infection: finite element analysis of spinal stability
Zhang Junhui, Chen Jinxu, Liang Zhuoxian, Deng Deli, Liu Jun
- Panyu Central Hospital Affiliated to Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 511400, Guangdong Province, China
-
Accepted:2025-06-27Online:2026-05-28Published:2025-11-05 -
Contact:Liu Jun, Associate chief physician, Panyu Central Hospital Affiliated to Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 511400, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Junhui, MS, Attending physician, Panyu Central Hospital Affiliated to Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 511400, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Panyu District Health and Family Planning Bureau, Panyu District Science, Technology, Industry, Commerce, and Information Technology Bureau - 2022 Panyu District Science and Technology Plan - General Medical and Health Project - Clinical Medicine Research, No. 2022-Z04-041 (to ZJH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Junhui, Chen Jinxu, Liang Zhuoxian, Deng Deli, Liu Jun. Fully visualized foraminoscopy for treating lumbar intervertebral space infection: finite element analysis of spinal stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(15): 3801-3809.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
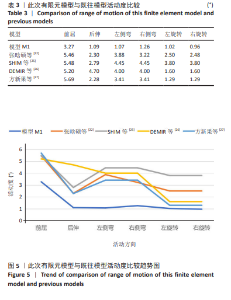
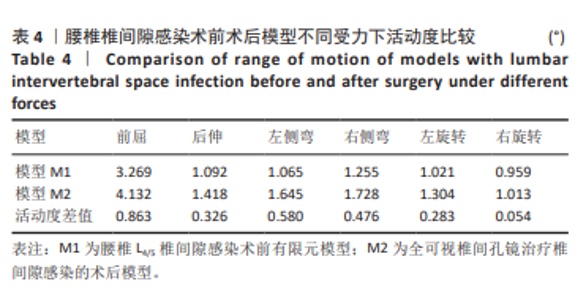
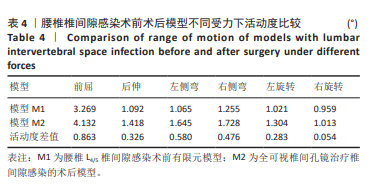
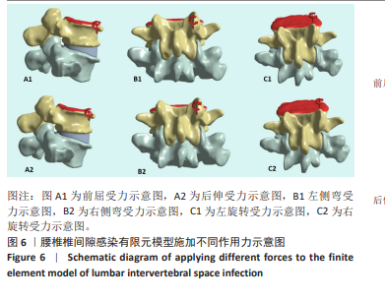
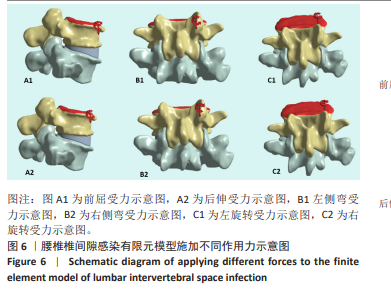
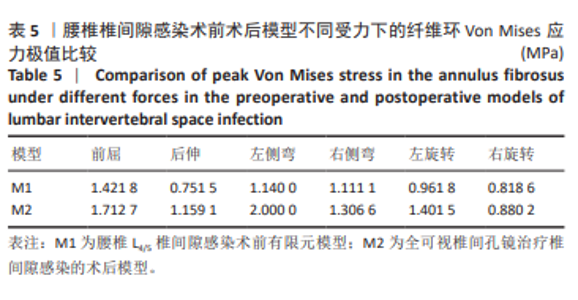
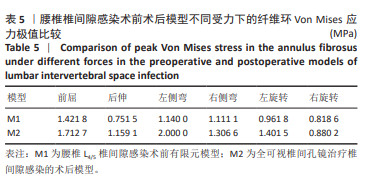
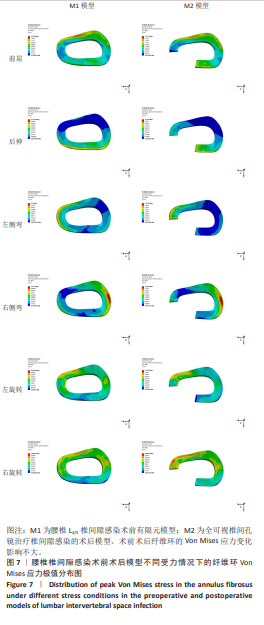
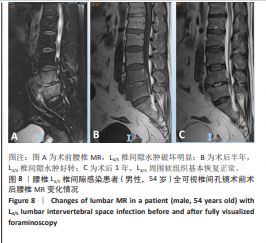
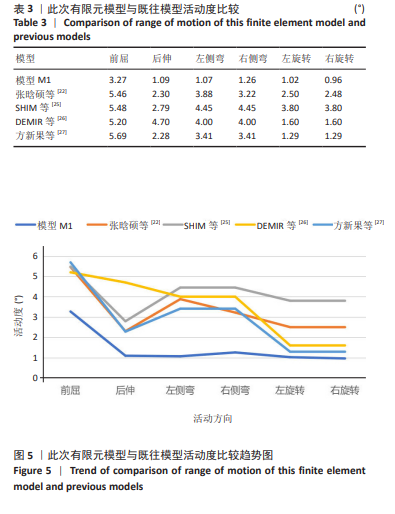
2.1 模型有效性验证 正常的对比模型建立后需要完成有效性验证,因纳入的患者并非正常模型,是腰椎椎间隙感染术前模型,在模型验证上对比正常模型而言,主要参考正常模型的活动度及变化趋势作为主要参考依据。常用的方法是将 L5下表面设置固定支撑限制其活动,在L4上表面均匀施加 500 N垂直轴向载荷,附加10 Nm力矩[23-24],通过调整X轴、Y轴、Z轴各分量数值,模拟前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋转、右旋转6种生理状态下的腰椎运动情况。此次研究对象是腰椎椎间隙感染患者,椎间隙丢失、周围骨赘增生稍明显。通过与既往SHIM等[25]、DEMIR等[26]、方新果等[27]、张晗硕等[22]的实体及有限元模型的生物力学分析结果对比,发现此次实验所建立的完整模型 M1,在前屈、后伸、左侧弯、右侧弯、左旋转、右旋转6种情况下的 L4/L5 活动度值与参考文献的数值相比,各种活动度均小于10°[28],趋势变化不大,各方向活动度均低于均值,仿真性较好,可应用于此次研究,具体结果见表3,图5。"
| [1] POLA E, LOGROSCINO CA, GENTIEMPO M, et al. Medical and surgical treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012;16 Suppl 2:35-49. [2] MADELAR RTR, ITO M. The Need for Comprehensive Medical Management in Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis: A Review Article. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2023;8(3):243-252. [3] YAW TEE LY, HUNTER S, BAKER JF. BMP use in the surgical treatment of pyogenic spondylodiscitis: Is it safe. J Clin Neurosci. 2022;95:94-98. [4] SKAF GS, DOMLOJ NT, FEHLINGS MG, et al. Pyogenic spondylodiscitis: an overview. J Infect Public Health. 2010;3(1):5-16. [5] ZARAJCZYK A, PONIEWOZIK P, FIDUT N, et al. Spondylodiscitis - a silent infection with loud consequences. Wiad Lek. 2025;78(3):651-656. [6] ZARGHOONI K, RÖLLINGHOFF M, SOBOTTKE R, et al. Treatment of spondylodiscitis. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):405-411. [7] KARADIMAS EJ, BUNGER C, LINDBLAD BE, et al. Spondylodiscitis. A retrospective study of 163 patients. Acta Orthop. 2008;79(5):650-659. [8] THAVARAJASINGAM SG, VEMULAPALLI KV, VISHNU KS, et al. Conservative versus early surgical treatment in the management of pyogenic spondylodiscitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):15647. [9] LIU Y, WU T, TAN J, et al. Minimally Invasive versus Traditional Surgery: Efficacy of PELD and PLIF in Treating Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis. Med Sci Monit. 