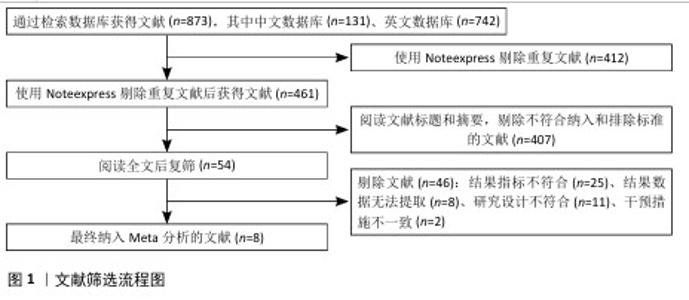
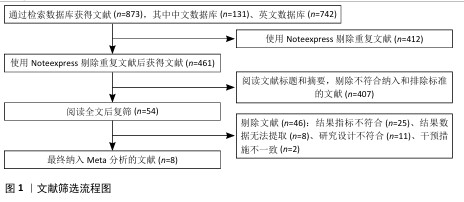
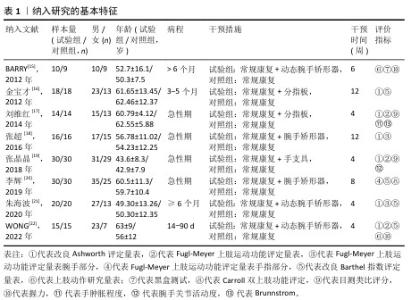
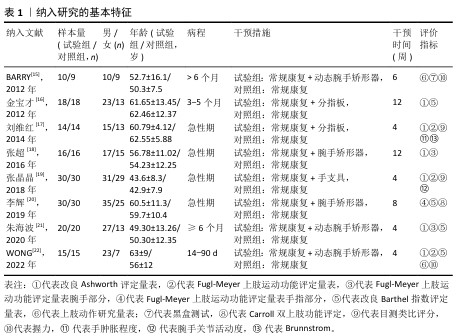
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 2124-2131.doi: 10.12307/2026.588
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of wrist-hand orthosis on hand dysfunction in stroke patients: a meta-analysis
Gao Feng1, Zhang Jun1, Yu Wenjun2, Chanyu Yujing2, Zhao Le1, Hu Yuting1, Wang Junhua1, Liu Yongfu1
- 1Shiyan Taihe Hospital (Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Medicine), Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China; 2Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2025-01-03Accepted:2025-03-14Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-29 -
Contact:Liu Yongfu, MS, Therapist-in-charge, Shiyan Taihe Hospital (Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Medicine), Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Gao Feng, MS, Associate professor, Shiyan Taihe Hospital (Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Medicine), Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:Advantages Discipline Group (Medicine) Project in Higher Education of Hubei Province during the “14th Five-Year Plan” Period, No. 2022XKQT1 (to WJH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Feng, Zhang Jun, Yu Wenjun, Chanyu Yujing, Zhao Le, Hu Yuting, Wang Junhua, Liu Yongfu. Effects of wrist-hand orthosis on hand dysfunction in stroke patients: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2124-2131.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
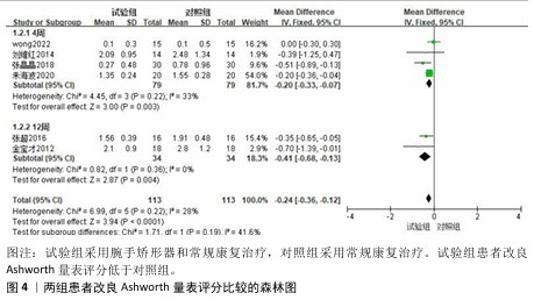
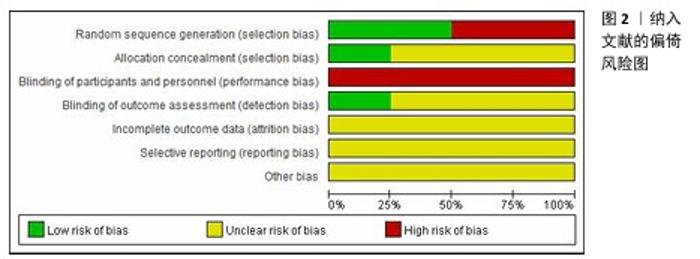
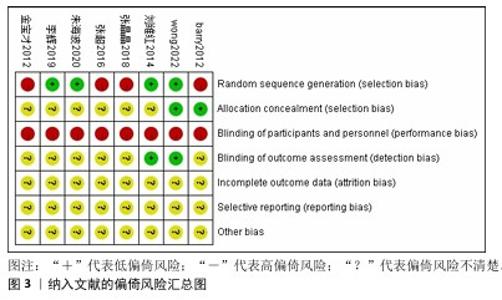
2.3 Meta分析结果 2.3.1 改良Ashworth量表 共有6篇文献采用改良Ashworth量表评估脑卒中后手功能障碍患者的腕手关节肌张力[16-19,21-22],包括226例患者。各研究间异质性较低(P=0.22,I2=28%),采用固定效应模型进行分析。Meta分析结果显示,试验组改良Ashworth量表评分低于对照组[MD=-0.24,95%CI(-0.36,-0.12),P < 0.000 1];以干预时间进行亚组分析,结果显示试验组干预4,12周的改良Ashworth评分均低于对照组[干预4周:MD=-0.20,95%CI(-0.33,-0.07),P=0.003;干预12周:MD=-0.41,95%CI(-0.68,-0.13),P=0.004],见图4。"
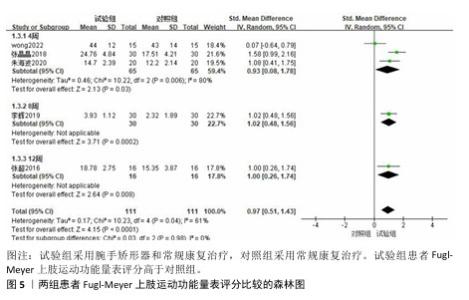
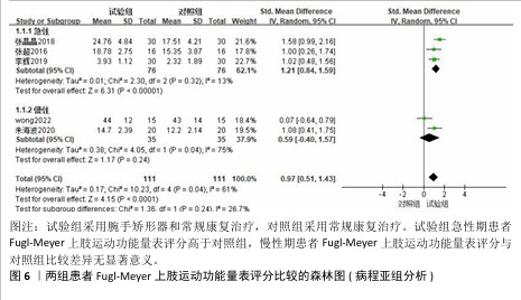
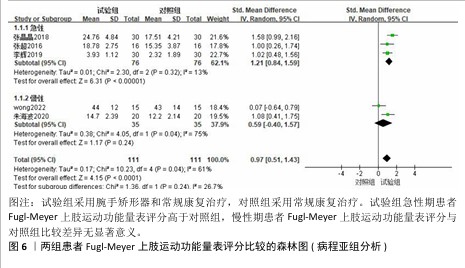
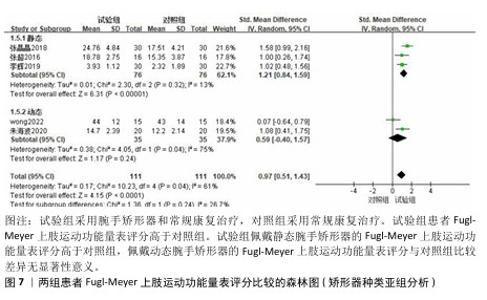
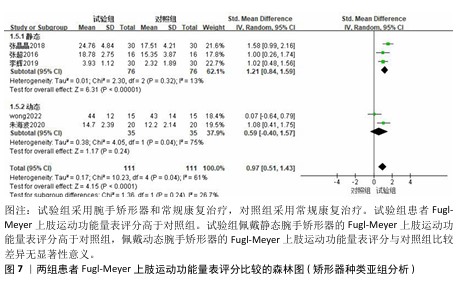
