Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (17): 4430-4445.doi: 10.12307/2026.131
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects and mechanisms of palmitoyl acyltransferase ZDHHC5 in tissue homeostasis and diseases
Ji Kaizhong, Kong Yihao, Zhi Yiqing, Jin Yingying, Chen Jianquan
- 1FSchool of Medicine, Hangzhou City University, Hangzhou 310015, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Received:2025-05-06Accepted:2025-08-07Online:2026-06-18Published:2025-12-03 -
Contact:Chen Jianquan, PhD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Medicine, Hangzhou City University, Hangzhou 310015, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Ji Kaizhong, School of Medicine, Hangzhou City University, Hangzhou 310015, Zhejiang Province, China Kong Yihao, School of Medicine, Hangzhou City University, Hangzhou 310015, Zhejiang Province, China Ji Kaizhong and Kong Yihao contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program, No. 202313021029
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ji Kaizhong, Kong Yihao, Zhi Yiqing, Jin Yingying, Chen Jianquan. Effects and mechanisms of palmitoyl acyltransferase ZDHHC5 in tissue homeostasis and diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4430-4445.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
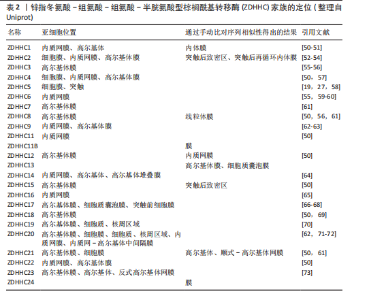
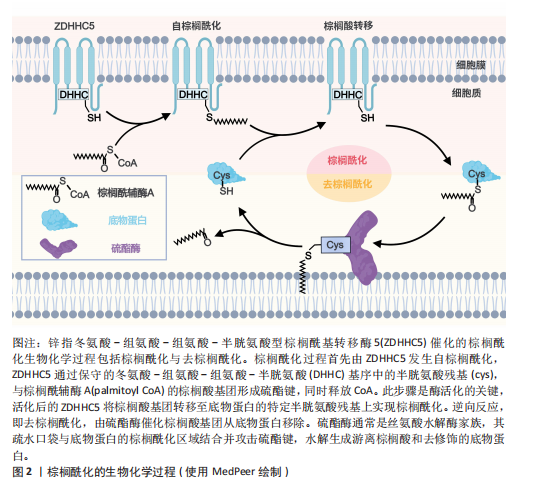
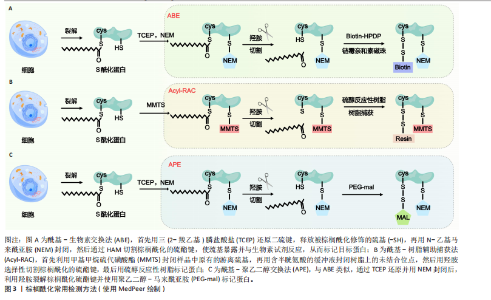
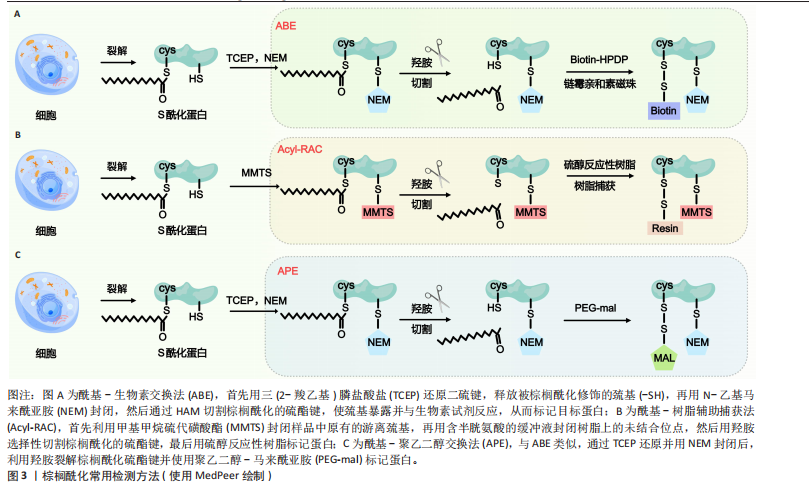
2.1 棕榈酰化及其调控酶 蛋白质棕榈酰化是一种重要的翻译后修饰,在细胞信号转导、跨膜运输和蛋白质功能调节中起着关键作用[11,38]。棕榈酰化循环由棕榈酰基转移酶催化棕榈酰化,并由三大类硫酯酶协同完成去棕榈酰化,主要包括棕榈酰蛋白硫酯酶(Palmitoyl Protein Thioesterase,PPT1/2)、酰基蛋白硫酯酶(Acyl-Protein Thioesterase,APT1/2)、含有α/β水解酶结构域的蛋白17A/B/C(Alpha/Beta Hydrolase Domain-Containing Protein,ABHD17A/B/C)等[38-40]。 在人类细胞中,棕榈酰基转移酶家族由23个成员组成,其成员具有特定的亚细胞定位特征[38]。该家族绝大多数为完整膜蛋白,具有至少4个跨膜结构域(4-6个),其N端和C端均朝向细胞质基质[41]。这些酶通过催化棕榈酸(16碳脂肪酸)与靶蛋白半胱氨酸残基(cys)的共价连接,介导蛋白质棕榈酰化修饰,进而精密调控底物蛋白的膜定位稳定性、蛋白互作网络构建及信号转导通路激活等关键生物学过程[8]。其中,ZDHHC5作为完整膜蛋白,通过4个跨膜结构域锚定于质膜系统,其保守的DHHC催化结构域朝向细胞内部[42]。 与棕榈酰基转移酶的催化功能相反,硫酯酶通过水解棕榈酸-半胱氨酸残基之间的硫酯键介导去棕榈酰化修饰,调控底物蛋白的膜解离、功能失活及蛋白酶体降解路径,从而影响细胞信号传导和蛋白质功能[43]。棕榈酰基转移酶和硫酯酶共同调控蛋白质的棕榈酰化状态,形成动态可逆的修饰循环。这种酶偶联的双向调控机制在细胞信号传导、膜运输、蛋白质相互作用以及疾病发生中具有重要作用,如控制焦亡中的信号激活[44-45],其稳态失衡被证实与肿瘤发生、神经退行性疾病以及炎症等病理进程密切相关[13,46-49]。ZDHHC家族定位见表2。 值得注意的是,在进行催化之前,ZDHHC5会先在其自身的半胱氨酸残基上进行自棕榈酰化,释放出游离的辅酶A(CoA),然后再将棕榈酸基团转移到底物蛋白的特异半胱氨酸位点。棕榈酰化的逆反应,即去棕榈酰化,由硫酯酶协同通过活性中心的丝氨酸残基亲核攻击硫酯键,其催化口袋的空间构象可精准识别底物的棕榈酰化半胱氨酸,从而进行去棕榈酰化反应(图2)[7]。 2.2 棕榈酰化的常用检测方法 目前,研究棕榈酰化水平和机制的主要方法包括酰基-生物素交换法(Acyl-Biotinyl Exchange,ABE)、酰基-树脂辅助捕获法(Acyl-Resin Assisted Capture,Acyl-RAC)和酰基-聚乙二醇交换法(Acyl-PEG Exchange,APE)等(图3)。这些方法利用棕榈酰化特有的硫酯键化学特性,通过切割棕榈酰化硫酯键并结合化学标记物来检测棕榈酰化蛋白。 ABE是检测棕榈酰化的经典方法,其核心步骤是通过羟胺(Hydroxylamine,HAM)切割棕榈酰化的半胱氨酸残基,使暴露的巯基与生物素试剂[如N-(6-生物素胺己基)-3’-(2’-吡啶二硫)丙酰胺,Biotin-HPDP]反应,从而标记目标蛋白[74]。随后,利用链霉亲和素磁珠富集标记蛋白,并通过凝胶电泳、质谱或免疫印迹进行检测。ABE的主要优点是不需要代谢标记,适用于多种样本类型(包括细胞、组织和临床样本),并且可以分析稳定蛋白。该方法在棕榈酰化与疾病关系的研究中具有广泛应用。然而,ABE的假阳性率较高,容易受到非S-酰化蛋白的干扰,且对低丰度棕榈酰化蛋白的检测灵敏度有限[75-76]。 Acyl-RAC方法与ABE类似,同样是利用羟胺选择性切割棕榈酰化的硫酯键,但使用硫醇反应性树脂代替生物素标记蛋白[76]。切割后暴露的半胱氨酸巯基直接与硫醇树脂反应,从而捕获棕榈酰化蛋白。树脂经过洗涤去除非特异性结合后,对捕获的蛋白进行洗脱与鉴定[77]。Acyl-RAC具有较高的灵敏度和特异性,能够准确检测活"
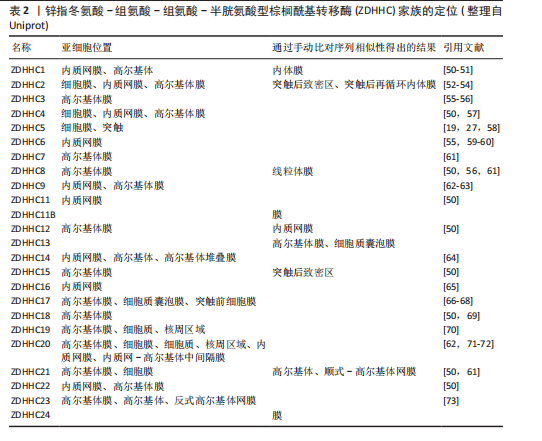
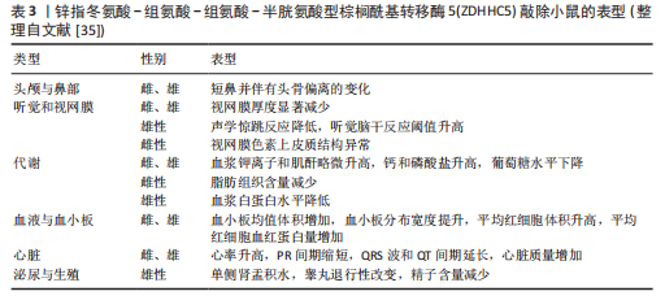
物,代替生物素或树脂[79],其步骤与ABE和Acyl-RAC类似,通过羟胺裂解棕榈酰化硫酯键后,使聚乙二醇-马来酰亚胺(PEG-Maleimide,PEG-mal)与暴露的半胱氨酸巯基结合。聚乙二醇标记通过增加蛋白质的分子质量,可利用凝胶电泳或质谱技术检测棕榈酰化蛋白[80]。APE方法的优势在于操作简单、灵活性高,且不需要代谢标记或亲和富集步骤,适用于定位蛋白质棕榈酰化亚型和评估内源性水平。此外,聚乙二醇标记稳定且易于追踪,可定量分析修饰位点的数量。然而,聚乙二醇标记可能存在非特异性结合,需要严格控制洗涤步骤以减少背景干扰。由于分辨率有限,APE在复杂蛋白样本中对低丰度棕榈酰化蛋白的检测可能存在一定难度。 综上所述,ABE、Acyl-RAC和APE是检测棕榈酰化水平的3种常用方法,均通过特异性裂解和化学修饰手段对棕榈酰化水平进行定量检测。这3种方法各有优缺点,在蛋白质棕榈酰化研究中发挥了重要作用,有助于更好地阐明棕榈酰化在细胞功能和疾病发展中的机制。 2.3 ZDHHC5的生理作用和机制 ZDHHC5在信号通路与细胞活动中具有重要作用,DA SILVA-BUTTKUS等[34]构建了ZDHHC5 敲除(knockout,KO)小鼠模型,发现ZDHHC5的缺失会导致多种表型,具体如表3所示。这些表型暗示了ZDHHC5可能参与多个关键生理过程,包括骨骼发育、感官功能调控、代谢稳态、血液循环系统调节、心功能维持以及生殖健康等,这不仅为进一步研究ZDHHC5调控生理作用的分子机制、全面认识其在健康和疾病中的作用提供了参考,还为ZDHHC5作为潜在靶点影响机体的多种生理作用和病理反应的研究提供了方向。接下来,该文将介绍ZDHHC5在促进胞质分裂、调节离子通量、促进突触形成与连接、抑制细胞自噬和坏死性凋亡等生理过程中的重要作用。 2.3.1 ZDHHC5在细胞质分裂中的功能 细胞分裂是生命活动的核心过程,在多种生物学功能中发挥重要作用,其中原钙黏蛋白7 (Protocadherin 7,PCDH7)被认为是完整有丝分裂过程所必需的蛋白质。?ZLü等[81]研究表明PCDH7与ZDHHC5在有丝分裂期间共定位于细胞表面并相互作用。 ZDHHC5通过棕榈酰化修饰调控PCDH7的功能,促进胞质分裂。具体而言,在分裂间期,PCDH7和ZDHHC5主要定位于细胞-细胞接触区域。随着有丝分裂的开始,二者共同定位于质膜。在有丝分裂中期,ZDHHC5定位于有丝分裂细胞表面和回缩纤维。当胞质分裂启动时,ZDHHC5集中在分裂沟,催化PCDH7以细胞周期依赖的方式向有丝分裂皮质和分裂沟易位,促进皮质重塑和胞质分裂的完成。OZKAN等[35]统计数据显示,ZDHHC5缺失会显著增加胞质分裂缺陷和多核细胞产生的概率。这表明,ZDHHC5可能通过将PCDH7等蛋白靶向质膜和分裂沟,在胞质分裂中发挥关键调节作用。 2.3.2 ZDHHC5调节离子通量 ZDHHC5通过调控转化受体电位阳离子通道亚家族M成员7 (Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Subfamily M Member 7,TrpM7)的棕榈酰化状态,"