2024;30:e943176. [10] WEI X, CHEN F, YU C, et al. Effectiveness of lumbar braces after lumbar surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024;144(4):1523-1533. [11] KANG TW, PARK SY, OH H, et al. Risk of reoperation and infection after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy and open lumbar discectomy : a nationwide population-based study. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(8):1392-1399. [12] WANG D, WEN J, XUE W, et al. [Channel-assisted minimally invasive interbody fusion and short segmental vertebral fixation for the treatment of non-specific lumbar intervertebral infection]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020;33(9):848-852. [13] YAMADA K, TAKAHATA M, NAGAHAMA K, et al. Posterolateral full-endoscopic debridement and irrigation is effective in treating thoraco-lumbar pyogenic spondylodiscitis, except in cases with large abscess cavities. Eur Spine J. 2023;32(3):859-866. [14] SCHATLO B, ROHDE V, ABBOUD T, et al. The Role of Diskectomy in Reducing Infectious Complications after Surgery for Lumbar Spondylodiscitis. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2023;84(1):3-7. [15] 黄群,朱现玮,严飞,等.经皮椎间孔镜下病灶清除治疗腰椎间隙感染的疗效分析[J].骨科,2022,13(2):97-101. [16] 陈志达,宋超,林斌,等.斜外侧椎间融合术治疗单节段非特异性腰椎间隙感染的临床疗效分析[J].骨科,2022,13(2):102-109. [17] WU Z, SUN H, ZHANG Y, et al. Biomechanical Finite Element Analysis of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy via a Transforaminal Approach. World Neurosurg. 2024;185:e291-e298. [18] 史经甫,吴东迎,袁峰,等.椎间孔镜术中行关节突成形有限元模型的建立及生物力学分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2023,44(6):912-916. [19] SUN W, LI D, ZHAO S, et al. The effect of large channel-based foraminoplasty on lumbar biomechanics in percutaneous endoscopic discectomy: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):402. [20] CAO L, LIU Y, MEI W, et al. Biomechanical changes of degenerated adjacent segment and intact lumbar spine after lumbosacral topping-off surgery: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):104. [21] SHI Y, XIE YZ, ZHOU Q, et al. The biomechanical effect of the relevant segments after facet-disectomy in different diameters under posterior lumbar percutaneous endoscopes: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):593. [22] 张晗硕,丁宇,蒋强,等.脊柱内镜下椎板开窗减压与单侧入路双侧减压治疗腰椎管狭窄症的生物力学稳定性及有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(13):1981-1986. [23] THEODOROU S, THEODOROU D, KAKITSUBATA Y, et al. Advanced ankylosing spondylitis: a multisite, multimodality densitometric analysis for investigation of bone loss in the axial and appendicular skeleton. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2021;67(11):1627-1632. [24] KIM AS, TAYLOR VE, CASTRO-MARTINEZ A, et al. Early and multiple doses of zoledronate mitigates rebound bone loss following withdrawal of RANKL inhibition. J Bone Miner Res. 2025;40(3):413-427. [25] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al.Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(22):E820-827. [26] DEMIR E, ELTES P, CASTRO AP, et al.Finite element modelling of hybrid stabilization systems for the human lumbar spine. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2020;234(12):1409-1420. [27] 方新果,赵改平,王晨曦,等.基于CT图像腰椎L4-L5节段有限元模型建立与分析[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2014,31(4):487-492. [28] DING Y, ZHANG H, JIANG Q, et al. Finite element analysis of endoscopic cross-overtop decompression for single-segment lumbar spinal stenosis based on real clinical cases. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1393005. [29] FAROOQI AS, NARAYANAN R, CANSECO JA, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Corticopedicular Spine Fixation versus Pedicle Screw Fixation in a Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Finite Element Analysis Model. World Neurosurg. 2024;190:e129-e136. [30] LIU C, KAMARA A, YAN Y. Investigation into the biomechanics of lumbar spine micro-dynamic pedicle screw. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018; 19(1):231. [31] RANA M, ROY S, BISWAS P, et al. Design and development of a novel expanding flexible rod device (FRD) for stability in the lumbar spine: A finite-element study. Int J Artif Organs. 2020;43(12):803-810. [32] WEI W, WANG T, LIU J, et al. Biomechanical effect of proximal multifidus injury on adjacent segments during posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):521. [33] 陈树东,李永津,杜炎鑫,等.经皮内镜病灶清除及灌洗引流治疗腰椎间隙感染15例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(8):59-62. [34] LAWSON MCLEAN A, SENFT C, SCHWARZ F. Management of Lumbar Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis in Germany: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Spine Specialists. World Neurosurg. 2023;173:e663-e668. [35] CHEN ZH, WANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Debridement and Drainage with Accurate Pathogen Detection for Infectious Spondylitis of the Thoracolumbar and Lumbar Spine. World Neurosurg. 2022;164:e1179-e1189. [36] LI Z, HE M, CHEN X, et al. Single-stage posterior resection of the transversal process combined with an intervertebral foraminal approach for debridement, interbody fusion, internal fixation for the treatment of lumbar tuberculosis and psoas major abscess. Int Orthop. 2022;46(2):331-339. [37] YEUNG AT. Minimally Invasive Disc Surgery with the Yeung Endoscopic Spine System (YESS). Surg Technol Int. 1999;8:267-277. [38] ITO M, ABUMI K, KOTANI Y, et al. Clinical outcome of posterolateral endoscopic surgery for pyogenic spondylodiscitis: results of 15 patients with serious comorbid conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(2):200-206. [39] LIM JS, KIM TH. Recurrence Rates and Its Associated Factors after Early Spinal Instrumentation for Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis: A Nationwide Cohort Study of 2148 Patients. J Clin Med. 2022;11(12):3356. [40] FAROOQI AS, NARAYANAN R, CANSECO JA, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Corticopedicular Spine Fixation versus Pedicle Screw Fixation in a Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis Finite Element Analysis Model. World Neurosurg. 2024;190:e129-e136. [41] MIYASAKA K, OHMORI K, SUZUKI K, et al. Radiographic analysis of lumbar motion in relation to lumbosacral stability. Investigation of moderate and maximum motion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(6): 732-737. [42] LI L, SHEN T, LI YK. A Finite Element Analysis of Stress Distribution and Disk Displacement in Response to Lumbar Rotation Manipulation in the Sitting and Side-Lying Positions. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2017;40(8):580-586. |
| [1] | Liu Wenlong, Dong Lei, Xiao Zhengzheng, Nie Yu. Finite element analysis of tibial prosthesis loosening after fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [2] | Zheng Wangyang, Fei Ji, Yang Di, Zhao Lang, Wang Lingli, Liu Peng, Li Haiyang. Finite element analysis of the force changes of the supraspinatus tendon and glenohumeral joint during the abduction and flexion of the humerus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2199-2207. |
