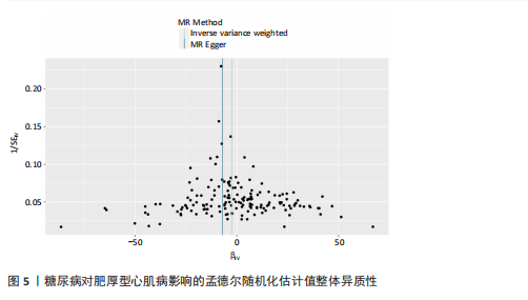
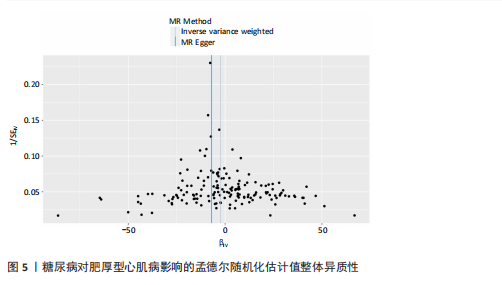
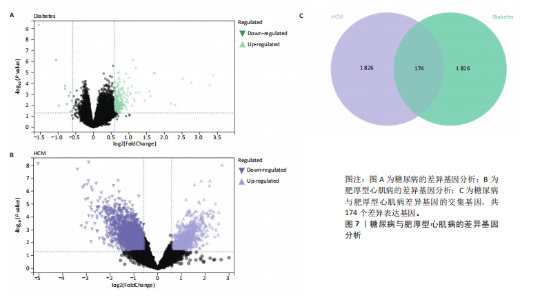
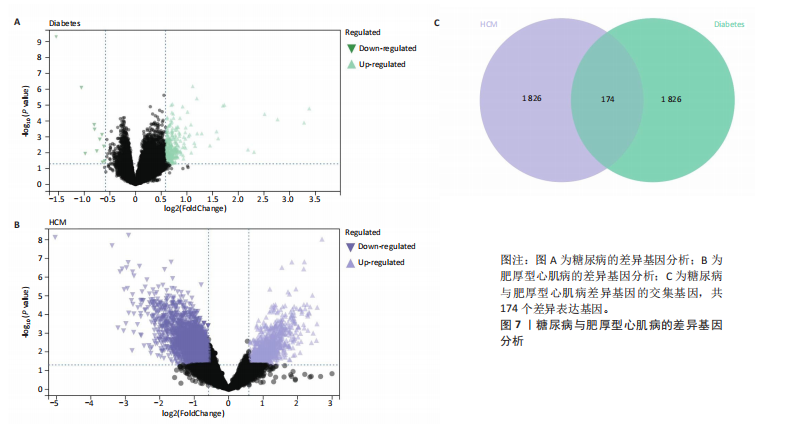
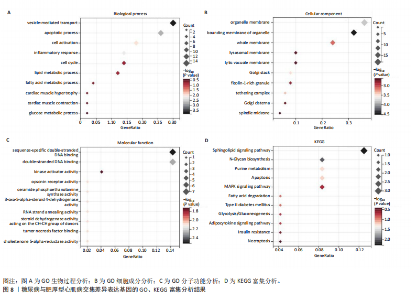
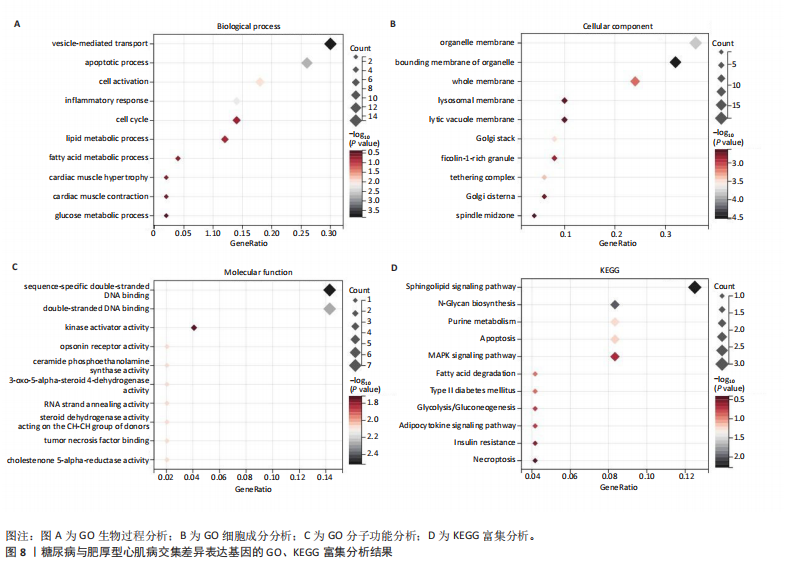
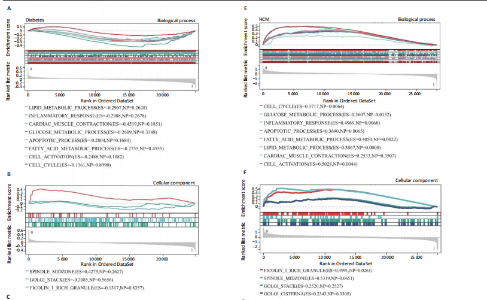