2.3.2 Fugl-Meyer上肢运动功能量表 共有6篇文献采用Fugl-Meyer上肢运动功能量表评估脑卒中后手功能障碍患者的手运动功能[17-22],包括250例患者。由于不同研究采用Fugl-Meyer上肢运动功能量表的不同部分来进行评价,故采用SMD进行合并。因刘维红[17]数据存疑,将该研究数据剔除后进行计算。各研究间异质性较大(P=0.04,I2=61%),通过逐篇去除文献进行敏感性分析,结果无显著性变化,表明Meta分析结果稳健,采用随机效应模型进行分析。Meta分析结果显示:试验组患者Fugl-Meyer上肢运动功能量表评分高于对照组[SMD=0.97,95%CI(0.51,1.43),P < 0.000 1];以干预时间进行亚组分析,结果显示,试验组干预4,8,12周的Fugl-Meyer上肢运动功能量表评分均高于对照组[干预4周:SMD=0.93,95%CI(0.08,1.78),P=0.03;干预8周:SMD=1.02,95%CI (0.48,1.56),P=0.000 2;干预12周: SMD=1.00,95%CI(0.26,1.74),P= 0.008],见图5。以病程(急性/慢性)进行亚组分析,结果显示,试验组急性期患者Fugl-Meyer上肢运动功能量表评分高于对照组[SMD=1.21,95%CI (0.84,1.59),P < 0.000 01],慢性期患者Fugl-Meyer上肢运动功能量表评分与对照组比较差异无显著意义[SMD=0.59,95%CI(-0.40,1.57),P=0.24],见图6。以矫形器种类(静态/动态)进行亚组分析,结果显示,试验组佩戴静态腕手矫形器的Fugl-Meyer上肢运动功能量表评分高于对照组[SMD=1.21,95%CI(0.84,1.59),P < 0.000 01],佩戴动态腕手矫形器的Fugl-Meyer上肢运动功能量表评分与对照组比较差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.59,95%CI(-0.40,1.57),P= 0.24],见图7。 "
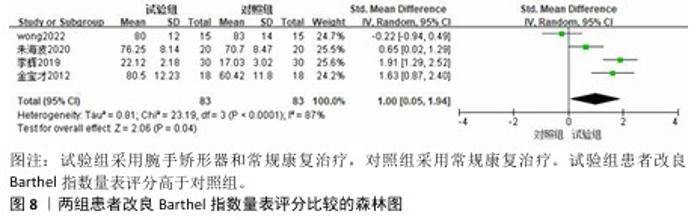
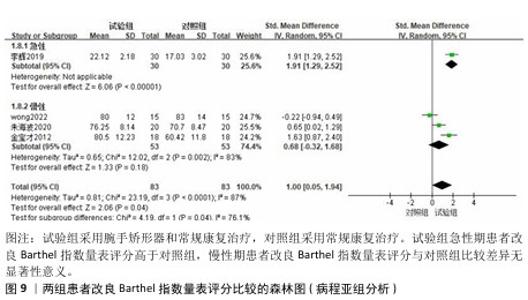
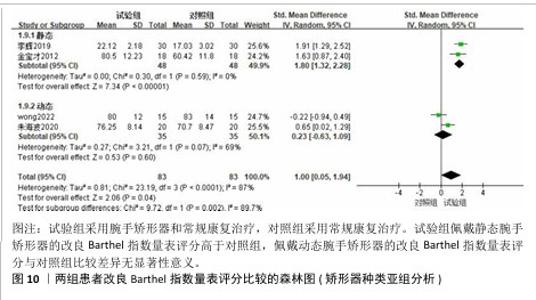
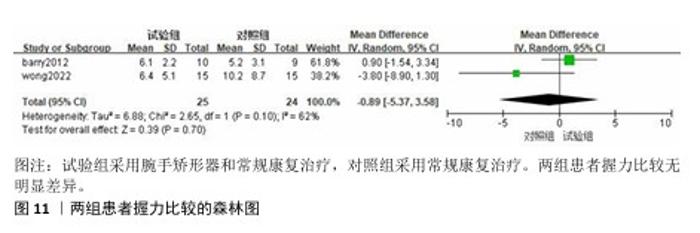
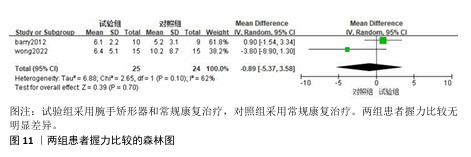
2.3.3 改良Barthel指数量表 共有4篇文献采用改良Barthel指数量表评估脑卒中后手功能障碍患者的日常生活活动能力[16,20-22],包括166例患者。由于不同研究采用改良Barthel指数量表的不同部分来进行评价,故采用SMD进行合并。各研究间异质性较大(P < 0.000 1,I2=87%),采用随机效应模型进行分析。Meta分析结果显示,试验组患者改良Barthel指数量表评分高于对照组[SMD=1.00,95%CI(0.05,1.94),P=0.04],见图8。 以病程(急性/慢性)进行亚组分析,结果显示,试验组急性期患者改良Barthel指数量表评分高于对照组[SMD=1.91,95%CI(1.29,2.52),P < 0.000 01],慢性期患者改良Barthel指数量表评分与对照组比较差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.68,95%CI(-0.32,1.68),P=0.18],见图9。以矫形器种类(静态/动态)进行亚组分析,结果显示,试验组佩戴静态腕手矫形器的改良Barthel指数量表评分高于对照组[SMD=1.80,95%CI(1.32,2.28),P < 0.000 01],佩戴动态腕手矫形器的改良Barthel指数量表评分与对照组比较差异无显著性意义[SMD=0.23,95%CI(-0.63,1.09),P=0.60],见图10。 "
| [1] FEIGIN VL, BRAININ M, NORRVING B, et al. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2022. Int J Stroke. 2022; 17(1):18-29. [2] LAWRENCE ES, COSHALL C, DUNDAS R, et al. Estimates of the prevalence of acute stroke impairments and disability in a multiethnic population. Stroke. 2001;32(6):1279-1284. [3] ARWERT H, SCHUT S, BOITEN J, et al. Patient reported outcomes of hand function three years after stroke. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2018;25(1):13-19. [4] BAGHI R, KIM D, KOH K, et al. Characterization of the influence of the dominant tract on hand closing post stroke based on the Fugl-Meyer score. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):2611. [5] NAM HU, HUH JS, YOO JN, et al. Effect of Dominant Hand Paralysis on Quality of Life in Patients With Subacute Stroke. Ann Rehabil Med. 2014;38(4):450-457. [6] 贾杰.