Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (13): 3474-3484.doi: 10.12307/2026.120
Natural killer cells in treatment of prostate cancer: a bibliometric analysis from basic research to clinical applications
Jiang Linglong1, 2, Zhang Yuan1, 2, Shen Yuwei1, Pan Jiawei1, Sun Yangyang1, Zhu Jundong1, Fan Min1, Shi Jian1
- 1Department of Urology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Suzhou Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Accepted:2025-07-10Online:2026-05-08Published:2025-12-26 -
Contact:Shi Jian, MS, Assistant researcher, Department of Urology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Jiang Linglong, Department of Urology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China; Suzhou Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Changzhou Municipal Health Commission Major Project, No. ZD202209 (to FM); Changzhou Applied Basic Research Project, No. CJ20220203 (to FM); Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation (General) Project, No. BK20231188 (to FM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Linglong, Zhang Yuan, Shen Yuwei, Pan Jiawei, Sun Yangyang, Zhu Jundong, Fan Min, Shi Jian. Natural killer cells in treatment of prostate cancer: a bibliometric analysis from basic research to clinical applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3474-3484.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
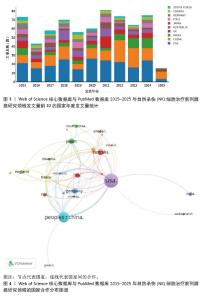
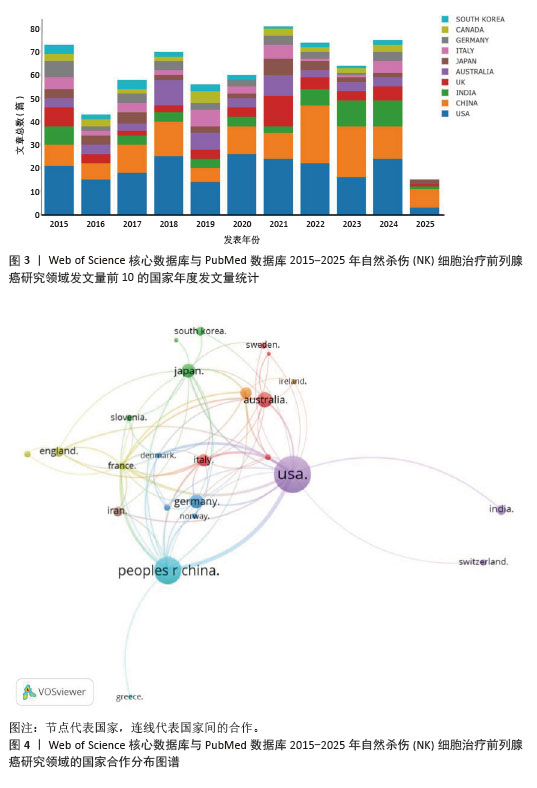
2.2 国家分析 参与相关研究的国家共计57个,历年文章数量变化以及国家发文占比见图3。发文量前3的国家为美国(247篇,34.9%)、中国(194篇,27.9%)、澳大利亚(56篇,6.8%);该领域中心性居于前3位的国家分别为美国(0.94)、中国(0.41)、澳大利亚(0.39)。运行VOS viewer软件将频次阈值设置为4,创建国家合作关系网络,见图4。图中共计26个节点,共同组成8个集群,74个链接,总链接强度为224。由国家网络图可知,美国与中国是进行相关研究的主要国家,且合作关系紧密。欧洲国家英国、法国等,北美洲国家美国等和亚洲国家中国等相互之间保持密切的合作关系,也有一些国家例如泰国、卢森堡以及一些南美洲国家等在该领域研究上合作较少。在发文量前10的国家中,4个来自欧洲,3个来自亚洲,2个来自北美,1个来自澳洲,由此可见该领域研究较为活跃的国家为欧洲、亚洲和北美洲,而南美洲和非洲科研能力相对较弱。"