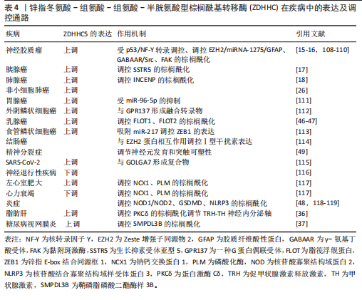
改变其通道行为,从而调节离子通量。GAO等[82]研究表明,TrpM7的棕榈酰化位点位于其C末端的Trp结构域,棕榈酰化通过影响瞬时受体电位蛋白结构域的构象变化来调节通道行为。TrpM7在内质网中合成后,首先由内质网驻留的ZDHHC进行棕榈酰化,随后转运至高尔基体,由ZDHHC17进一步修饰并通过棕榈酰化形成与质膜结合的囊泡。当TrpM7到达质膜时,ZDHHC5通过改变其棕榈酰化状态调节通道活性。值得注意的是,TrpM7只有在棕榈酰化后才能从高尔基体转运至质膜,未棕榈酰化的TrpM7则滞留在细胞内囊泡中,导致钙离子跨膜通量显著下降。此外,TrpM7介导的Mg2?和Zn2?通量也可能受到棕榈酰化的调控。 除了通过调控TrpM7的棕榈酰化,LIN等[83]发现,ZDHHC5通过棕榈酰化调控钠钙交换蛋白1 [sodium-calcium (Na-Ca) exchanger 1,NCX1]的表面定位和内化。而G?K等[84]进一步揭示了ZDHHC5通过催化NCX1细胞内环的C739位点的棕榈酰化,诱导其二聚体结构的重组,从而增强内源性交换抑制肽与细胞内环的结合能力,促进NCX1失活并降低其钙内流能力。这种动态且可逆的棕榈酰化过程由ZDHHC5和APT1共同调控,使NCX1能够根据细胞内外环境变化灵活调整功能。此外,棕榈酰化还增强了NCX1对脂筏的亲和力,影响其在质膜的形成和稳定性。有趣的是, G?K团队[33]还发现胰岛素可以通过诱导ZDHHC5活性位点的棕榈酰化,触发NCX1细胞内环的局部构象变化,进一步增强其对内源性交换抑制肽的敏感性,从而维持胞质钙稳态并改善心脏功能。 2.3.3 ZDHHC5参与突触形成和连接 在大脑中,棕榈酰化是最常见的翻译后脂质修饰之一,参与调控多种神经元生理过程,对突触可塑性具有重要作用[85-86]。ZDHHC5在突触可塑性中的作用也是近年来的一个研究主题,突触可塑性是由蛋白质进出突触的动态定位介导的[87]。SHIMELL等[9]发现ZDHHC5主要定位于兴奋性突触,在ZDHHC5敲低的神经元中,树突棘密度显著下降,表明ZDHHC5能够调节兴奋性突触密度。然而,通过测量微型树突棘Ca2?瞬变,他们发现Ca2?事件的幅度和数量并未发生变化,提示ZDHHC5不影响基础突触传递的其他特性。进一步研究发现,ZDHHC5的膜定位对其功能至关重要。在新生突触膜上,ZDHHC5通过催化蛋白质棕榈酰化,调控突触连接的形成和维持,这一过程依赖于其酶活性、膜表面定位以及C端结构域的相互作用。此外,在啮齿动物海马体神经元中,Wnt蛋白(一种分泌性糖蛋白)通过卷曲蛋白受体5 (Frizzled-5,Fz5)促进突触组装,而Fz5蛋白C末端的的3个半胱氨酸可以被ZDHHC5棕榈酰化,这一过程对于Fz5的定位至关重要,棕榈酰化缺陷将会导致Fz5无法诱导和促进突触组装[88]。 相较于其他棕榈酰基转移酶家族成员,ZDHHC特异性富集于背部神经节的轴突中,与ZDHHC8共同调控Gp130依赖性轴突逆行信号传导,Gp130是神经生成细胞因子(如白细胞介素6、纤毛神经营养因子)的受体复合体的关键组分,其棕榈酰化对于细胞表面定位和信号传导至关重要[89]。 有趣的是,ZDHHC5与ZDHHC8又同时作为PDZ结构域蛋白GRIP1b的特异性调节因子以靶向树突状内体。THOMAS等[90]基于ZDHHC5与ZDHHC8在C端序列的相似性和N端序列的独特性,发现ZDHHC5能够特异性棕榈酰化GRIP1b蛋白的N端半胱氨酸(Cys11)。通过特异性抗体的免疫定位,ZDHHC5在树突轴中强烈表达,被认为是GRIP1b的主要神经元棕榈酰基转移酶,这进一步揭示了ZDHHC5在神经系统中的分布特征。 此外,ZDHHC5与突触后致密蛋白 95 (post-synaptic density protein-95,PSD-95)的 PDZ3 结构域相互作用,在学习和记忆中发挥作用[91]。在此基础上,BRIGIDI等[27]进一步探究了ZDHHC5与底物δ连环蛋白(δ-catenin)的棕榈酰化过程在突触可塑性中的重要意义。在基础条件下,ZDHHC5通过与PSD-95和Fyn激酶结合,稳定在突触膜上,而其底物δ-catenin主要定位于树突轴,导致酶与底物对分离。神经元活动破坏这种复合物后,增强了ZDHHC5的内吞作用,促使其转位到树突干,与δ-catenin结合并进行棕榈酰化,再共同被运输回突触膜。棕榈酰化后的δ-catenin增加了钙黏蛋白的稳定性和α-氨基-3-羟基-5-甲基-4-异恶唑丙酸受体向突触膜的募集。 在突触稳定性的研究中,ABAZARI等[87]发现突触活动通过翻译后修饰(包括磷酸化和棕榈酰化)调节ZDHHC2、ZDHHC5和ZDHHC9的活性,影响酶的稳定性、蛋白质相互作用和酶功能,从而调节突触稳定性。相比之下,去棕榈酰化酶APT2和ABHD17的活性和翻译后修饰在突触活动增加后没有显著变化。此外,ZDHHC5的活性依赖性降解是由其C末端的polo-box结构域的磷酸化介导的,这一过程涉及PLK2和CDK5等激酶。 综上,ZDHHC5在突触可塑性中的作用不仅体现在其对底物的棕榈酰化调控上,还体现在其动态的亚细胞定位变化上,这些变化对于维持正常的突触功能和大脑高级认知功能至关重要。 2.3.4 调节细胞死亡 (1)调节细胞自噬:ZDHHC5在调节细胞自噬中具有重要作用。LIU等[92]在间充质干细胞中过表达ZDHHC5的实验中发现ZDHHC5与间充质干细胞的衰老和自噬密切相关。具体的讲,ZDHHC5通过激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路而抑制细胞自噬,从而促进间充质干细胞衰老,损害组织再生能力。然而,ZDHHC5调控磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路的具体分子机制仍有待深入研究。有意思的是,C-藻蓝蛋白可通过与ZDHHC5相互作用而下调其表达,由此促进细胞自噬、抑制细胞衰老,从而展现出抗肿瘤、抗氧化和抗衰老等多种功能。 此外,ZHOU等[5]发现ZDHHC5还通过棕榈酰化核苷酸寡聚结构域蛋白2(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain protein 2,NOD2)调控其自噬降解。ZDHHC5通过棕榈酰化NOD2,减弱其与自噬接头蛋白SQSTM1/p62的相互作用,并促进NOD2的膜募集,从而抑制NOD2递送到自噬体进行降解。虽然提高了NOD2的稳定性,但同时也可能降低NOD2的激活阈值,增加NOD2介导的炎症反应和炎症性疾病的风险。ZDHHC5敲除能够降低NOD2的丰度,减轻过度炎症反应。基于ZDHHC5通过修饰NOD2诱导炎症反应的发生这一机制,周程继等[93]通过心肺复苏小鼠模型进一步探讨其在小鼠心肺复苏后脑损伤中的作用,结果显示,抑制ZDHHC5的表达可以明显抑制NOD2的表达,这意味着小鼠脑内的炎症因子释放水平下降,从而减少脑组织的损伤,改善神经状态。这些发现揭示了ZDHHC5在NOD2自噬降解中的关键作用及潜在治疗价值。 除了NOD2,GUO等[94]证明了ZDHHC5通过调节自噬关键蛋白Beclin 1 C137位点的棕榈酰化影响自噬,这一修饰促进Beclin 1与接头蛋白ATG14L和VPS15的疏水相互作用,从而增强含ATG14L的Ⅲ类磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶复合物Ⅰ的形成及其脂质激酶活性,最终调控自噬体的生成。在衰老过程中,ZDHHC5表达下降导致Beclin 1棕榈酰化减少,进而导致自噬功能衰退。 (2)调节坏死性凋亡:ZDHHC5通过调控混合谱系激酶样蛋白(mixed lineage kinase like protein,MLKL)和磷酸化MLKL(pMLKL)的棕榈酰化,参与坏死性凋亡的调控。PRADHAN等[95]的研究发现,MLKL和pMLKL在坏死性凋亡过程中的棕榈酰化修饰由ZDHHC5介导,且这一修饰发生在磷酸化和寡聚化之后。此外,ZDHHC5催化的pMLKL极长链脂肪酸(Very Long-Chain Fatty Acids,VLCFAs)酰化修饰在坏死性凋亡中也起重要作用。VLCFAs通过酰化修饰促进pMLKL的膜定位和膜透化过程,推动细胞死亡,而VLCFAs下调能够减少MLKL和pMLKL的膜募集,从而延缓膜透化的发生,挽救细胞死亡。另外,ZHANG等[96]发现ZDHHC5还能通过调控丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶1在Cys257位点的棕榈酰化修饰,增强其激酶结构域的同源相互作用,从而激活其激酶活性,促进细胞凋亡和坏死性凋亡。 (3)调节新型非凋亡性细胞死亡:ZDHHC5通过与Golgin A7(GOLGA7)形成复合物调控新型非凋亡性细胞死亡。KO等[30]发现小分子化合物含肟的小分子半胱天冬酶非依赖性致命56(containing small molecule caspase-independent lethal 56,CIL56)可通过一种新型非凋亡性细胞死亡机制诱导细胞死亡,这与ZDHHC5- GOLGA7复合物的关系密切。CIL56诱导的细胞死亡不同于凋亡、铁死亡和坏死性凋亡。具体的讲,CIL56通过抑制顺行蛋白质从高尔基体到质膜的转运,并依赖ZDHHC5-GOLGA7复合物的逆行运输作用,导致蛋白质错误定位和细胞内积累,最终引发细胞死亡。因此,ZDHHC5的催化活性和C末端酰化对于CIL56诱导的细胞死亡至关重要。有趣的是,CIL56对血液癌细胞表现出选择性杀伤作用,为抗癌药物开发提供了新的潜在靶点。 (4)外源性凋亡:ZDHHC5与外源性凋亡密切相关。研究聚焦于ZDHHC5与肿瘤坏死因子(Tumor Necrosis Factor,TNF)相关凋亡诱导配体(TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand,TRAIL)之间的作用关系。TRAIL作为一种促进肿瘤细胞凋亡的配体,能够在不损伤正常宿主细胞的情况下诱导肿瘤细胞的凋亡。研究发现,ZDHHC5主要于半胱氨酸蛋白酶级联效应的上游发挥作用,调控细胞凋亡过程。敲除ZDHHC5能够显著促进TRAIL诱导的细胞凋亡途径的发生,同时这也使得炎症通路的激活受阻。这一研究表明了ZDHHC5与细胞凋亡机制的高度相关性,也印证了ZDHHC5在肿瘤治疗中广泛的研究前景[97]。 2.3.5 ZDHHC5调节细胞内膜运输 内体到高尔基体的修复途径是细胞内膜运输的关键环节,而ZDHHC5在这一过程中发挥关键作用[98]。