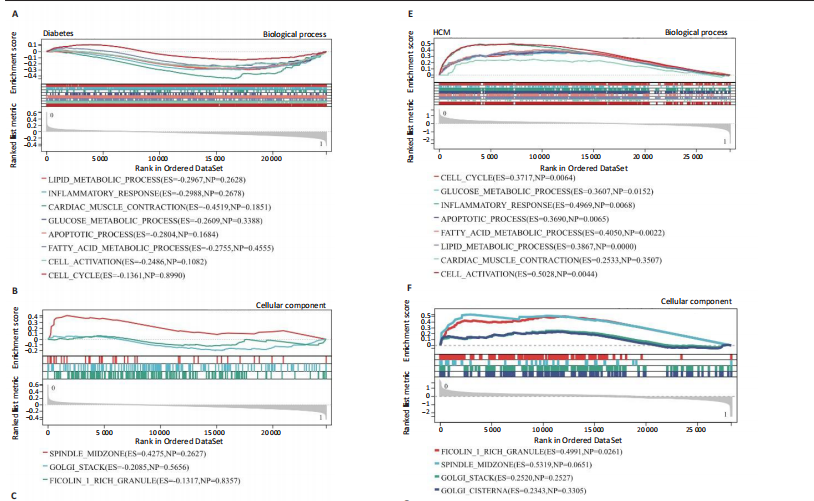
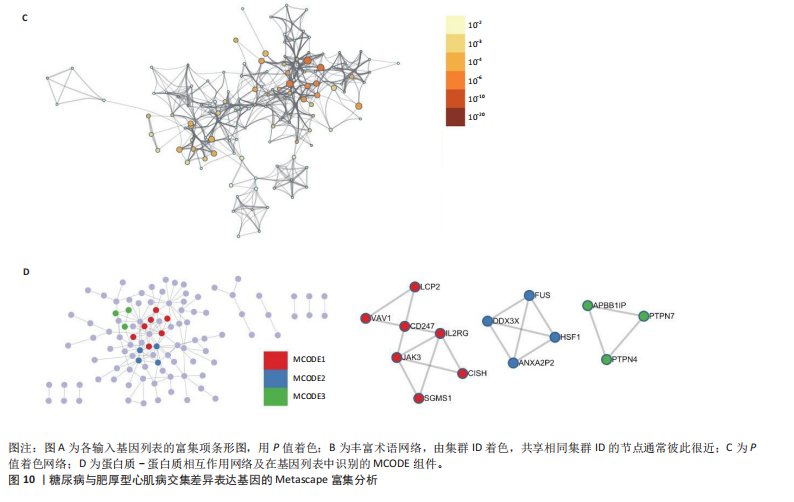
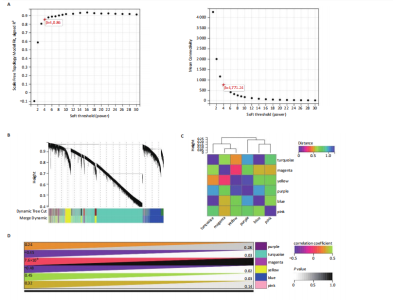
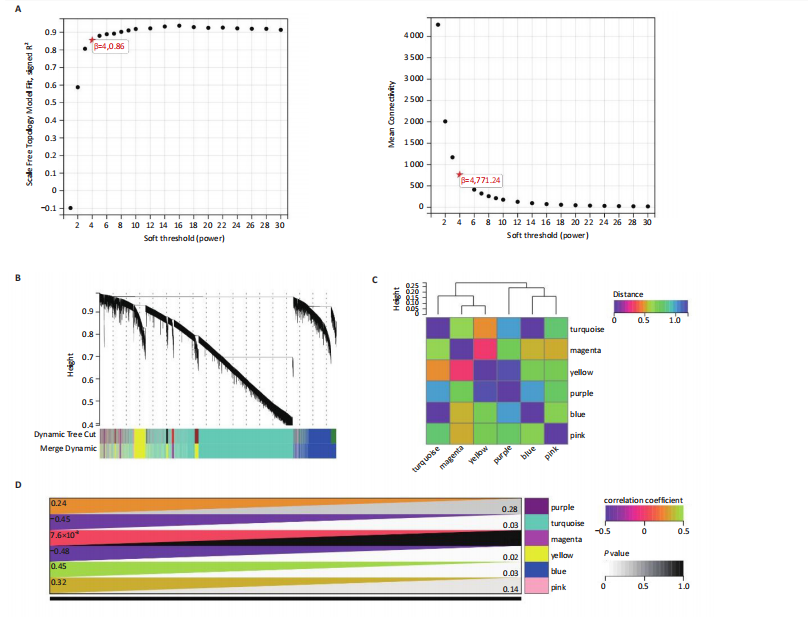
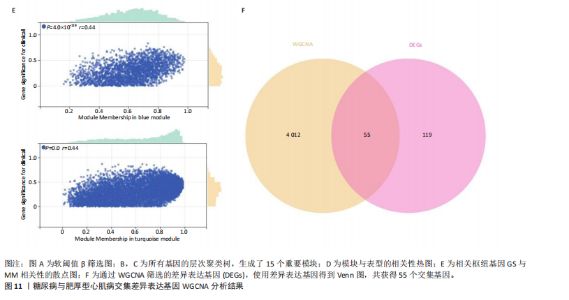
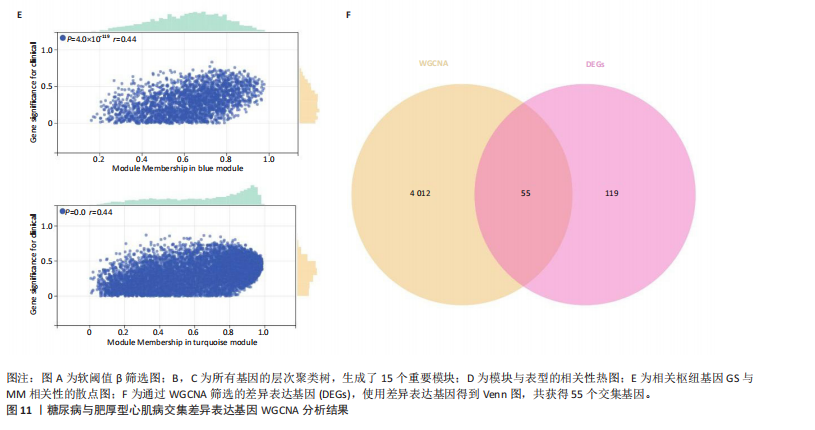
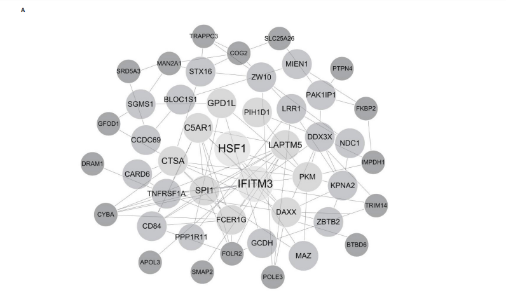
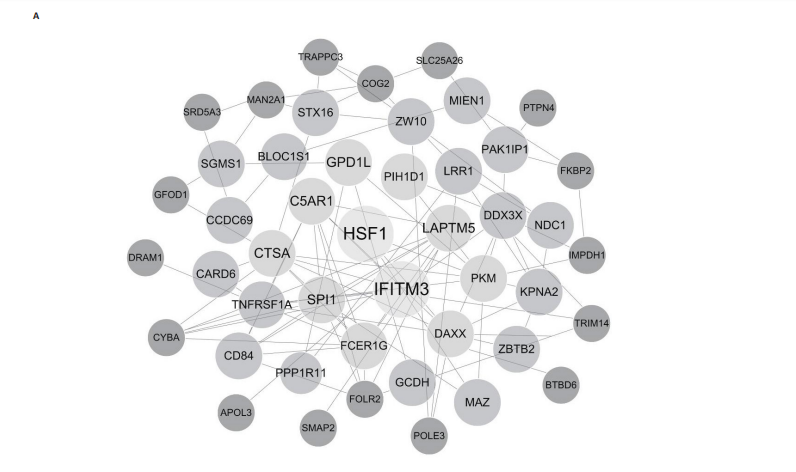