2.3 文献发文机构合作分析 根据机构网络分析,发表文献的机构有821所。发表文献量排名前3的机构分别是National Institutes of Health (57篇),Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (20篇),University of California(11篇);该领域中心性居于前3位的机构分别是Cornell University(0.19)、Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (0.18)、Cancer Research UK(0.06)。由合作关系图可知,大学是该领域主要研究力量,拥有极高的科研水平和科研活力。此外,美国的机构在世界范围内有较强的影响力,与多个国家合作密切,合作范围最广,见图5。"

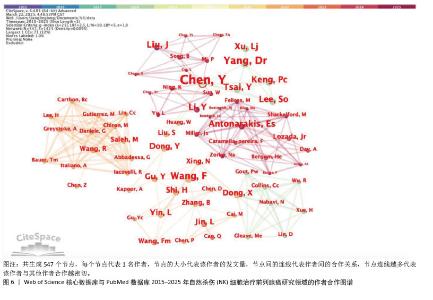
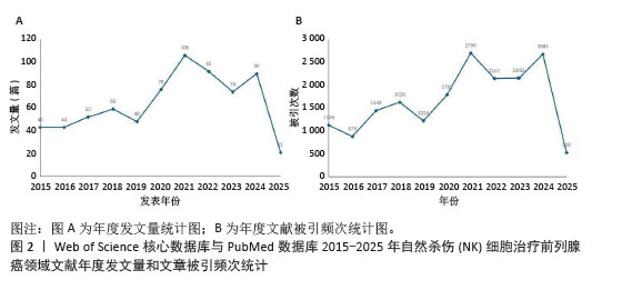
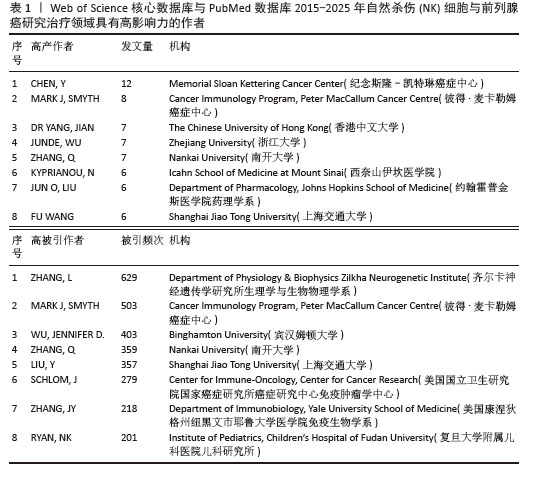
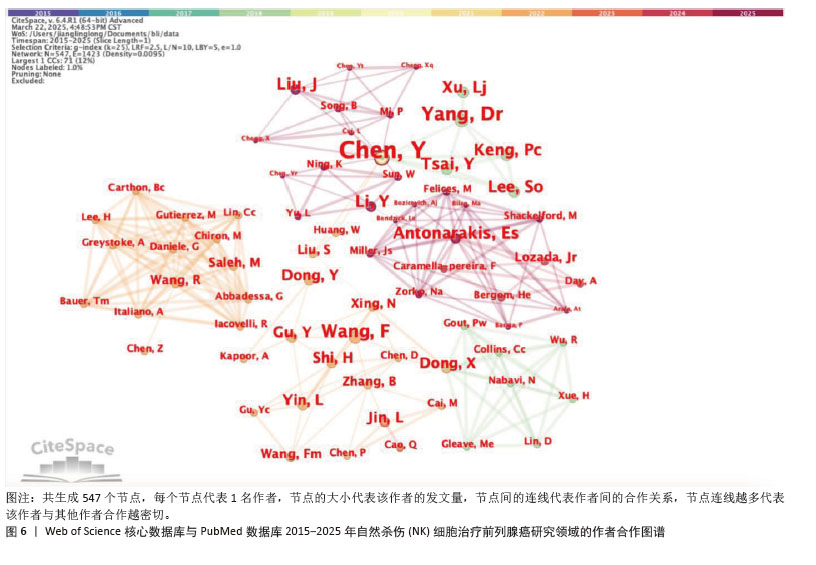
2.4 高影响力作者可视化分析 通过CiteSpace生成作者共现图(图6),可见文献图谱N=547,E=1 423,说明共有547名作者之间有合作关系,合作了1 423次。根据检索出的文献,相关领域的作者共有2 685人。发表文献量排名前3的作者为Chen, Y (12篇),Mark J, Smyth (8篇),Dr YANG, Jian (7篇);而发表文献被引频次排名前3的作者为Zhang L(629次),Mark J, Smyth(503次),Wu, Jennifer d.(403次)。表1列举了被引频次和发文量前8的作者,他们的研究对于该领域的研究进展具有更加积极的意义。通过表格可以看出在该领域中美国的研究人员无论是被引频次还是发文量都居于领先地位,表明美国学者在该领域具有较高水平,是该领域的研究 主体。"
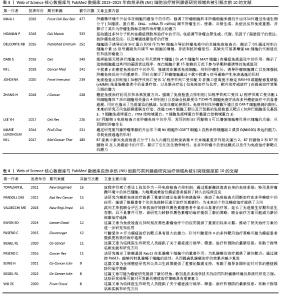
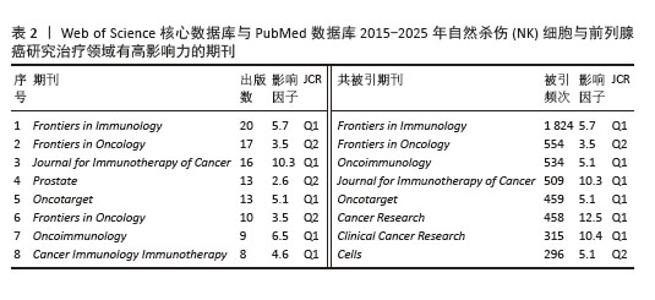
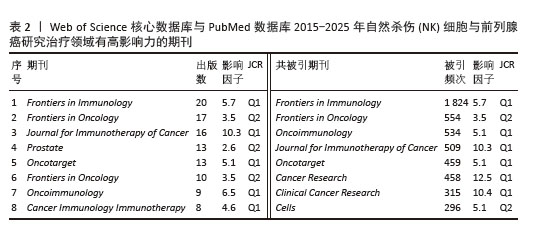
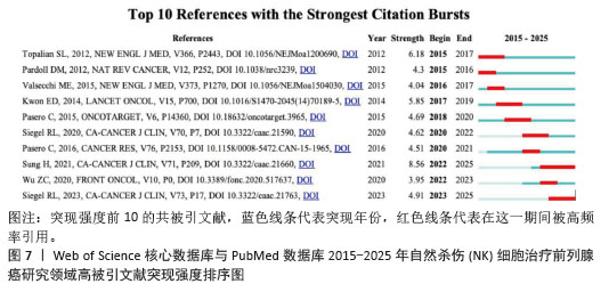
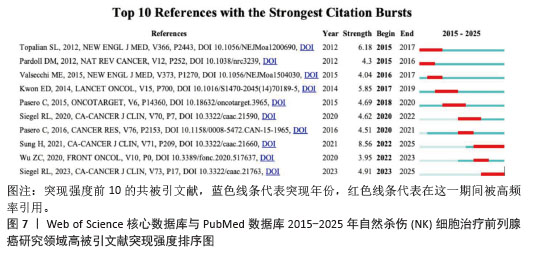
2.6 文献分析 2.6.1 文献共被引分析 文献共被引分析指1篇文献被其他文献引用的次数。文献共被引频次显示1篇文章的学术价值,文章被引用次数越多证明这篇文献的学术价值越高。通过文献共被引分析可以反映该领域的主要研究主体和主要研究策略。使用VOS viewer软件进行共被引频次可视化,得到文献共被引频次前10,见表3。表中可以看出肿瘤微环境及相关分子机制是肿瘤免疫治疗的新靶点和新趋势,具有高影响力,受到广泛关注。 2.6.2 文献突现分析 利用Citespace软件分析2015-2025年共被引突现强度前10的文献,见表4和图7,体现出一段时间内被引用频次最高的文献。其中突现强度最大的文献为来自约翰·霍普金斯大学Kimmel癌症中心的Topalian SL学者,突现强度为6.18。研究了免疫检查点抑制剂的作用机制,反映出肿瘤微环境在肿瘤免疫逃逸中发挥出重要作用,对于肿瘤微环境如何影响肿瘤免疫逃逸的研究是值得关注的研究热点,通过研究肿瘤微环境来抑制肿瘤的免疫逃逸和加强免疫细胞的杀伤能力是当下的主流研究趋势。"
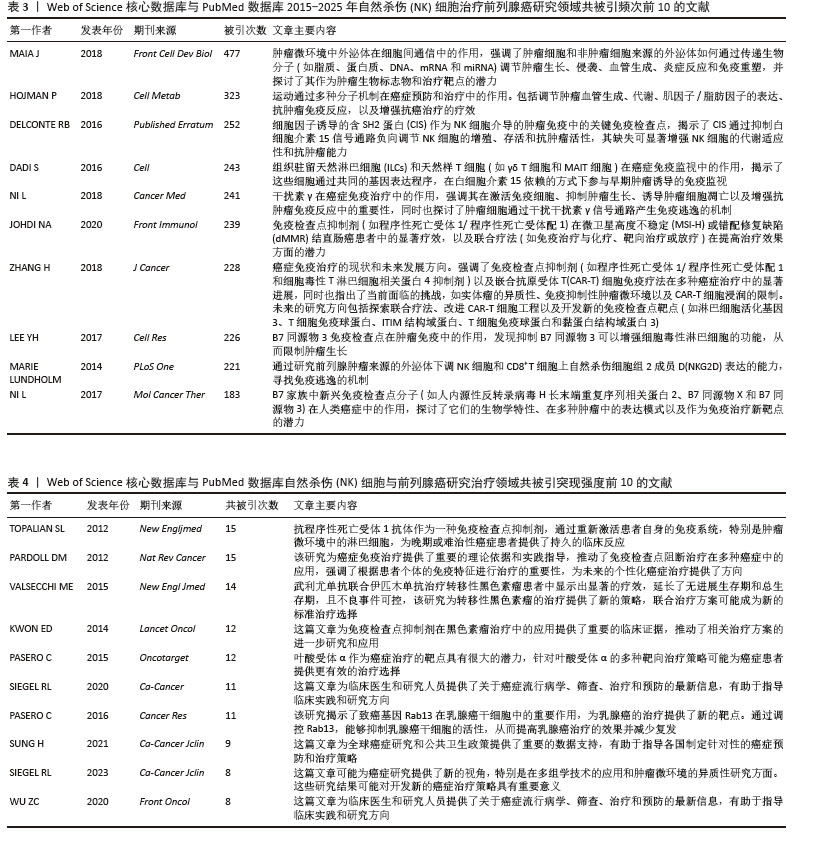
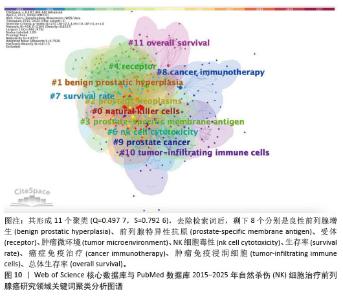
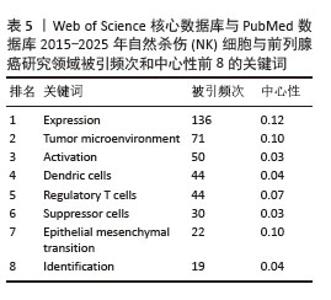