BREUSEGEM等[42]揭示了ZDHHC5能够调控其底物SFT2结构域包含蛋白2 (SFT2 domain containing 2,SFT2D2)的定位,并在含EH结构域包含蛋白质1(EH-domain-containing proteins,EHD1)阳性的内体回收小管中定位,EHD1是内体到高尔基体修复的关键调控蛋白[99]。同时,ZDHHC5缺失会影响阳离子非依赖性甘露糖6-磷酸受体(cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor,CIMPR)的运输,CIMPR是该途径中的关键转运蛋白,负责将溶酶体水解酶从内体运输到高尔基体,并改变内体到高尔基体途径中其他货物蛋白的水平。这表明ZDHHC5对维持内体到高尔基体修复和细胞稳态至关重要。 2.3.6 脂肪酸代谢 ZDHHC5还参与脂肪酸代谢。WANG等[28]揭示了ZDHHC4和ZDHHC5通过棕榈酰化修饰调节清道夫受体CD36的质膜定位和脂肪酸摄取活性,在脂肪酸代谢中具有重要作用。具体的讲,CD36是ZDHHC4和ZDHHC5的共同生理底物,其棕榈酰化对于靶向质膜至关重要,且这一过程对CD36介导的脂肪酸摄取功能是必需的。CRISPR-Cas9敲除ZDHHC4或ZDHHC5基因的小鼠表现出CD36的质膜定位均受损和脂肪酸摄取能力下降以及对寒冷暴露的不耐受性,这与CD36缺陷小鼠的表型相似。有趣的是,ZDHHC4和ZDHHC5在功能上并非冗余,ZDHHC4负责将CD36棕榈酰化并分选至质膜,而ZDHHC5则通过保护CD36免受去棕榈酰化来维持其在质膜上的定位。ZDHHC4和ZDHHC5调控CD36棕榈酰化途径不仅促进CD36在细胞膜的定位,同时还增加了CD36的疏水性,这一过程促进细胞对脂肪酸的摄取[100]。最近,LI等[101]的研究证明花青素的主要代谢产物原儿茶酸通过抑制ZDHHC5的棕榈酰化来抑制CD36的棕榈酰化,从而减少肝细胞中脂质的摄取和积累。除了CD36,ZDHHC5还能通过调控巨噬细胞的炎症通路影响脂肪组织的功能[102]。这些发现为理解脂肪酸代谢的调控机制和代谢性疾病的治疗提供了新的视角和潜在靶点。 2.3.7 其他生理功能 除了上述几种生理功能,ZDHHC5在调节G蛋白信号、细胞黏附、少突胶质细胞发育、免疫细胞运输等生理过程中也具有重要作用。 (1)调节心肌细胞G蛋白信号与成肌细胞分化:ZDHHC5能调节心脏功能与成肌细胞分化。SHEN等[103]研究表明,ZDHHC5通过响应β-AR的刺激,维持其在膜上的稳定性,并调控下游信号蛋白Gαs和Gαi的棕榈酰化,从而调节心脏功能[31]。此外,ZDHHC5还能够通过与去棕榈酰化酶 ABHD7反向催化核纤层蛋白A,从而影响成肌细胞的分化。 (2)调节细胞黏附:ZDHHC5通过与GOLGA7b相互作用及其棕榈酰化调控,促进桥粒组装和细胞黏附。WOODLEY等[29]揭示了ZDHHC5通过与其辅助蛋白GOLGA7b之间相互作用调控细胞黏附。GOLGA7b的棕榈酰化通过阻止ZDHHC5内吞维持其在质膜上的稳定性和功能。此外,ZDHHC5和GOLGA7b还通过调节桥粒核心糖蛋白2和嗜热蛋白3的棕榈酰化共同在桥粒组装和细胞黏附中发挥作用。这些发现为理解细胞黏附相关疾病(如心脏病和癌症转移)提供了新的视角。有趣的是,SAY等[104]通过全转录组测序和基因分型数据,鉴定出GOLGA7b是高血糖指数(GI)/血糖负荷(GL)饮食与痤疮之间的新关联基因,这可能意味着ZDHHC5与痤疮风险相关。 (3)调节神经干细胞分化:ZDHHC5不仅与神经元发育、神经传递与突触可塑性有关,还可以通过调节脂筏浮舰蛋白2(Flotillin-2,FLOT2)的棕榈酰化影响神经干细胞发育。LI等[105]通过定量蛋白质组学分析技术,在细胞培养中用氨基酸稳定同位素标记(stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture,SILAC)方法,利用17-十八碳炔酸孵育细胞标记,鉴定神经干细胞中的棕榈酰化蛋白质组,结果发现约300个高置信度的羟胺敏感棕榈酰化蛋白。通过比较野生型和ZDHHC5敲除细胞的SILAC比值,筛选出20个潜在ZDHHC5底物(WT/GT≥2),其中脂筏蛋白FLOT2差异最显著(WT/GT=3.06);接下来,他们进一步通过ABE证实ZDHHC5敲除细胞中的FLOT2棕榈酰化水平降低10倍以上,而异源表达实验显示ZDHHC5可以直接催化FLOT2在Cys-4和Cys-20位点的棕榈酰化,且过表达ZDHHC5显著增强了FLOT2的棕榈酰化,这进一步证实了两者的相互作用关系。这些发现不仅明确了FLOT2是ZDHHC5的关键生理底物,还证实了ZDHHC5通过调控FLOT2棕榈酰化影响其寡聚化及神经突延伸功能的分子机制。 (4)调节少突胶质细胞及髓鞘形成:蛋白质棕榈酰化被证明在髓鞘形成蛋白的转运和功能中起关键作用。MA等[106]揭示了ZDHHC5通过调节转录激活因子3(signal transducer and activator of transcription 3,STAT3)的棕榈酰化影响少突胶质细胞的功能。他们通过少突胶质细胞特异性敲除ZDHHC5基因的小鼠模型,发现ZDHHC5缺失降低了STAT3的棕榈酰化水平,进而抑制了STAT3的磷酸化和激活。STAT3激活对于少突胶质细胞的成熟和髓鞘相关基因的表达至关重要。因此,ZDHHC5缺失导致的STAT3活性下降,最终抑制了髓鞘相关基因和抗细胞凋亡基因的转录,从而阻碍了少突胶质细胞的发育和髓鞘形成。此外,通过在ZDHHC5缺失的少突胶质细胞中引入组成型激活的STAT3,可以部分恢复细胞分化和存活。这进一步证实了STAT3在ZDHHC5 调控少突胶质细胞发育中的关键作用。除了STAT3,LIU等[107]发现ZDHHC5还可以通过调控转铁蛋白受体1在C98半胱氨酸位点的棕榈酰化修饰,抑制其内吞作用,从而减少少突胶质细胞内的铁超载和铁死亡,最终缓解髓鞘形成障碍及神经元损伤。 (5)免疫信号调控:ZDHHC5介导的棕榈酰化还能够参与免疫细胞运输和血管通透性的调节。BADAWY等[58]发现ZDHHC5通过调控1-磷酸鞘氨醇受体1(S1P receptors1,S1PR1)的棕榈酰化修饰,调控其与抑制性G蛋白(Inhibitory G-protein,Gi)的偶联,从而在免疫细胞运输和血管通透性调节中发挥关键作用。在基础条件下,S1PR1与质膜中的ZDHHC5功能相关,并完全棕榈酰化,从而实现Gi偶联。而ZDHHC5缺陷鼠表现出S1PR1介导的Gi功能受损,棕榈酰化缺陷的S1PR1突变体(3CA)在激动剂诱导的Gi亚基解离中无反应,表明ZDHHC5介导的S1PR1棕榈酰化是受体与Gi功能偶联的先决条件,为理解S1PR1在免疫细胞运输和血管通透性调节中的功能提供了新的视角。 2.4 ZDHHC5的病理作用及机制 ZDHHC5的生理功能(如调控胞质分裂、离子通道、细胞黏附、细胞自噬等)高度依赖其酶活性、亚细胞定位及底物动态修饰的精确平衡。然而,在疾病状态下,ZDHHC5的表达异常或功能失调会导致其底物棕榈酰化网络紊乱,进而影响疾病的发生发展,表4总结"
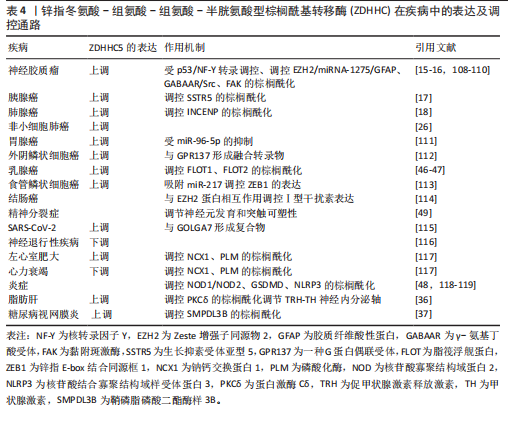

了ZDHHC5在疾病中的表达特征及核心调控通路。ZDHHC5在8种癌症的细胞和组织中以及SARS-CoV-2、左心室肥大、炎症、脂肪肝和糖尿病视网膜炎中表达上调。同时,ZDHHC5在神经退行性疾病、心力衰竭中表达较低。值得注意的是,ZDHHC5在精神分裂症中的表达未有明确报道。 2.4.1 癌症 (1)神经胶质瘤:ZDHHC5通过棕榈酰化修饰其底物,包括人类Zeste增强子同源物2 (enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit,EZH2)和黏附斑激酶(focal adhesion kinase,FAK),从而调控神经胶质瘤的发生与发展。CHEN等[108]发现突变型p53(一种经典的肿瘤抑制因子和转录因子)通过与核转录因子Y(nuclear transcription factor,NF-Y)启动子一起转录上调ZDHHC5的表达,且随着神经胶质瘤级别的增加而增加。ZDHHC5能够通过调控EZH2的棕榈酰化调节EZH2活性,激活组蛋白H3的第27位赖氨酸上发生3次甲基化,降低了miR-1275的表达,增加了神经胶质纤维酸性蛋白(glial fibrillary acidic protein,GFAP)的表达并削弱DNA甲基转移酶3A与Oct4(正常干细胞维持的基因之一)的启动子区域结合,这将会影响到人类神经干细胞中的RAS、TERT和p53癌基因的恶性转化,并最终诱导胶质瘤的发生与恶化[15-16]。有意思的是,FAN等[109]发现临床麻醉剂异丙酚能激活对γ-氨基丁酸受体(GABAAR)/Src/ZDHHC5/EZH2信号轴,通过激活GABAAR,增加Src和p-Src的表达,增强Src与p53的相互作用,从而上调ZDHHC5的表达,最终增强EZH2和Oct4的棕榈酰化,促进神经胶质瘤干细胞的自我更新及肿瘤干细胞特性。此外,ZDHHC5还能够影响FAK在神经胶质瘤中的膜定位和上皮-间质转移。FAK的异常激活往往与肿瘤的发生息息相关,其通过影响生物体内信号分子的相互作用促进肿瘤细胞的迁移与侵袭。敲除ZDHHC5可以消除FAK的棕榈酰化和膜分布,这表明靶向ZDHHC5/FAK轴有可能成为胶质母细胞瘤治疗干预的一个策略[110]。总之,靶向ZDHHC5或其下游效应分子,可能为胶质瘤的精准治疗提供新策略。 (2)胰腺癌:生长抑素受体亚型 5 (Somatostatin receptor 5,SSTR5)同样是棕榈酰化的蛋白质底物,其尾部被鉴定为棕榈酰化的位点,目前已经被证实为胰腺细胞中的抗增殖受体[120]。 ZDHHC5与SSTR5相互作用,并通过棕榈酰化影响SSTR5的定位[25]。WANG 等[17]发现ZDHHC5在肿瘤样本中的大多数细胞类型中表达,敲低胰腺癌症细胞中的ZDHHC5可显著抑制胰腺癌细胞生长,表明它是潜在的治疗靶点。随后,他们从FDA批准的药物中筛选了2 513种可以作为ZDHHC5拮抗剂的小分子药物,结果显示一种用于罕见病治疗的孤儿药洛美他派(Lomitapide)可以作为ZDHHC5抑制剂,通过抑制ZDHHC5的活性阻断SSTR5尾部的棕榈酰化抑制胰腺癌症细胞生长和增殖,为癌症治疗提供了一种更有效的方法。 (3)肺腺癌:肺腺癌是目前最常见的肺部癌症。