“中枢-外周-中枢”闭环康复:脑卒中后手功能康复新理念[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016,31(11):1180-1182. [7] 贾杰.脑卒中上肢康复:手脑感知与手脑运动[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(4): 385-389. [8] Tang Q, Li G, Liu T, et al. Modulation of interhemispheric activation balance in motor-related areas of stroke patients with motor recovery: Systematic review and meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015:392-400. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.09.003. [9] LANNIN NA, CUSICK A, HILLS C, et al. Upper limb motor training using a Saebo(™) orthosis is feasible for increasing task-specific practice in hospital after stroke. Aust Occup Ther J. 2016;63(6):364-372. [10] GUO Z, ZHOU S, JI K, et al. Corticomuscular integrated representation of voluntary motor effort in robotic control for wrist-hand rehabilitation after stroke. J Neural Eng. 2022;19(2). doi:10.1088/1741-2552/ac5757. [11] 杨名珍,黄崧华,白玉龙.动态腕手矫形器应用于慢性期脑卒中患者上肢及手功能康复的疗效[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(11):1361-1364. [12] ELISABETH B, DANIÈLE K, FINCKH A, et al. Neutral functional realignment orthosis prevents hand pain in patients with subacute stroke: a randomized trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(10):1857-1862. [13] 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南撰写组.中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2010[J]. 中国临床医生,2011,2(3):50-59. [14] CUMPSTON M, LI T, PAGE MJ, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;10(10):ED142. [15] BARRY JG, ROSS SA, WOEHRLE J. Therapy incorporating a dynamic wrist-hand orthosis versus manual assistance in chronic stroke: A pilot study. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2012; 36(1):17-24. [16] 宝金才,陈晁,陈晓亮.分指板结合康复治疗对脑卒中后手指痉挛的影响[J].医药前沿,2012(32):96. [17] 刘维红.手部矫形器分指板对脑卒中早期患者手功能恢复的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2014,36(5):399-400. [18] 张超,刘璇,何斌.前臂掌侧腕手矫形器应用于脑卒中急性期的康复疗效[J].中国康复,2016,31(2):156-157. [19] 张晶晶,任钰,刘玲,等.手休息位支具在脑卒中急性期手功能恢复中的效果研究[J].中国康复,2018, 33(1):71-73. [20] 李辉,史岩,傅建明,等.腕手矫形器对早期脑卒中患者上肢及手功能的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2019,41(2): 148-149. [21] 朱海波,郭艳萍,杨占宇,等.动态腕手矫形器辅助下的动作观察疗法训练对脑卒中患者手功能的影响[J].中华脑科疾病与康复杂志(电子版),2020,10(6):361-364. [22] WONG Y, LI CJ, ADA L, et al. Upper Limb Training with a Dynamic Hand Orthosis in Early Subacute Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Trial. J Rehabil Med. 2022;54:jrm00279. [23] 凌骏麒,蒋留军,白玉龙.