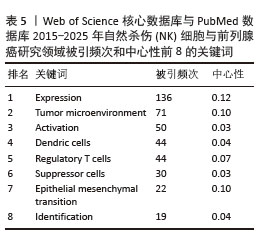
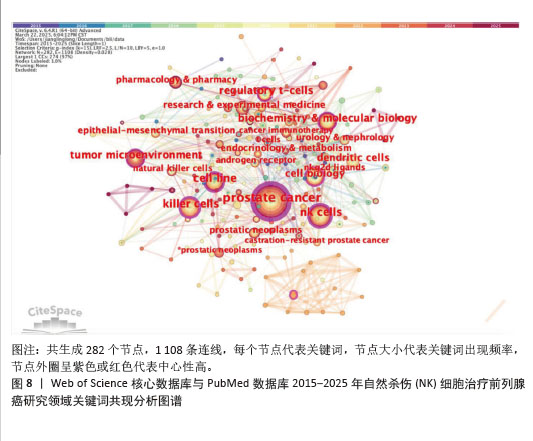
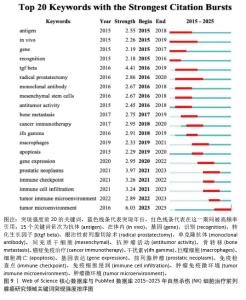
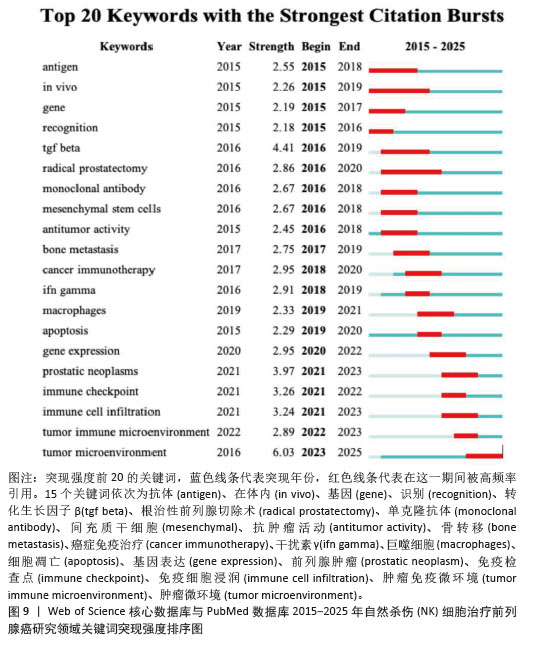
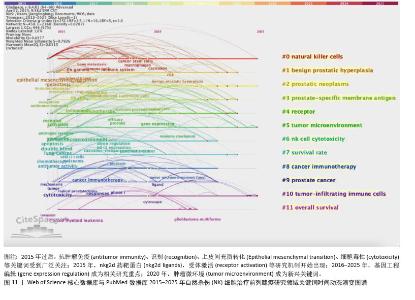
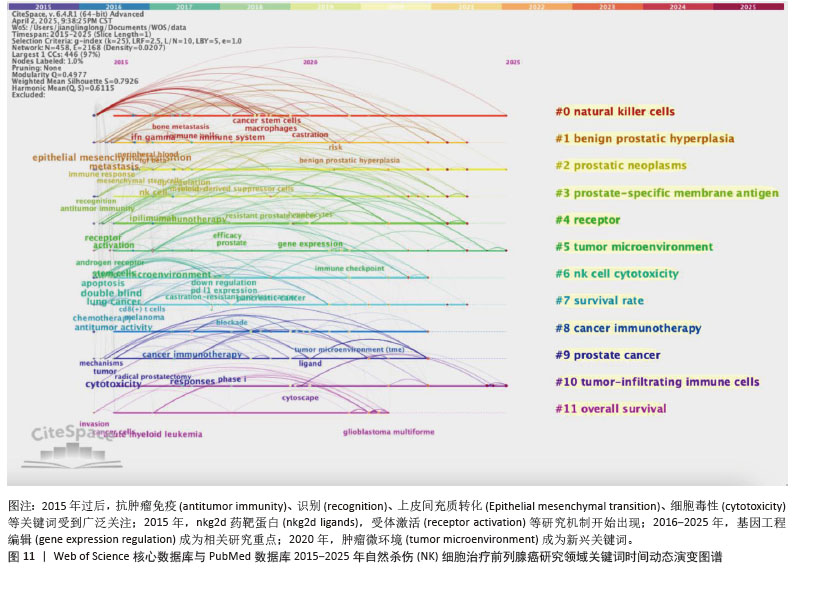
2.7.3 关键词聚类分析 对纳入关键词进行聚类分析,见图10。文献共形成11个聚类(Q=0.497 7,S=0.792 6)。文献聚类图代表性关键词为刺激NK细胞增殖与激活的细胞因子、肿瘤微环境对NK细胞的作用。该领域研究的热点关键词为NK细胞的代谢调控、NK细胞与其他免疫细胞的相互结合、NK细胞的异体移植。时间线图可以直观地展现各聚类发展的时间跨度和研究进展,见图11。由图可知,2015年过后,抗肿瘤免疫(antitumor immunity)、识别(recognition)、上皮间充质转化(Epithelial mesenchymal transition)、细胞毒性(cytotoxicity)等关键词受到广泛关注;2015年,nkg2d药靶蛋白(nkg2d ligands),受体激活(receptor activation)等研究机制开始出现;2016-2025年,基因编辑调控(gene expression regulation)成为相关研究重点;2020年以来,肿瘤微环境(tumor microenvironment)成为新兴关键词。这表明该领域的研究热点从单纯的研究NK细胞对于前列腺肿瘤细胞杀伤以及相关的分子机制,并通过靶向药物单纯加强NK细胞的细胞活性和对肿瘤细胞的杀伤能力,逐渐演变为通过工程化基因改造来调控NK细胞的活性和对肿瘤细胞的杀伤能力,同时肿瘤微环境对于肿瘤细胞的免疫逃逸以及抑制免疫细胞活性也开始成为该领域关注的研究热点,如何通过影响肿瘤微环境来抑制肿瘤细胞的免疫逃逸以及加强免疫细胞的活性和靶向性已经成为当下值得研究和探讨的问题。"
| [1] SIEGEL RL, GIAQUINTO AN, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(1):12-49. [2] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. [3] JAMES ND, TANNOCK I, N’DOW J, et al. The Lancet Commission on prostate cancer: planning for the surge in cases. Lancet. 2024;403(10437):1683-1722. [4] 张正,张莉芳,刘彦廷,等.《2022全球癌症统计报告》解读[J].中国医院统计, 2024,31(5):393-400. [5] 鲁欣,蒋栋铭,胡明,等.2004—2018年全国前列腺癌死亡率的流行特征及时间趋势[J].上海预防医学,2021,33(10):899-904. [6] RUAN X, ZHANG N, WANG D, et al. The Impact of Prostate-Specific Antigen Screening on Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality in China: 13-Year Prospective Population-Based Cohort Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024;10:e47161. [7] HIGANO CS, SCHELLHAMMER PF, SMALL EJ, et al. Integrated data from 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials of active cellular immunotherapy with sipuleucel-T in advanced prostate cancer. Cancer. 