Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (16): 2555-2560.doi: 10.12307/2024.326
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regularity and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine compound prescriptions in the treatment of primary osteoporosis
Zhang Jingtao1, Hu Minhua1, Liu Shitao1, Li Shuyuan2, Jiang Zexin1, Zeng Wenxing1, Ma Luyao1, Zhou Qishi3
- 1The First Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510499, Guangdong Province, China; 2The Third Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; 3The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-09Accepted:2023-05-25Online:2024-06-08Published:2023-07-31 -
Contact:Zhou Qishi, MD, Chief physician, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jingtao, Master candidate, The First Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510499, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81674001 (to ZQS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jingtao, Hu Minhua, Liu Shitao, Li Shuyuan, Jiang Zexin, Zeng Wenxing, Ma Luyao, Zhou Qishi. Regularity and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine compound prescriptions in the treatment of primary osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2555-2560.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
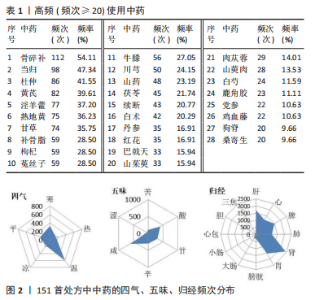
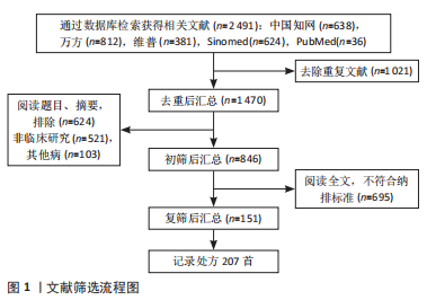
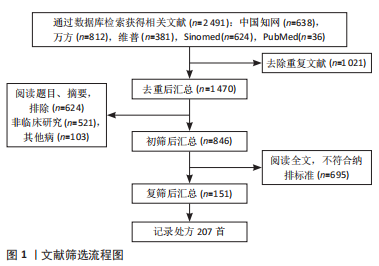
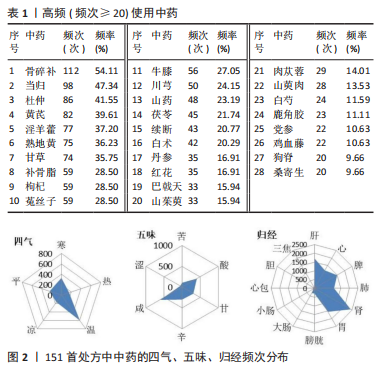