腕-手矫形器在脑卒中患者手功能障碍康复治疗中的应用研究进展[J].上海医药,2023, 44(13):48-51+109. [24] KIM T, SALAZAR FAJARDO JC, JANG H, et al. Effect of optimized transcranial direct current stimulation on motor cortex activation in patients with sub-acute or chronic stroke: a study protocol for a single-blinded cross-over randomized control trial. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1328727. [25] YANG Z, QIAO L, HE J, et al. Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with functional electrical stimulation on hand function of stroke: A randomized controlled trial. NeuroRehabilitation. 2022;51(2):283-289. [26] MA ZZ, WU JJ, CAO Z, et al. Motor imagery-based brain-computer interface rehabilitation programs enhance upper extremity performance and cortical activation in stroke patients. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2024;21(1):91. [27] LI Y, LIAN Y, CHEN X, et al. Effect of task-oriented training assisted by force feedback hand rehabilitation robot on finger grasping function in stroke patients with hemiplegia: a randomised controlled trial. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2024;21(1):77. [28] PETERS HT, PAGE SJ, PERSCH A. Giving Them a Hand: Wearing a Myoelectric Elbow-Wrist-Hand Orthosis Reduces Upper Extremity Impairment in Chronic Stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;98(9):1821-1827. [29] WONG Y, ADA L, MÅNUM G, et al. Upper limb practice with a dynamic hand orthosis to improve arm and hand function in people after stroke: a feasibility study. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2023;9(1):132. [30] CHOO YJ, BOUDIER-REVÉRET M, CHANG MC. 3D printing technology applied to orthosis manufacturing: narrative review. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9(6):4262-4270. [31] BADINI S, REGONDI S, LAMMI C, et al. Computational Mechanics of Form-Fitting 3D-Printed Lattice-Based Wrist-Hand Orthosis for Motor Neuron Disease. Biomedicines. 2023;11(7):1787. [32] SAHOO S, MOHANTY RK, MOHAPATRA J, et al. Efficacy of extension wrist hand orthosis on pain, grip strength and electromyographic activities in lateral epicondylitis: A randomized single-blind clinical trial. J Hand Ther. 2023;36(4):796-804. [33] WINDT J, AKKERMAN W, HOFSTRA M, et al. Reduced pain and improved daily activities for individuals with hand osteoarthritis using a silicone wrist hand orthosis. J Hand Ther. 2023;36(3):669-677. [34] TAN X, CHEN W, CAO J, et al. A preliminary study to identify data needs for improving fit of hand and wrist orthosis using verbal protocol analysis. Ergonomics. 