2009; 115(16):3670-3679. [8] 汪清,艾克拜尔·吾曼尔,王胜军,等.三种经尿道前列腺切除术治疗良性前列腺增生的疗效比较[J].现代泌尿外科杂志, 2008,13(1):44-47. [9] CHOI E, BUIE J, CAMACHO J, et al. Evolution of Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) and Its New Emerging Modalities in Prostate Cancer: An Update for Practicing Urologists, Clinicians and Medical Providers. Res Rep Urol. 2022;14:87-108. [10] 秦庆伟,李那,王胜,等.多西他赛化疗对局限期高危前列腺癌疗效及安全性的荟萃分析[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2019, 40(11):853-858. [11] 沃奇军,祁小龙,刘锋,等.微创根治性前列腺切除术后非计划再次手术的原因分析及应对策略[J].中华泌尿外科杂志, 2019,40(12):905-908. [12] 杨文博,张斌,吴佳慧,等.去势抵抗性前列腺癌免疫微环境的研究现状与治疗方向[J].中国癌症杂志,2023,33(10): 945-953. [13] UNAL B, KUZU OF, JIN Y, et al. Targeting IRE1α reprograms the tumor microenvironment and enhances anti-tumor immunity in prostate cancer. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):8895. [14] LYU A, FAN Z, CLARK M, et al. Evolution of myeloid-mediated immunotherapy resistance in prostate cancer. Nature. 2025;637(8048):1207-1217. [15] LIU S, GALAT V, GALAT Y, et al. NK cell-based cancer immunotherapy: from basic biology to clinical development. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):7. [16] ABEL AM, YANG C, THAKAR MS, et al. Natural Killer Cells: Development, Maturation, and Clinical Utilization. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1869. [17] PHUNG SK, ZORKO NA, SOIGNIER Y, et al. A PSMA-Targeted Tri-Specific Killer Engager Enhances NK Cell Cytotoxicity against Prostate Cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 2025;13(2):258-272. [18] CÓZAR B, GREPPI M, CARPENTIER S, et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Natural Killer Cells. Cancer Discov. 2021;11(1):34-44. [19] 郑淑珍.近十年我国网络舆情研究现状及热点趋势:基于知识图谱的可视化分析[J].