尽管目前放疗、化疗以及免疫疗法能改善肺腺癌患者的存活率,但是复发率仍然很高,因此迫切需要确定新的治疗靶点[121]。ZHANG等[18]通过比较肺腺癌病例和正常肺组织之间的差异表达基因,发现ZDHHC5是唯一在肺腺癌中具有差异表达与预后的基因,其在肺腺癌中高表达,与不良预后密切相关,并通过棕榈酰化调控癌症干性基因INCENP的功能,从而对肺腺癌产生重要的影响。其中,Cys15是INCENP棕榈酰化的位点。这一发现为针对ZDHHC5在肺腺癌中的抗癌策略提供了新的思路。 (4)非小细胞肺癌:非小细胞肺癌是一种复杂且具有显著特异性的疾病,吸烟是常见的致病因素[122]。TIAN等[26]发现ZDHHC5在非小细胞肺癌细胞系增殖和肿瘤异种移植物形成方面具有重要作用。敲低ZDHHC5的表达可显著抑制体外癌症细胞的增殖、侵袭以及形成集落的能力,表明ZDHHC5可能是非小细胞肺癌治疗中的潜在靶点。 (5)胃癌:胃癌是最常见的恶性癌症之一,其中以由胃腺体细胞恶变来的胃腺癌最为常见[123]。由于胃腺癌的不良预后与许多分子生物标志物有关,ZHOU等[111]发现miR-96-5p在胃腺癌肿瘤样本的表达水平较对照组显著升高,而ZDHHC5被定义为miR-96-5p的直接靶基因,下调miR-96-5p的表达会导致ZDHHC5在MGC-803 (一种人胃癌细胞系)的表达量上升,从而显著诱导细胞凋亡,抑制癌细胞的增殖和迁移能力,为胃腺癌的诊断和治疗方法提供了新的策略。 (6)外阴鳞状细胞癌:外阴癌症是第四大妇科癌症,其中以外阴鳞状细胞癌最为常见[124]。BRUNETTI等[112]指出外阴鳞状细胞癌肿瘤样本中存在应激诱导磷蛋白1(STIP1,一种衔接蛋白)与CREB3L1(一种转录因子)融合转录物以及ZDHHC5与GPR137(一种G蛋白偶联受体)融合转录物,然而,这两种融合基因在健康的正常外阴组织中并没有检测到。因此,特异性融合转录物的鉴定不仅可以帮助研究人员进一步理解肿瘤潜在的致病过程,而且可以为诊断和预后提供参考,甚至为抗癌提供治疗靶点。 (7)乳腺癌:MCCLELLAN等[46]发现,浮舰蛋白1(Flotillin-1,FLOT1)在三阴性乳腺癌中高表达,而ZDHHC5是负责棕榈酰化内源性FLOT1的主要酶,它通过阻止FLOT1的多泛素化和蛋白酶体降解来维持稳定性。此外,表达FLOT1的肿瘤生长和肺转移能力减弱。有趣的是,他们还设计了一种与细胞穿透肽序列融合的竞争性肽,能够特异性阻断FLOT1的棕榈酰化,从而促进其降解,在三阴性乳腺癌异种移植模型中肿瘤生长和肺转移显著减弱。同时,FLOT2的表达也影响着肿瘤的存活。由于肝X受体在细胞胆固醇稳态中起着核心作用,脂筏微结构域过度表达通常诱导肿瘤细胞的凋亡,因此刺激肝X受体具有潜在抑制癌症细胞增殖的能力[125]。CARBONNELLE等[47]发现ZDHHC5与FLOT2共同定位于膜上的脂筏结构,通过催化FLOT2的棕榈酰化调节脂筏微结构域的形成。而肝X受体激动剂T0901317通过下调ZDHHC5在mRNA与蛋白水平的表达,调节FLOT2的转录,在mRNA水平降低FLOT2的表达,最终导致脂筏结构域的破坏,诱导癌症细胞凋亡。虽然肝X受体激动剂诱导脂筏破坏的机制尚不清楚,但是为乳腺癌的治疗提供新的探索道路。 (8)食管鳞状细胞癌:食管鳞状细胞癌是一类常发生于发展中国家,而在发达国家发病率低的疾病,主要的诱因包括大量饮酒和吸烟[126]。WANG等[113]以环状RNA(circRNA)为工具进行研究,发现circ-ZDHHC5在食管鳞状细胞癌患者的血浆和组织中的表达水平显著高于正常组织,并且在细胞系中也显著上调。有趣的是,circ-ZDHHC5通过类似海绵的作用,吸附miR-217调控锌指E-box结合同源框1(zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1,ZEB1)缓解其对ZEB1的抑制作用,从而促进肿瘤的增殖和侵袭。circ-ZDHHC5通过miR-217/ZEB1轴在食管鳞状细胞癌进展中发挥关键作用,表明其可能成为食管鳞状细胞癌治疗的潜在靶点和预后生物标志物。然而,该研究存在一定局限性,例如样本量较小且主要来自单一族群。未来研究需扩大样本量,验证不同地区人群中的结果,并进一步探索circ-ZDHHC5是否通过其他机制调控食管鳞状细胞癌的发展。 (9)结肠癌:EZH2被认为在多种肿瘤中都有高表达[127]。邱晋等[114]探讨了ZDHHC5对结肠癌细胞中Ⅰ型干扰素表达的调控作用,他们发现ZDHHC5能够与EZH2蛋白相互结合,这可能影响了EZH2的甲基化修饰,最终有效抑制Ⅰ型干扰素的表达,促进小鼠结肠癌细胞的迁移与增殖能力。ZDHHC5是一种能够促进多种肿瘤细胞增殖与迁移的关键致癌因子,在多种类型的癌症中,ZDHHC5能够基于不同的致癌机制而表现出多种潜在的致癌能力。未来的研究有望聚焦于以ZDHHC5作为靶向治疗各类癌症的关键因子,为癌症的治疗探索提供更加深刻的思考。 2.4.2 呼吸道疾病 作为一种高度传播和致病的β-冠状病毒,SARS-CoV-2可以产生刺突蛋白,这是一种高度糖基化的表面膜蛋白,其棕榈酰化过程对于刺突介导的细胞融合很重要,能够决定病毒进入靶细胞[128-130]。 GORDON等[115]发现ZDHHC5和GOLGA7与SARS-CoV-2的刺突蛋白具有高置信度相互作用。GOLGA7是一种酰化的高尔基蛋白,它与ZDHHC5形成蛋白酰基转移酶复合物并定位于质膜,催化各种蛋白质中内部半胱氨酸残基的蛋白质棕榈酰化,因此可能在 SARS-CoV-2潜在的发病机制中发挥作用[131]。无论是ZDHHC5还是GOLGA7敲除,对S蛋白的亚细胞定位或棕榈酰化均没有影响,但能显著降低SARS-CoV-2假病毒颗粒进入靶细胞的效率。这意味着可能还存在其他ZDHHC酶参与刺突蛋白的棕榈酰化。后来LI等[132]研究证明多个ZDHHC能参与刺突蛋白的棕榈酰化,如ZDHHC 2,3,4,5,8,9,11,14,16,19,20。此外,COLACO等[133]发现,ZDHHC5的转录本在发育中的大多数胚胎细胞中表达,并与冠状病毒的S蛋白相互作用,作为非经典进入机制参与病毒感染过程。ZDHHC5与SARS受体血管紧张素转换酶2、蛋白酶跨膜蛋白酶丝氨酸2等其他与冠状病毒进入相关的因子共表达,即使在上述水平较低的情况下,冠状病毒也可能通过ZDHHC5进入胚胎细胞,表明ZDHHC5不仅可能增加胚胎细胞对冠状病毒的敏感性,还能作为替代受体促进病毒感染。总之,ZDHHC5作为冠状病毒感染宿主细胞的潜在受体,可能成为抗病毒治疗的靶点。 2.4.3 精神分裂症 精神分裂症被认为具有较高的遗传性,是极为严重的精神疾病之一[134]。MITCHELL等[49]通过检测与精神分裂症相关的基因,发现ZDHHC5是影响精神分裂症最显著的5个基因之一,表明ZDHHC5在调节参与神经元发育和突触可塑性的多种神经元蛋白运输中发挥重要作用。此外,SADHUKHAN等[116]还发现ZDHHC5是催化APT1棕榈酰化的关键酶之一,而PPT1缺陷会显著降低这两种酶的水平,进而影响APT1的膜定位。在PPT1缺陷的Cln1?/?小鼠模型中,这种变化导致质膜上H-Ras(一种癌基因)水平升高,进而引起小胶质细胞增殖和星形胶质细胞向A1表型转化。而PPT1模拟小分子NtBuHA能够通过抑制H-Ras信号通路发挥神经保护作用,为突破神经退行性疾病的治疗瓶颈提供了重要的理论基础。 2.4.4 心脏疾病 ZDHHC5的表达在左心室肥大和心力衰竭等心脏疾病中都失调。ZDHHC5可以调控磷酸化酶的棕榈酰化和心脏中重要离子转运蛋白和辅助蛋白的棕榈酰化。MAIN等[117]发现ZDHHC5的表达由于左心室肥大的发作迅速增加,而在缺血心力衰竭模型兔、猪以及人类患者的样本中,ZDHHC5的表达分别为无变化、适度降低以及显著降低。此外,ZDHHC5的底物NCX1在心力衰竭和左心室肥大动物模型中显著减少,但是在人类心力衰竭样本中棕榈酰化水平增加。而另一种ZDHHC5的底物磷酸化酶的棕榈酰化在左心室肥大和心力衰竭中都没有变化。也就是说,ZDHHC5表达和底物棕榈酰化的变化在不同动物模型和人类心力衰竭之间并不一致。尽管ZDHHC5在上述两种心脏病中的表达量发生改变,但这与底物的棕榈酰化没有关系,提示存在上游调节途径驱动包括ZDHHC5在内的底物棕榈酰化的变化,这表明ZDHHC5的棕榈酰化在心脏病发展中具有潜在作用,但由于动物模型的局限性,对其功能的进一步研究仍面临挑战。 2.4.5 炎症 ZDHHC5通过介导关键分子的棕榈酰化在炎症中发挥重要作用。ZDHHC5能够介导NOD1和NOD2更有效地募集到细胞膜上,激活相关的免疫信号通路,从而导致炎症的发生[118]。 此外,细胞焦亡分子Gasdermin D (GSDMD)是炎症小体激活下游细胞因子分泌和细胞焦亡的常见效应物,可经炎症性半胱氨酸蛋白酶切割后产生GSDMD N-末端结构域(GSDMD-NT,GSDMD最活跃的形式)以形成大的质膜孔道。而ZDHHC5通过介导GSDMD的Cys191位点棕榈酰化促进其膜定位和孔道组装,提高焦亡效率,从而在炎症性细胞死亡中发挥核心作用。然而,DU等[48]发现,在炎症小体激活时,仅有棕榈酰化的GSDMD-NT可完成膜定位与孔道组装,这一修饰使孔道形成效率提升3倍以上。其中,ZDHHC5与ZDHHC9是介导该过程的主要转移酶,当炎症小体激活时活性氧水平大幅提升可同步增加全长GSDMD (GSDMD-FL)及其裂解产物的棕榈酰化水平,促进焦亡信号级联放大。裂解的棕榈酰化GSDMD可以快速定位到质膜,而GSDMD-NT可以作为低聚体定位在细胞膜上而不导致细胞死亡,这可能为ZDHHC5对GSDMD进行棕榈酰化提供了条件。 然而,诱发炎症的递质具有多样性,核苷酸结合寡聚结构域样受体蛋白3 (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3,NLRP3)炎症小体也是先天免疫反应的关键递质。ZHENG团队[119]发现ZDHHC5在NLRP3的LRP结构域介导其棕榈酰化,促进NLRP3炎症小体的激活与活动,驱动炎症小体组装。JIANG等[135]进一步研究发现ZDHHC5在NLRP3的C837/C838位点进行棕榈酰化修饰,这一过程对于NLRP3的寡聚化和与丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶7的结合至关重要。这种协同调控机制为治疗过度炎症反应(如脓毒症、自身免疫病)提供了新靶点。 有趣的是,ZHU等[136]设计了一种基于铜、白皮杉醇和透明质酸的多功能纳米材料(Cu-Pic/HA NPs),这种纳米材料通过耗竭细胞内多胺,进而触发了炎症小体的激活,导致半胱氨酸蛋白酶1的激活和GSDMD的裂解,进而诱导焦亡。