2021;64(2): 259-272 [35] MOHAMMED MEERAN RA, DURAIRAJ V, SEKARAN P, et al. Assistive technologies, including orthotic devices, for the management of contractures in adults after a stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024;9(9):CD010779. [36] LEDOUX ED, KUMAR NS, BARTH EJ. Design, modeling, and preliminary evaluation of a simple wrist-hand stretching orthosis for neurologically impaired patients. Wearable Technol. 2024;5:e19. [37] LANGER D, HORWITZ A, MELCHIOR H, et al. Understanding the implications of hand impairments in light of the International Classification of Function model. J Hand Ther. 2025;38(1):122-128. [38] ISRAELY S, LEISMAN G, CARMELI E. Improvement in arm and hand function after a stroke with task-oriented training. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017:bcr2017219250. [39] HAYWARD KS, BERNHARDT J. Aspiring to restore arm and hand function after stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(6):464-465. [40] MAREK K, OLEJNICZAK A, MILLER E, et al. Novel Robotic Balloon-Based Device for Wrist-Extension Therapy of Hemiparesis Stroke Patients. Sensors (Basel). 2025; 25(5):1360. [41] 黄崧华,凌骏麒,高天昊,等.动态腕手矫形器结合改良强制性运动疗法对脑卒中偏瘫患者上肢和手功能障碍的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2024,30(5):606-612. [42] 龙耀斌.配戴腕手矫形器进行爬行训练对脑卒中患者偏瘫上肢功能的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2007,29(5): 331-333. [43] BOHANNON RW, SMITH MB. Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys Ther. 1987;67(2): 206-207. |
| [1] | Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing. Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090. |
| [2] | Zheng Yin, Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Cheng, Ruan Kexin, Gang Xiaolin, Ji Hong. Safety and efficacy of immunoadsorption therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [3] | Chen Qiang, Wu Wenjuan, Jiang Shuhua, Huang Da. Physical exercise improves physical function in burn patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1269-1281. |
| [4] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Zhao Yuxin, Liu Xihua. Effects of different neuromodulatory stimulation modalities on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [5] | Wen Xiaolong, Weng Xiquan, Feng Yao, Cao Wenyan, Liu Yuqian, Wang Haitao. Effects of inflammation on serum hepcidin and iron metabolism related parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