东南传播,2018(11):70-74. [20] WANG F, WU L, YIN L, et al. Combined treatment with anti-PSMA CAR NK-92 cell and anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody enhances the antitumour efficacy against castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Transl Med. 2022;12(6):e901. [21] HUSAIN Z, HUANG Y, SETH P, et al. Tumor-derived lactate modifies antitumor immune response: effect on myeloid-derived suppressor cells and NK cells. J Immunol. 2013;191(3):1486-1495. [22] JIANG T, ZHOU C, REN S. Role of IL-2 in cancer immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5(6):e1163462. [23] ROSENBERG SA, LOTZE MT, MUUL LM, et al. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985;313(23):1485-1492. [24] DEVILLIER R, CHRÉTIEN AS, PAGLIARDINI T, et al. Mechanisms of NK cell dysfunction in the tumor microenvironment and current clinical approaches to harness NK cell potential for immunotherapy. J Leukoc Biol. 2021;109(6):1071-1088. [25] MANTESSO S, GEERTS D, SPANHOLTZ J, et al. Genetic Engineering of Natural Killer Cells for Enhanced Antitumor Function. Front Immunol. 2020;11:607131. [26] DAHER M, REZVANI K. Next generation natural killer cells for cancer immunotherapy: the promise of genetic engineering. Curr Opin Immunol. 2018;51: 146-153. [27] WU SY, FU T, JIANG YZ, et al. Natural killer cells in cancer biology and therapy. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):120. [28] KWOK M, LIU R, FANG C, et al. IL-2 transpresentation promotes human NK cell expansion and cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 2011;186(11):6175-6184. [29] 吴天根.Fidarestat通过下调AKR1B10促进NK细胞糖抗肝癌作用的研究[D].昆明:昆明医科大学,2021. [30] JIA H, YANG H, XIONG H, et al. NK cell exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1303605. [31] ZHENG X, QIAN Y, FU B, et al. Mitochondrial fragmentation limits NK cell-based tumor immunosurveillance. Nat Immunol. 