2.2 中药复方治疗POP的四气、五味、归经频次分析 将207 首处方录入Microsoft office Excel 2019,对数据进行提取、分类、数理统计等处理。此次研究的处方包含中药285 味,其中有28 味使用频次大于20,骨碎补的使用频次最高,共112 次(54.11%),频次第二、三分别是当归98 次(47.34%)、杜仲86 次(41.55%),其它高频使用中药分布见表1。处方使用的中药药性总体是以温为主(605 次,41.75%),以寒(331 次,22.84%)、平(240 次,16.56%)为辅。药味中,咸味和苦味占据了绝大部分,具体为咸味607 次(34.08%),苦味411 次(23.08%)。归经前三名为:肾经(2 401 次,23.08%)、肝经(1 710 次,16.44%)、胃经(1 551 次,15.00%);具体四气五味归经情况见图2。"
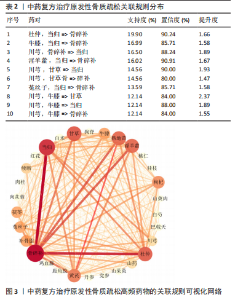
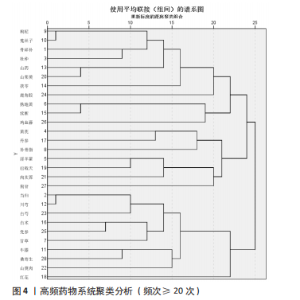
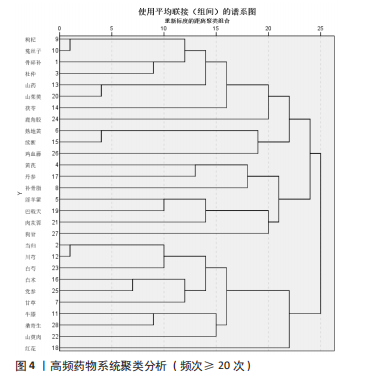
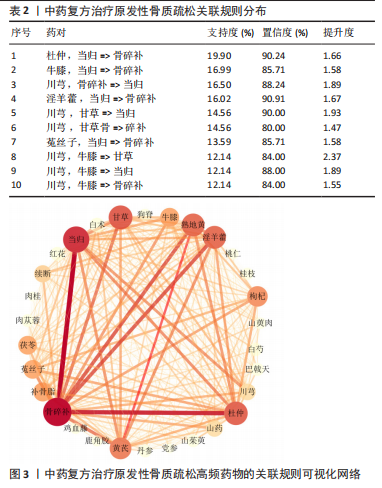
2.3 治疗POP的中药组方关联规则 将处理好的数据导入IBM SPSS Modeler 18.0,对285 味中药进行关联规则分析,设置重要计算参数:最大前项数为3;将关联度综合排名前10的药对进行展示,见表2。排名前3的药对为“杜仲,当归=>骨碎补”(支持度0.199)、“牛膝,当归=>骨碎补”(支持度0.170)、“川芎,骨碎补=>当归”(支持度0.165)。将关联规则结果的强链接、中链接、弱链接数据导入Cytoscape 3.8.0,对关联规则进行可视(图3)。药物颜色越深表示药物出现的频数越高,两个药物之间的连线越粗、颜色越深,表示两个药物同时出现的次数越多,联系越密切。由图可知,骨碎补、杜仲、当归的联系最为紧密。"
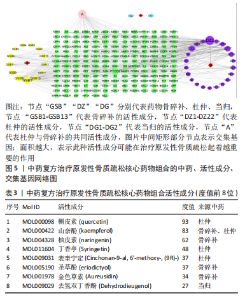
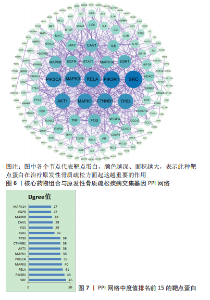
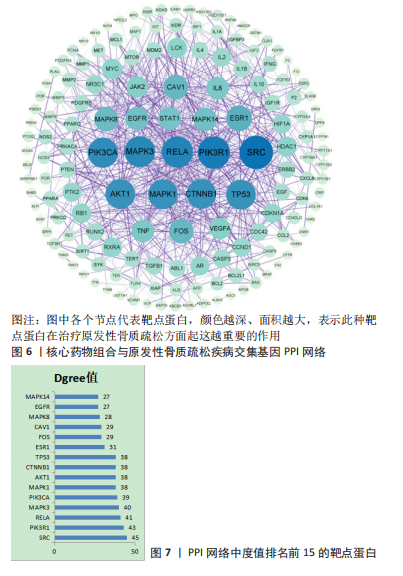
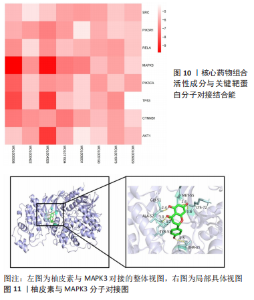
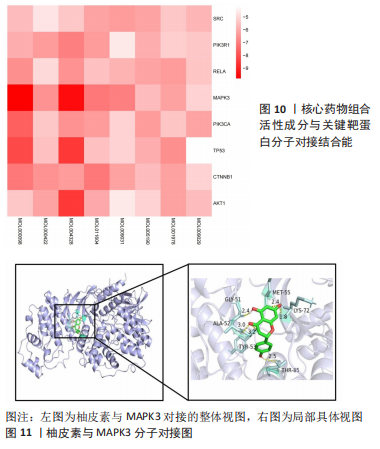
2.5 药物及POP疾病相关靶点的筛选 综合上述分析结果,确定“骨碎补-杜仲-当归”为核心药物组合,在TCMSP数据库中,按照筛选要求可得到48 个核心药物的活性成分,其中骨碎补18 个,杜仲28 个,当归2 个。通过预测共得到活性成分的相关靶点601 个;通过OMIM、GeneCards、TTD、Drugbank、Disgenet数据库检索得到1 491 个与POP发病相关的重要靶点。先取药物靶点的交集,然后取疾病发病相关靶点的交集,最后将这两者的交集再取交集,共得到骨碎补、杜仲和当归治疗POP的177 个潜在作用靶点。 2.6 “药物-活性成分-潜在作用靶点”的网络构建 运用Cytoscape 3.8.0软件构建“药物-活性成分-潜在作用靶点”网络(图5),网络共包含3 味中药,37 个药物活性成分(其中1 个共同活性成分),177 个交集基因。成分度值越大,表明该成分在网络中的地位越重要,度值排名前8的成分见表3;其中槲皮素(quercetin)、山奈酚(kaempferol)、柚皮素(naringenin)等为核心药物组合治疗POP的关键活性成分。将交集基因导入STRING数据库进行PPI分析,得到中药活性成分作用于POP的PPI网络;通过Cytoscape 3.8.0软件得到PPI可视化网络(图6);利用网络拓扑学参数筛选出网络中度值排名前15的靶点蛋白(图7),这15 个靶点为网络中重要的靶点,是核心药物组合治疗POP的关键靶点。"

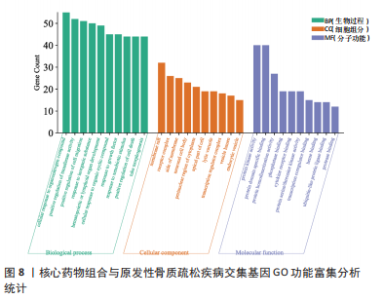
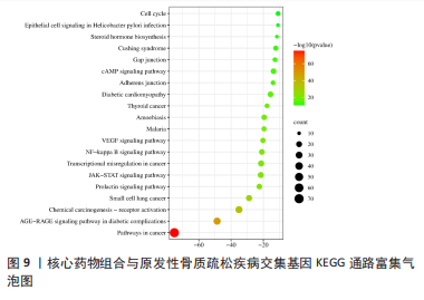
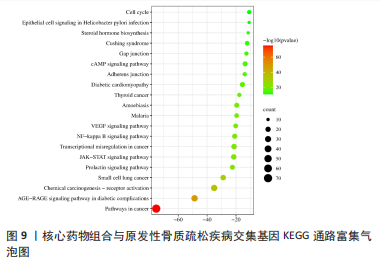