| [6] | Jiang Yang, Peng Hao, Song Yanping, Yao Na, Song Yueyu, Yin Xingxiao, Li Yanqi, Chen Qigang. Isometric exercise reduces resting blood pressure: a meta-analysis of moderating factors and dose effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 975-986. |
| [7] | Li Hanyue, Li Yini, Xiang Linmei, Li Sen. Effects of resistance exercise therapy on pain and function in patients with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 987-996. |
| [8] | Sun Jiahe, Shi Jipeng, Zhu Tianrui, Quan Helong, Xu Hongqi. Effect of exercise intervention in elderly individuals with sarcopenia and its comorbidities: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 997-1007. |
| [9] | Yang Yuanyuan, Zhou Shanshan, Cheng Xiaofei, Feng Luye, Tang Jiqin. Network meta-analysis of non-invasive brain stimulation in the treatment of lower limb motor dysfunction after stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1008-1018. |
| [10] | Yang Peng, Xu Chenghan, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie, Li Lin, Shi Jinyu. A meta-analysis of risk factors for residual back pain after vertebral augmentation for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 731-739. |
| [11] | Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing. Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-10. |
| [12] | Zhang Xinxin, Gao Ke, Xie Shidong, Tuo Haowen, Jing Feiyue, Liu Weiguo. Network meta-analysis of non-surgical treatments for foot and ankle ability and dynamic balance in patients with chronic ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1931-1944. |
| [13] | Sun Yundi, Cheng Lulu, Wan Haili, Chang Ying, Xiong Wenjuan, Xia Yuan. Effect of neuromuscular exercise for knee osteoarthritis pain and function: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [14] | Wang Yida, Liu Jun, Wang Xiaoling, Wang Liyan, Yang Chengru, Zhang Xuexiao. Effects of wearable electronic device-based interventions on physical activity and sedentary behavior in healthy adolescents: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1693-1704. |
| [15] | Zhang Zixian, Xu Youliang, Wu Shaokui, Wang Xiangying. Effects of blood flow restriction training combined with resistance training on muscle indicators in college athletes: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1705-1713. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||