2019; 20(12):1656-1667. [32] TERRÉN I, ORRANTIA A, VITALLÉ J, et al. NK Cell Metabolism and Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2019; 10:2278. [33] PORTALE F, CARRIERO R, IOVINO M, et al. C/EBPβ-dependent autophagy inhibition hinders NK cell function in cancer. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):10343. [34] POZNANSKI SM, SINGH K, RITCHIE TM, et al. Metabolic flexibility determines human NK cell functional fate in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab. 2021;33(6):1205-1220.e5. [35] 刘敏.人外周血来源自然杀伤细胞的高效制备及其细胞毒活性表征的研究[D].北京:中国医学科学院,2021. [36] KNORR DA, NI Z, HERMANSON D, et al. Clinical-scale derivation of natural killer cells from human pluripotent stem cells for cancer therapy. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(4):274-283. [37] 原艺佳.基于期刊论文的国内外学术评价研究比较[D].郑州:郑州大学,2020. [38] 王红霞,潘俊斐,蒋丹,等.嵌合抗原受体T(CAR-T)细胞体外培养体系及慢病毒侵染条件的优化[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2020,36(5):390-397. [39] 张红,吴昊,姜磊,等.人NK细胞的体外扩增及其基因表达通路的研究[J].精准医学杂志,2022,37(2):170-174. [40] 姜红堃.原发性肾病综合征激素冲击治疗前后白细胞介素13及白细胞介素18基因表达[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2004. [41] FANG F, XIE S, CHEN M, et al. Advances in NK cell production. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022;19(4):460-481. [42] YAN J, ZHANG C, XU Y, et al. GPR34 is a metabolic immune checkpoint for ILC1-mediated antitumor immunity. Nat Immunol. 2024;25(11):2057-2067. [43] GONG Y, KLEIN WOLTERINK RGJ, WANG J, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor natural killer (CAR-NK) cell design and engineering for cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2021; 14(1):73. [44] 卢鹏,纪猛,王皓,等.自然杀伤细胞免疫疗法在恶性肿瘤治疗中的研究进展[J].