| [3] | Cai Qirui, Dai Xiaowei, Zheng Xiaobin, Jian Sili, Lu Shaoping, Liu Texi, Liu Guoke, Lin Yuanfang. Mechanical effects of Long’s traction orthopedic method on cervical functional units: quantitative analysis of biomechanical model of head and neck [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2208-2216. |
| [4] | Rao Jingcheng, Li Yuwan, Zheng Hongbing, Xu Zhi, Zhu Aixiang, Shi Ce, Wang Bing, Yang Chun, Kong Xiangru, Zhu Dawei. Biomechanical differences between the new proximal femoral stable intramedullary nail and traditional intramedullary nail#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2217-2225. |
| [5] | Chen Long, Wang Xiaozhen, Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin. Biomechanical performance of short-segment screw fixation combined with expandable polyetheretherketone vertebral body replacement in osteoporotic vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [6] | Yan Xiangning, Chen Lei, Chen Yonghuan, Wang Chao, Li Xiaosheng. Influence of different depths and loads on knee joint mechanics and peripheral muscle force characteristics during squatting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2236-2247. |
| [7] | Zhang Zizheng, Luo Wang, Liu Changlu. Application value of finite element analysis on unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for medial knee compartmental osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2313-2322. |
| [8] | Zhang Xianxu, Ma Zhong, Liu Xin, Huang Lei, Shen Wenxiang, Luo Zhiqiang . Lumbar fusion combined with unilateral fixation for lumbar degenerative diseases: biomechanics, technical evolution, and clinical applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2334-2342. |
| [9] | Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming. Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [10] | Zeng Xuan, Weng Rui, Ye Shicheng, Tang Jiadong, Mo Ling, Li Wenchao. Two lumbar rotary manipulation techniques in treating lumbar disc herniation: a finite element analysis of biomechanical differences [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [11] | Cheng Qisheng, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xiao Yang, Zhang Chenwei, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [12] | Wu Hongxu, Liu Xuanyu, Wang Taoyu, Wang Shiyao, Cheng Jingyi, Zhang Mingwen, Zhang Yinxia, Liu Zhihua, Wang Xiaojie. Finite element simulation of scoliosis with muscle unit introduction: verification of correction effect under bidirectional load [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2172-2181. |
| [13] | Liu Jiafu, Ren Ruxia, Liao Zhouwei, Zhou Xiali, Wu Yihong, Zhang Shaoqun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cervical spine biomechanical characteristics in a rat model of cervical vertigo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2182-2190. |
| [14] | Zhou Daobin, Wang Kehao, Xie Yang, Ning Rende. Biomechanical characteristics of volar locking plate only versus combined dorsal mini-plate fixation of distal radius fractures with dorsal ulnar fragment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2255-2261. |
| [15] | Zhang Nan, Meng Qinghua, Bao Chunyu. Characteristics and clinical application of ankle joint finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2343-2349. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||