此外,Cu-Pic/HA NPs诱导的活性氧积累上调了ZDHHC5和ZDHHC9的表达,促进了GSDMD-NT的棕榈酰化及孔道组装效率,进一步增强了焦亡。增强的焦亡和铜死亡导致损伤相关分子模式的释放,重塑了免疫抑制性的肿瘤微环境,激活了抗肿瘤免疫反应。 2.4.6 脂肪肝 脂肪肝是指肝脏细胞堆积过多脂肪而引起的病理反应,是肝脏对各种损伤产生的最常见反应[137]。WANG等[36]研究发现,抗疟药蒿甲醚通过阻断ZDHHC5与蛋白激酶Cδ的结合,抑制其棕榈酰化修饰,从而减少神经炎症信号传导(如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6水平下降),保护促甲状腺激素释放激素神经元功能,促进促甲状腺激素释放激素释放至外周循环。促甲状腺激素释放激素进一步刺激甲状腺激素合成,显著改善肝脏脂质代谢紊乱。此外,他们发现蒿甲醚的代谢改善作用完全依赖于下丘脑小胶质细胞蛋白激酶Cδ的调控,而非肝脏的直接作用。这一研究首次揭示下丘脑小胶质细胞通过蛋白激酶Cδ-神经内分泌轴(促甲状腺激素释放激素-甲状腺激素)调控外周脂代谢的分子机制,为脂肪肝治疗提供了全新靶点。 2.4.7 糖尿病视网膜病变 在糖尿病视网膜病变中,血管内皮细胞的异常炎症是一种经常发生的现象[138]。ZHOU等[37]发现鞘磷脂磷酸二酯酶样3B(sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase acid-like 3B,SMPDL3B)作为一种脂筏酶,能够在糖尿病视网膜病变小鼠视网膜组织和高葡萄糖处理的人视网膜微血管内皮细胞中的表达显著上调,且这种上调与ZDHHC5介导的棕榈酰化修饰密切相关。在糖尿病视网膜病变小鼠模型中,SMPDL3B的敲除不仅加剧了视网膜病变,还激活了核因子κB/NLRP3炎症通路,进一步加重了视网膜的炎症反应。这一研究揭示了SMPDL3B的棕榈酰化修饰在糖尿病视网膜病变进展中的保护机制并提出其作为糖尿病视网膜病变治疗新靶点的潜力。"

| [1] SONG L, LUO ZQ. Post-translational regulation of ubiquitin signaling. J Cell Biol. 2019;218(6):1776-1786. [2] CHAMBERLAIN LH, SHIPSTON MJ. The physiology of protein S-acylation. Physiol Rev. 2015;95(2):341-376. [3] DE I, SADHUKHAN S. Emerging Roles of DHHC-mediated Protein S-palmitoylation in Physiological and Pathophysiological Context. Eur J Cell Biol. 2018;97(5):319-338. [4] DENNIS KMJH, HEATHER LC. Post-translational palmitoylation of metabolic proteins. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1122895. [5] ZHOU L, HE X, WANG L, et al. Palmitoylation restricts SQSTM1/p62-mediated autophagic degradation of NOD2 to modulate inflammation. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(8):1541-1551. [6] PEI S, PIAO HL. Exploring Protein S-Palmitoylation: Mechanisms, Detection, and Strategies for Inhibitor Discovery. ACS Chem Biol. 2024;19(9): 1868-1882. [7] S MESQUITA F, ABRAMI L, LINDER ME, et al. Mechanisms and functions of protein S-acylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(6):488-509. [8] ZHOU B, HAO Q, LIANG Y, et al. Protein palmitoylation in cancer: molecular functions and therapeutic potential. Mol Oncol. 2023;17(1):3-26. [9] SHIMELL JJ, GLOBA A, SEPERS MD, et al. Regulation of hippocampal excitatory synapses by the Zdhhc5 palmitoyl acyltransferase. J Cell Sci. 2021;134(9): jcs254276. [10] KONG Y, LIU Y, LI X, et al. Palmitoylation landscapes across human cancers reveal a role of palmitoylation in tumorigenesis. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):826. [11] LI M, ZHANG L, CHEN CW. Diverse Roles of Protein Palmitoylation in Cancer Progression, Immunity, Stemness, and Beyond. Cells. 2023;12(18):2209. [12] LIN DT, CONIBEAR E. Enzymatic protein depalmitoylation by acyl protein thioesterases. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015; 43(2):193-198. [13] HE Q, QU M, SHEN T, et al. Control of mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes by protein S-palmitoylation: Novel therapeutic targets for neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;87:101920. [14] ZHAO Y, HE A, ZHU F, et al. Integrating genome-wide association study and expression quantitative trait locus study identifies multiple genes and gene sets associated with schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018;81:50-54. [15] TANG B, KANG W, DONG Q, et al. Research progress on S-palmitoylation modification mediated by the ZDHHC family in glioblastoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024;12:1413708. [16] GONG M, FAN X, YU H, et al. Loss of p53 Concurrent with RAS and TERT Activation Induces Glioma Formation. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(6):3452-3463. [17] WANG Y, ZHANG S, HE H, et al. Repositioning Lomitapide to block ZDHHC5-dependant palmitoylation on SSTR5 leads to anti-proliferation effect in preclinical pancreatic cancer models. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9(1):60. [18] ZHANG Y, LI F, FU K, et al. Potential Role of S-Palmitoylation in Cancer Stem Cells of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:734897. [19] HAO JW, WANG J, GUO H, et al. CD36 facilitates fatty acid uptake by dynamic palmitoylation-regulated endocytosis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):4765. [20] WOODLEY KT, COLLINS MO. Regulation and function of the palmitoyl-acyltransferase ZDHHC5. FEBS J. 2021;288(23):6623-6634. [21] QIAN YR, ZHAO YJ, ZHANG F. Protein palmitoylation: biological functions, disease, and therapeutic targets. MedComm (2020). 2025;6(3):e70096. [22] PUTILINA T, WONG P, GENTLEMAN S. The DHHC domain: a new highly conserved cysteine-rich motif. Mol Cell Biochem. 