浙江理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022,47(6):915-922. [45] TAKAHASHI K, YAMANAKA S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006; 126(4):663-676. [46] VAN OOST K, QUINE TA, GOVERS G, et al. The impact of agricultural soil erosion on the global carbon cycle. Science. 2007; 318(5850):626-629. [47] LIU Y, CHAI L, LIU Y, et al. Generation of functional natural killer cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8(6):648-654. [48] SAITO S, NISHIMURA S, ARAI Y, et al. Generation of CAR-expressing natural killer cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2016;65(11):1477-1486. |
| [1] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Yuping, Ba Yinying, Chi Li, Wang Wenjuan, Wang Jiajia. Research context and trend of TBK1 in autoimmunity, signaling pathways, gene expression, tumor prevention and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Zhu Xiaolong, Zhang Wei, Yang Yang. Visualization analysis of research hotspots and cutting-edge information in the field of intervertebral disc regeneration and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2391-2402. |
| [3] | Wen Fayan, Li Yan, Qiang Tianming, Yang Chen, Shen Linming, Li Yadong, Liu Yongming. Unilateral biportal endoscopic technology for treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases: global research status and changing trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2380-2390. |
| [4] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [5] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| [6] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [7] | Peng Hao, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. A visual analysis of research hotspots of H-type vessels in various bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 760-769. |