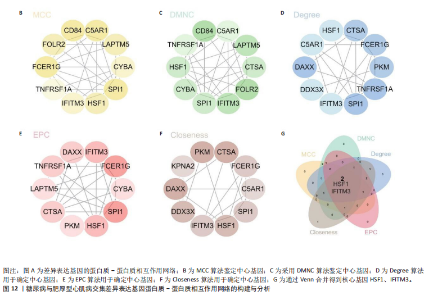
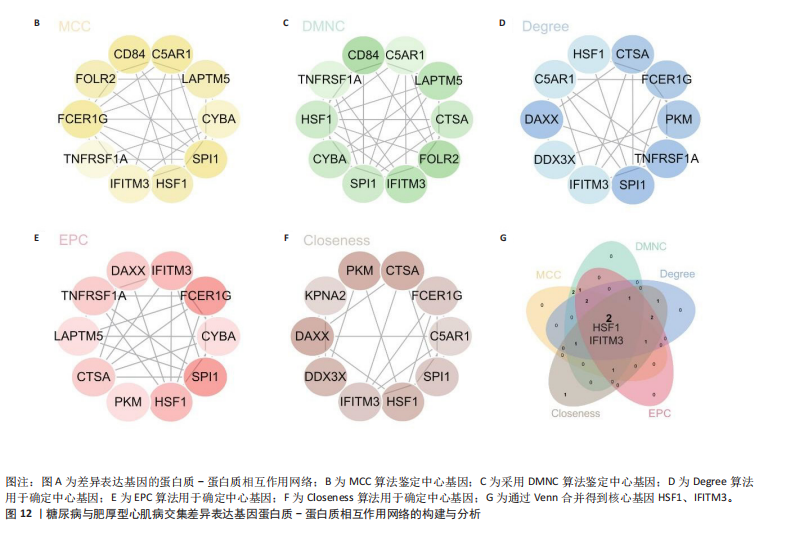
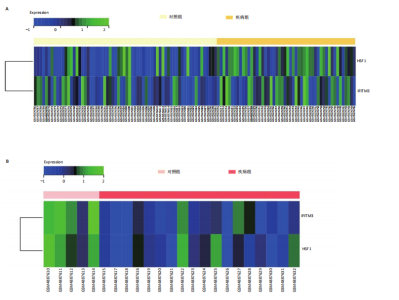
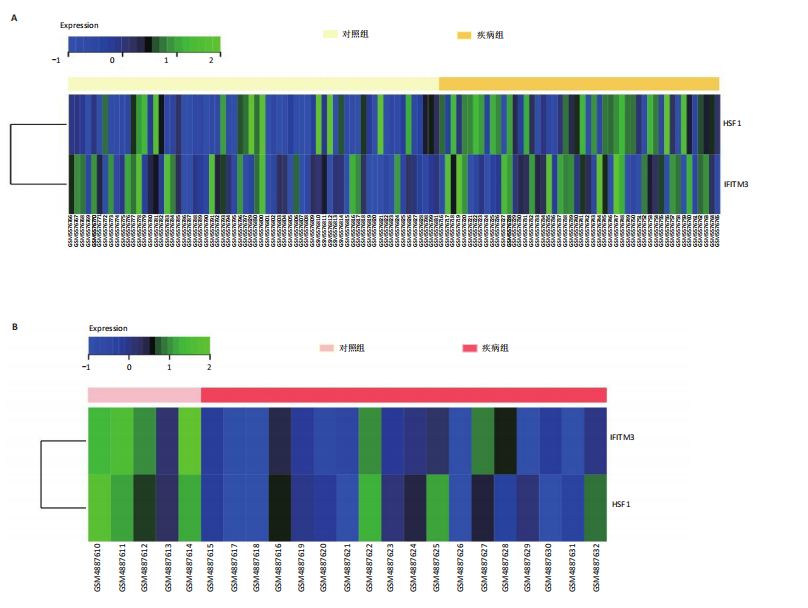
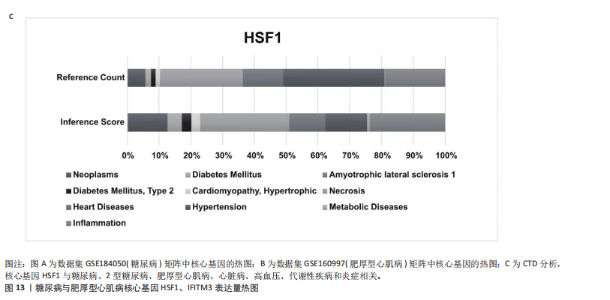
[1] TEEKAKIRIKUL P, ZHU W, HUANG HC, et al. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: An Overview of Genetics and Management. Biomolecules. 2019;9(12):878
[2] LI X, FAN H, SONG X, et al. DNA methylome and transcriptome profiling reveal key electrophysiology and immune dysregulation in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Epigenetics. 2023;18(1):2195307.
