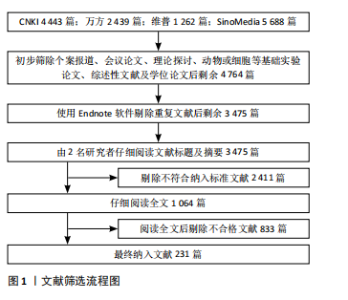
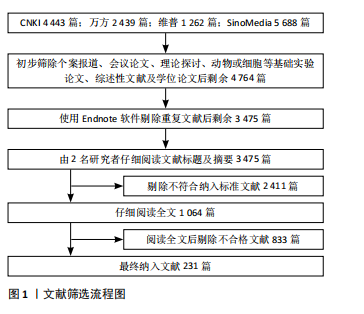
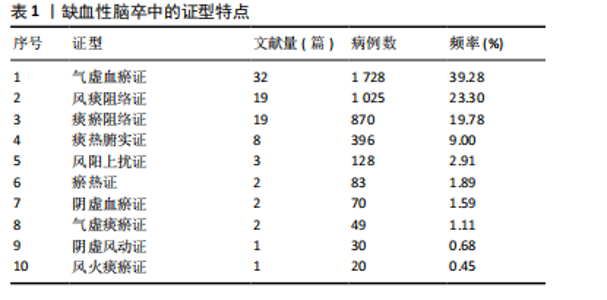
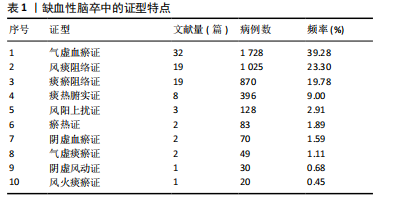
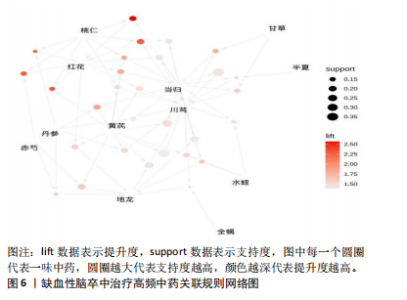
[1] 陈孝男,杨爱琳,赵亚楠,等.缺血性脑中风的发病机制及其常用治疗中药研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2019,44(3):422-432.
[2] 《中国脑卒中防治报告2021》编写组,王陇德. 中国脑卒中防治报告2021》概要[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2023,20(11):783-792,封3.
[3] GBD 2019 STROKE COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(10):795-820.
[4] PHIPPS MS, CRONIN CA. Management of acute ischemic stroke. BMJ. 2020;368:l6983.
[5] FERRARI J, REYNOLDS A, KNOFLACH M, et al. Acute Ischemic Stroke With Mild Symptoms-To Thrombolyse or Not to Thrombolyse? Front Neurol. 2021;12:760813.
[6] CHAMORRO Á, DIRNAGL U, URRA X, et al. Neuroprotection in acute stroke: targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(8):869-881.
[7] 邱文然,徐榛敏,申伟,等.中医药治疗缺血性脑卒中优势定位评价情况概述[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(12):225-232.
[8] 严世芸,朱邦贤,李德新,等. GB/T 16751.2-2021,中医临床诊疗术语 第2部分:证候[S].国家标准化管理委员会,2021.
[9] 高长玉,吴成翰,赵建国,等.中国脑梗死中西医结合诊治指南(2017)[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2018,38(2):136-144.
[10] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典(一部)[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2020.
[11] 国家中医药管理局《中华本草》编委会.中华本草:精选本(上、下册)[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,1998.
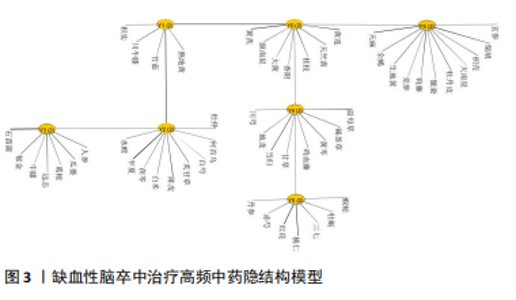
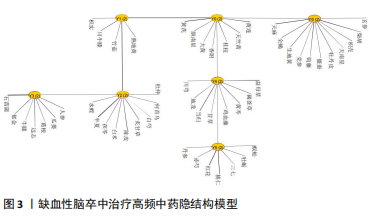
[12] 刘砚泽,王新陆,韩文杰,等.基于隐结构模型结合关联规则分析高脂血症合并高血压病的方药规律[J].中国中药杂志,2024,49(18): 5045-5054.
[13] 刘艳华,周德生,张梦雪,等.周德生教授辨治缺血性中风临床经验[J].亚太传统医药,2022,18(5):129-132.
[14] 李志更,岳利峰,马培,等.从“痰瘀互结”论治缺血性中风[J].辽宁中医杂志,2023,50(12):55-57.
[15] 葛亮,曹慧玲,张洁,等.川芎嗪对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后氧化应激、Ca2+-ATP酶活性及炎症因子的影响[J].国际检验医学杂志, 2021,42(5):517-520.
[16] 赵世英,张慧,邵笑笑,等.中药川芎治疗缺血性脑卒中药理机制研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学院,2024,26(9):185-189.
[17] 武彤.基于NLRP3/Caspase-1通路探讨藁本内酯调控小胶质细胞炎症反应的实验研究[D].天津:天津中医药大学,2022.