1999;195(1-2):219-226. [23] LINDER ME, DESCHENES RJ. Model organisms lead the way to protein palmitoyltransferases. J Cell Sci. 2004; 117(Pt 4):521-526. [24] FUKATA M, FUKATA Y, ADESNIK H, et al. Identification of PSD-95 palmitoylating enzymes. Neuron. 2004;44(6):987-996. [25] KOKKOLA T, KRUSE C, ROY-POGODZIK EM, et al. Somatostatin receptor 5 is palmitoylated by the interacting ZDHHC5 palmitoyltransferase. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(17):2665-2670. [26] TIAN H, LU JY, SHAO C, et al. Systematic siRNA Screen Unmasks NSCLC Growth Dependence by Palmitoyltransferase DHHC5. Mol Cancer Res. 2015;13(4):784-794. [27] BRIGIDI GS, SANTYR B, SHIMELL J, et al. Activity-regulated trafficking of the palmitoyl-acyl transferase DHHC5. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8200. [28] WANG J, HAO JW, WANG X, et al. DHHC4 and DHHC5 Facilitate Fatty Acid Uptake by Palmitoylating and Targeting CD36 to the Plasma Membrane. Cell Rep. 2019; 26(1):209-221.e5. [29] WOODLEY KT, COLLINS MO. S-acylated Golga7b stabilises DHHC5 at the plasma membrane to regulate cell adhesion. EMBO Rep. 2019;20(10):e47472. [30] KO PJ, WOODROW C, DUBREUIL MM, et al. A ZDHHC5-GOLGA7 Protein Acyltransferase Complex Promotes Nonapoptotic Cell Death. Cell Chem Biol. 2019;26(12):1716-1724.e9. [31] CHEN JJ, MARSDEN AN, SCOTT CA, et al. DHHC5 Mediates β-Adrenergic Signaling in Cardiomyocytes by Targeting Gα Proteins. Biophys J. 2020;118(4):826-835. [32] VARMA P, LYBRAND ZR, ANTOPIA MC, et al. Novel Targets of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein in Human Fetal Brain Development Suggest Early Pregnancy Vulnerability. Front Neurosci. 2021;14:614680. [33] GÖK C, ROBERTSON AD, FULLER W. Insulin-induced palmitoylation regulates the Cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger NCX1. Cell Calcium. 2022;104:102567. [34] DA SILVA-BUTTKUS P, SPIELMANN N, KLEIN-RODEWALD T, et al. Knockout mouse models as a resource for the study of rare diseases. Mamm Genome. 2023;34(2):244-261. [35] OZKAN NE, YIGIT BN, DEGIRMENCI BS, et al. Cell cycle-dependent palmitoylation of protocadherin 7 by ZDHHC5 promotes successful cytokinesis. J Cell Sci. 2023; 136(6):jcs260266. [36] WANG YH, CHEN X, BAI YZ, et al. Palmitoylation of PKCδ by ZDHHC5 in hypothalamic microglia presents as a therapeutic target for fatty liver disease. Theranostics. 2024;14(3):988-1009. [37] ZHOU Y, YUE S, LI L, et al. SMPDL3B is palmitoylated and stabilized by ZDHHC5, and its silencing aggravates diabetic retinopathy of db/db mice: Activation of NLRP3/NF-κB pathway. Cell Signal. 2024;116:111064. [38] LIU Z, XIAO M, MO Y, et al. Emerging roles of protein palmitoylation and its modifying enzymes in cancer cell signal transduction and cancer therapy. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(8):3447-3457. [39] PENG J, LIANG D, ZHANG Z. Palmitoylation of synaptic proteins: roles in functional regulation and pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024;29(1):108. [40] LIN X, SHI Y, ZHAN Y, et al. Advances of Protein Palmitoylation in Tumor Cell Deaths. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(23):5503. [41] LIAO D, HUANG Y, LIU D, et al. The role of s-palmitoylation in neurological diseases: implication for zDHHC family. Front Pharmacol. 2024;14:1342830. [42] BREUSEGEM SY, SEAMAN MNJ. Genome-wide RNAi screen reveals a role for multipass membrane proteins in endosome-to-golgi retrieval. Cell Rep. 2014;9(5):1931-1945. [43] WON SJ, CHEUNG SEE KIT M, MARTIN BR. Protein depalmitoylases. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018;53(1):83-98. [44] ZHANG N, ZHANG J, YANG Y, et al. A palmitoylation-depalmitoylation relay spatiotemporally controls GSDMD activation in pyroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2024;26(5):757-769. [45] SHI X, LI X, XU Z, et al. ABHD16A Negatively Regulates the Palmitoylation and Antiviral Function of IFITM Proteins. mBio. 2022; 13(6):e0228922. [46] MCCLELLAN B, WILSON CN, BRENNER AJ, et al. Flotillin-1 palmitoylation is essential for its stability and subsequent tumor promoting capabilities. Oncogene. 2024;43(14):1063-1074. [47] CARBONNELLE D, LUU TH, CHAILLOU C, et al. LXR Activation Down-regulates Lipid Raft Markers FLOT2 and DHHC5 in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2017; 37(8):4067-4073. [48] DU G, HEALY LB, DAVID L, et al. ROS-dependent S-palmitoylation activates cleaved and intact gasdermin D. Nature. 