[3] LYNCH A, TATANGELO M, AHUJA S, et al. Risk of Sudden Death in Patients With RASopathy Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;81(11):1035-1045.
[4] LOPES LR, LOSI MA, SHEIKH N, et al. Association between common cardiovascular risk factors and clinical phenotype in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) EurObservational Research Programme (EORP) Cardiomyopathy/Myocarditis registry. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes. 2022;9(1):42-53.
[5] ZHAO X, LIU S, WANG X, et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Clinical phenotype and practice. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13: 1032268.
[6] MENG L, LU Y, WANG X, et al. NPRC deletion attenuates cardiac fibrosis in diabetic mice by activating PKA/PKG and inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad pathways. Sci Adv. 2023;9(31):eadd4222.
[7] GERBER B, MANSER C, WIESLI P, et al. A family with diabetes and heart failure. BMJ Case Rep. 2010;2010:bcr0120102613.
[8] LARSSON SC, BUTTERWORTH AS, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization for cardiovascular diseases: principles and applications. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(47):4913-4924.
[9] GOMEZ-PASTOR R, BURCHFIEL ET, THIELE DJ. Regulation of heat shock transcription factors and their roles in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(1):4-19.
[10] ZININGA T, RAMATSUI L, SHONHAI A. Heat Shock Proteins as Immunomodulants. Molecules. 2018;23(11):2846.
[11] CHAI AC, CUI M, CHEMELLO F, et al. Base editing correction of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in human cardiomyocytes and humanized mice. Nat Med. 2023;29(2):401-411.
[12] COLE JB, FLOREZ JC. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(7):377-390.
[13] AKERFELT M, MORIMOTO RI, SISTONEN L. Heat shock factors: integrators of cell stress, development and lifespan. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(8):545-555.
[14] ANCKAR J, SISTONEN L. Regulation of HSF1 function in the heat stress response: implications in aging and disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:1089-1115.
[15] DAI C, DAI S, CAO J. Proteotoxic stress of cancer: implication of the heat-shock response in oncogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2012; 227(8):2982-2987.
[16] PURWANA I, LIU JJ, PORTHA B, et al. HSF1 acetylation decreases its transcriptional activity and enhances glucolipotoxicity-induced apoptosis in rat and human beta cells. Diabetologia. 2017;60(8):1432-1441.
[17] UCHIYAMA T, TOMONO S, UTSUGI T, et al. Constitutively active heat shock factor 1 enhances glucose-driven insulin secretion. Metabolism. 2011;60(6):789-798.
[18] MORIMOTO RI. Regulation of the heat shock transcriptional response: cross talk between a family of heat shock factors, molecular chaperones, and negative regulators. Genes Dev. 1998;12(24):3788-3796.
[19] HOOPER PL. Hot-tub therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(12):924-925.
[20] CHEN Z, WANG J, YANG W, et al. FAM3C activates HSF1 to suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis and attenuate hyperglycemia of type 1 diabetic mice. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(62):106038-106049.
[21] KAVANAGH K, FLYNN DM, JENKINS KA, et al. Restoring HSP70 deficiencies improves glucose tolerance in diabetic monkeys. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011;300(5):E894-901.
[22] KLYOSOVA E, AZAROVA I, POLONIKOV A. A Polymorphism in the Gene Encoding Heat Shock Factor 1 (HSF1) Increases the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study Supports a Role for Impaired Protein Folding in Disease Pathogenesis. Life (Basel). 2022;12(11):1936.
[23] BARNA J, CSERMELY P, VELLAI T. Roles of heat shock factor 1 beyond the heat shock response. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(16):2897-2916.
[24] MAHAT DB, SALAMANCA HH, DUARTE FM, et al. Mammalian Heat Shock Response and Mechanisms Underlying Its Genome-wide Transcriptional Regulation. Mol Cell. 2016;62(1):63-78.
[25] POZNYAK A, GRECHKO AV, POGGIO P, et al. The Diabetes Mellitus-Atherosclerosis Connection: The Role of Lipid and Glucose Metabolism and Chronic Inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(5):1835.
[26] ESSER N, LEGRAND-POELS S, PIETTE J, et al. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;105(2):141-150.
[27] PADMALAYAM I. The heat shock response: its role in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes and its complications, and implications for therapeutic intervention. Discov Med. 2014;18(97):29-39. |