| [8] | Zhang Anqi, Hua Haotian, Cai Tianyuan, Wang Zicheng, Meng Zhuo, Zhan Xiaoqian, Chen Guoqian . Pain after total knee arthroplasty: current status and trend analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 795-804. |
| [9] | Li Shu, Zhao Zhengyi, Zeng Qin, Zhu Xiangdong. Nanohydroxyapatite induces immunogenic cell death in tumors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5143-5151. |
| [10] | Jiang Kan, Alimujiang·Abudourousuli, Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Biomaterials and bone regeneration: research hotspots and analysis of 500 influential papers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| [11] | Yang Jiangxi, Li Huangyan, Zhang Yeting, Yu Zuoyin . Research hotspots and thematic evolution in the field of exercise interventions for multiple sclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4771-4781. |
| [12] | Chen Yuanyue, Shen Junfan, Yu Cui, Lu Jianxia, Hu Wenxuan, Zhu Jun, Guo Chuan. Knowledge structure and evolutionary trends in the application of surface electromyography in musculoskeletal pain rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4791-4801. |
| [13] | Meng Zhuo, Zhao Renghao, Zhang Anqi, Hua Haotian, Wang Zicheng, Xu Yingtian, Tong Peijian. Literature visualization analysis of brain-computer interface applications in stroke rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4802-4813. |
| [14] | Li Ruiying, Xia Hong. Visual analysis of cuproptosis research: global landscape of hotspots and frontiers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4529-4541. |
| [15] | Zou Shunyi, Yi Jin, Zeng Hao, Li Jianqi, Wu Zhongping. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: visualization analysis of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4229-4239. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||