2024;630(8016):437-446. [49] MITCHELL DA, VASUDEVAN A, LINDER ME, et al. Protein palmitoylation by a family of DHHC protein S-acyltransferases. J Lipid Res. 2006;47(6):1118-1127. [50] OHNO Y, KIHARA A, SANO T, et al. Intracellular localization and tissue-specific distribution of human and yeast DHHC cysteine-rich domain-containing proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1761(4):474-483. [51] ZHOU Q, LIN H, WANG S, et al. The ER-associated protein ZDHHC1 is a positive regulator of DNA virus-triggered, MITA/STING-dependent innate immune signaling. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;16(4):450-461. [52] GREAVES J, CARMICHAEL JA, CHAMBERLAIN LH. The palmitoyl transferase DHHC2 targets a dynamic membrane cycling pathway: regulation by a C-terminal domain. Mol Biol Cell. 2011;22(11):1887-1895. [53] SHARMA C, YANG XH, HEMLER ME. DHHC2 affects palmitoylation, stability, and functions of tetraspanins CD9 and CD151. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19(8):3415-3425. [54] ZEIDMAN R, BUCKLAND G, CEBECAUER M, et al. DHHC2 is a protein S-acyltransferase for Lck. Mol Membr Biol. 2011;28(7-8):473-486. [55] GORLEKU OA, BARNS AM, PRESCOTT GR, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum localization of DHHC palmitoyltransferases mediated by lysine-based sorting signals. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(45):39573-39584. [56] EBERSOLE B, PETKO J, WOLL M, et al. Effect of C-Terminal S-Palmitoylation on D2 Dopamine Receptor Trafficking and Stability. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0140661. [57] TSUTSUMI R, FUKATA Y, NORITAKE J, et al. Identification of G protein alpha subunit-palmitoylating enzyme. Mol Cell Biol. 2009; 29(2):435-447. [58] BADAWY SMM, OKADA T, KAJIMOTO T, et al. DHHC5-mediated palmitoylation of S1P receptor subtype 1 determines G-protein coupling. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16552. [59] LAKKARAJU AK, ABRAMI L, LEMMIN T, et al. Palmitoylated calnexin is a key component of the ribosome-translocon complex. EMBO J. 2012;31(7):1823-1835. [60] ABRAMI L, DALLAVILLA T, SANDOZ PA, et al. Identification and dynamics of the human ZDHHC16-ZDHHC6 palmitoylation cascade. Elife. 2017;6:e27826. [61] PEDRAM A, RAZANDI M, DESCHENES RJ, et al. DHHC-7 and -21 are palmitoylacyltransferases for sex steroid receptors. Mol Biol Cell. 2012; 23(1):188-199. [62] MESQUITA FS, ABRAMI L, SERGEEVA O, et al. S-acylation controls SARS-CoV-2 membrane lipid organization and enhances infectivity. Dev Cell. 2021;56(20):2790-2807.e8. [63] SWARTHOUT JT, LOBO S, FARH L, et al. DHHC9 and GCP16 constitute a human protein fatty acyltransferase with specificity for H- and N-Ras. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(35):31141-31148. [64] ADACHI N, HESS DT, MCLAUGHLIN P, et al. S-Palmitoylation of a Novel Site in the β2-Adrenergic Receptor Associated with a Novel Intracellular Itinerary. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(38):20232-20246. [65] ZHANG F, DI Y, LI J, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of human Aph2 gene, involved in AP-1 regulation by interaction with JAB1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006; 1759(11-12):514-525. [66] GOYTAIN A, HINES RM, QUAMME GA. Huntingtin-interacting proteins, HIP14 and HIP14L, mediate dual functions, palmitoyl acyltransferase and Mg2+ transport. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(48):33365-33374. [67] HUANG K, YANAI A, KANG R, et al. Huntingtin-interacting protein HIP14 is a palmitoyl transferase involved in palmitoylation and trafficking of multiple neuronal proteins. Neuron. 2004;44(6):977-986. [68] STOWERS RS, ISACOFF EY. Drosophila huntingtin-interacting protein 14 is a presynaptic protein required for photoreceptor synaptic transmission and expression of the palmitoylated proteins synaptosome-associated protein 25 and cysteine string protein. J Neurosci. 2007;27(47):12874-12883. [69] SHI C, YANG X, LIU Y, et al. ZDHHC18 negatively regulates cGAS-mediated innate immunity through palmitoylation. EMBO J. 2022;41(11):e109272. [70] BAUMGART F, CORRAL-ESCARIZ M, PÉREZ-GIL J, et al. Palmitoylation of R-Ras by human DHHC19, a palmitoyl transferase with a CaaX box. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1798(3):592-604. [71] RANA MS, KUMAR P, LEE CJ, et al. Fatty acyl recognition and transfer by an integral membrane S-acyltransferase. Science. 2018;359(6372):eaao6326. [72] RUNKLE KB, KHARBANDA A, STYPULKOWSKI E, et al. Inhibition of DHHC20-Mediated EGFR Palmitoylation Creates a Dependence on EGFR Signaling. Mol Cell. 2016; 62(3):385-396. [73] TIAN L, MCCLAFFERTY H, KNAUS HG, et al. Distinct acyl protein transferases and thioesterases control surface expression of calcium-activated potassium channels. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287(18):14718-14725. [74] SCHEK N, LEE JY, BURSLEM GM, et al. Chemical probe mediated visualization of protein S-palmitoylation in patient tissue samples. Front Physiol. 2023;14: 1063247. [75] ZHOU B, WANG Y, YAN Y, et al. Low-Background Acyl-Biotinyl Exchange Largely Eliminates the Coisolation of Non-S-Acylated Proteins and Enables Deep S-Acylproteomic Analysis. Anal Chem. 2019;91(15):9858-9866. [76] MOTIPALLY SI, MYERS B, SECHREST ER, et al. A Modified Acyl-RAC Method of Isolating Retinal Palmitoyl Proteome for Subsequent Detection through LC-MS/MS. Bio Protoc. 2023;13(8):e4654. [77] LI X, SHEN L, XU Z, et al. Protein Palmitoylation Modification During Viral Infection and Detection Methods of Palmitoylated Proteins. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12:821596. [78] FORRESTER MT, THOMPSON JW, FOSTER MW, et al. Proteomic analysis of S-nitrosylation and denitrosylation by resin-assisted capture. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27(6):557-559. [79] GAL J, BONDADA V, MASHBURN CB, et al. S-acylation regulates the membrane association and activity of Calpain-5. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2022; 1869(9):119298. |
| [1] | Zhang Xianxu, Ma Zhong, Liu Xin, Huang Lei, Shen Wenxiang, Luo Zhiqiang . Lumbar fusion combined with unilateral fixation for lumbar degenerative diseases: biomechanics, technical evolution, and clinical applications [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2334-2342. |
| [2] | Wen Fayan, Li Yan, Qiang Tianming, Yang Chen, Shen Linming, Li Yadong, Liu Yongming. Unilateral biportal endoscopic technology for treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: global research status and changing trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2380-2390. |
| [3] | Fu Lyupeng, Yu Peng, Liang Guoyan, Chang Yunbing. Electroactive materials applied in spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2113-2123. |
| [4] | Yang Xuetao, Zhu Menghan, Zhang Chenxi, Sun Yimin, Ye Ling. Applications and limitations of antioxidant nanomaterials in oral cavity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
| [5] | Chen Yulin, He Yingying, Hu Kai, Chen Zhifan, Nie Sha Meng Yanhui, Li Runzhen, Zhang Xiaoduo , Li Yuxi, Tang Yaoping. Effect and mechanism of exosome-like vesicles derived from Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. in preventing and treating atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1768-1781. |
| [6] | Tao Daiju, Su Haiyu, Wang Yuqi, Shen Zhiqiang, He Bo . Construction and identification of stable PC12 cell lines with high/low expression of miR-122-5p [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1790-1799. |
| [7] | Liu Anting, Lu Jiangtao, Zhang Wenjie, He Ling, Tang Zongsheng, Chen Xiaoling. Regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase by platelet lysate inhibits cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1800-1807. |
| [8] | Fan Yongjing, Jin Wulong, Bai Haoyu, Ma Ping, Wang Shu. Role and mechanism of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth in tissue regeneration and disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1850-1857. |
| [9] | Lai Jiaming, , Song Yuling, Chen Zixi, Wei Jinghuan, Cai Hao, , Li Guoquan, . Screening of diagnostic markers for endothelial cell Senescence in mice with radiation-induced heart disease and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1450-1463. |
| [10] | Sun Yaotian, Xu Kai, Wang Peiyun. Potential mechanisms by which exercise regulates iron metabolism in immune inflammatory diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1486-1498. |
| [11] | You Huijuan, Wu Shuzhen, Rong Rong, Chen Liyuan, Zhao Yuqing, Wang Qinglu, Ou Xiaowei, Yang Fengying. Macrophage autophagy in lung diseases: two-sided effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526. |
| [12] | Liu Huan, Zeng Shaopeng, Chen Jun, He Linqian, Yang Ying, Zhang Jing. Aging-related dysregulation of glucose metabolism: crossroads of cancer and neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1527-1538. |
| [13] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [14] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Zhao Yuxin, Liu Xihua. Effects of different neuromodulatory stimulation modalities on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [15] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||