[18] 徐雷,王宝祥.蚓激酶在缺血再灌注模型中的作用及机制研究[J].浙江医学,2023,45(11):1135-1139+1237.
[19] WANG YH, LIAO JM, CHEN KM, et al. Lumbrokinase regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress to improve neurological deficits in ischemic stroke. Neuropharmacology. 2022;221:109277.
[20] 袁庆,殷孟兰,张彤,等.中药地龙治疗缺血性脑损伤的药理研究进展[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2022,20(19):3574-3577.
[21] 闫安,谢云亮.当归多糖对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠脑组织氧化应激水平及炎症因子表达的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2018,24(2): 123-127.
[22] 周美丽,韩妮萍.当归的有效成分及药理作用研究进展[J].环球中医药,2024,17(7):1420-1427.
[23] CHENG CY, HO TY, HSIANG CY, et al. Angelica sinensis Exerts Angiogenic and Anti-apoptotic Effects Against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Activating p38MAPK/HIF-1[Formula: see text]/VEGF-A Signaling in Rats. Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(8):1683-1708.
[24] 李广从,靳春晓,刘宁.黄芪甲苷对脑缺血-再灌注损伤大鼠神经的影响及作用机制[J].西北药学杂志,2024,39(3):46-51.
[25] SONG Z, FENG J, ZHANG Q, et al. Tanshinone IIA Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Regulating Microglial Activation and Polarization via NF-κB Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:641848.
[26] HUANG Y, MA S, WANG Y, et al. The Role of Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicines and Bioactive Ingredients on Ion Channels: A Brief Review and Prospect. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2019;18(4):257-265.
[27] 吴永惠.缺血性中风病的中医药治疗[J].医学信息,2022,35(12): 89-92.
[28] 刘穗琦,明淑萍,董欢欢,等.从脾论治缺血性中风恢复期及验案举隅[J].中医药临床杂志,2024,36(3):467-470.
[29] 张宛秋,张瑞,许玉龙.隐结构分析在中医药研究的应用进展[J].中医研究,2020,33(6):68-71.
[30] 王桐,李辰,江铭倩,等.基于关联规则及隐结构模型探讨《温病条辨》湿温病用药规律[J].时珍国医国药,2023,34(12):3065-3069.
[31] 张艺琳,卫靖靖,郭红鑫,等.基于隐结构模型结合关联规则探讨冠脉微血管疾病中医“症-证-药”规律[J].中药新药与临床药理,2024,35(5):730-740.
[32] 王雪,张明雪.基于隐结构模型结合关联规则研究冠心病稳定型心绞痛中医证候特征[J].辽宁中医杂志,2024,51(4):1-6+221.
[33] 黄淑敏,廖晓倩,范星宇,等.基于“以方测证”理论探讨异丙肾上腺素诱导慢性心力衰竭大鼠模型的制备及中医证型[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2023,43(3):368-375.
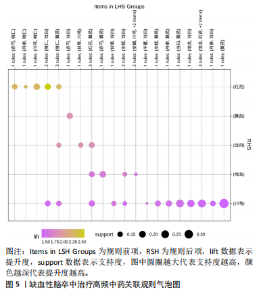
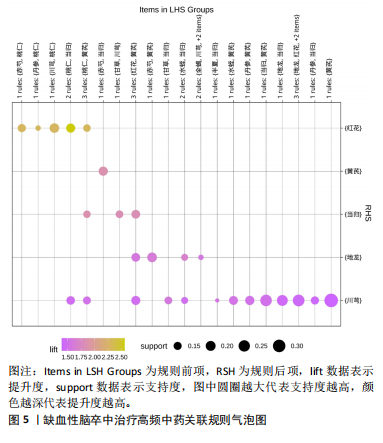
[34] 王华,胡学钢.基于关联规则的数据挖掘在临床上的应用[J].安徽大学学报(自然科学版),2006,30(2):21-25.
[35] 石淇允,许晓彤,卢敏,等.关联规则的中医药防治骨质疏松数据库构建及聚类有效性研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(4):474-481.
[36] 泥文娟,张书琦,王晓艳,等.当归-川芎药对对脑缺血/再灌注损伤大鼠JAK-STAT信号通路的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2021, 37(9):1305-1311.
[37] 王晓禹,张柂儇,房敏,等.基于改善脑缺血效应的混合均匀设计法优化加味佛手散的处方研究[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2023,25(9):3087-3097.
[38] 陈敏纯,闫抗抗,曹青,等.赤芍对缺血性脑卒中大鼠PGC-1α/Nrf2通路促血管新生作用研究[J].现代中药研究与实践,2021,35(4):36-40.
[39] 房爱娟,王艳莉,上官鑫超,等.桃红四物汤治疗脑梗死的临床效果及对炎症状态及神经功能的影响[J].黑龙江医药科学,2023, 46(2):167-168.
[40] 钱丽华,晁海鹏,岳豪祥.桃红四物汤对急性脑缺血再灌注损伤小鼠神经功能缺损评分及脑梗死体积的影响研究[J].中国现代药物应用,2023,17(7):177-180.
[41] 李帆,李鹏飞,高峰,等.基于数据挖掘的中药治疗缺血性脑卒中临床用药规律分析[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(7):1368-1372.
[42] 陈祥宇,张晶涵,赖嘉豪,等.基于数据挖掘的益气活血类方防治脑缺血再灌注损伤用药规律及其作用机制研究[J].中草药,2023, 54(10):3221-3236.
|