2.7 GO功能富集与KEGG通路富集分析 通过GO分析筛选得到236 种生物过程(biologicalprocess,BP),包括细胞对有机氮化合物的反应、转移酶活性的正调节、细胞迁移的正调节、对无机物质的反应等;获得123 种细胞组分(cellular component,CC),主要包括薄膜筏、受体复合物、膜侧、神经元细胞体等;得到194 组分子功能(molecular function,MF),涉及蛋白激酶活性、蛋白质结构域特异性结合、蛋白质同源二聚活性、磷酸酶结合等生物学功能。根据count值排序,分别取BP、CC及MF排名前10 位者进行可视化(图8)。KEGG分析共富集到信号通路37 条(P < 0.01),选择count值前20 条通路进行可视化展示,见图9。其中10 条通路与POP显著相关,包括癌症途径(Pathways in cancer)、糖尿病并发症中的AGE-RAGE信号通路(AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications)、化学致癌-受体激活(Chemical carcinogenesis- receptor activation)、小细胞肺癌(Small cell lung cancer)、催乳素信号通路(Prolactin signaling pathway)、JAK-STAT信号通路(JAK-STAT signaling pathway)、癌症中的转录失调(Transcriptional misregulation in cancer)、NF-κB信号通路(NF-kappa B signaling pathway)、VEGF信号通路(VEGF signaling pathway)。"

| [1] 吴秀芳,秦飞,亓强,等.TEAS联合腰痛宁胶囊治疗原发性骨质疏松症疼痛的效果观察[J].川北医学院学报,2022,37(9):1157-1160. [2] 揭威,黄小红,王燕玲,等.补肾益气化瘀汤治疗原发性骨质疏松症的临床疗效[J].临床合理用药杂志,2022,15(30):107-110. [3] 董俊党,王其静,杨宁,等.唑来膦酸联合碳酸钙D3治疗骨质疏松骨痛的临床效果[J].临床合理用药杂志,2022,15(29):106-109. [4] 宋敏,刘涛,巩彦龙,等.基于中医传承辅助平台系统的骨质疏松症组方用药规律分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(4):519-523. [5] 汤静,潘慧,徐松,等.抗骨质疏松药物不良反应回顾性分析[J].中国医院用药评价与分析,2008,8(12):950-951. [6] 李焱,窦群立,杨锋.“肾为封藏之本”理论与原发性骨质疏松症发病机制的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(9):1369-1372. [7] 翟子豪,谢义松.活血壮骨汤治疗肾虚血瘀型原发性骨质疏松症临床观察[J].山西中医,2022,38(4):33-35. [8] 薛堃,邢秋娟,吴佶,等.益气化瘀补肾方联合抗阻运动治疗原发性骨质疏松症疗效研究[J].陕西中医,2022,43(3):321-324. [9] 汤辰明,庞坚,石瑛.补肾中药改善原发性骨质疏松症慢性疼痛有效性的Meta分析[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2021,23(8):2663-2671. [10] 王佳辰,严红梅,周庆华,等.补益肝肾法治疗原发性骨质疏松症的临床研究[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2018,16(14):50-51. [11] 牛建明,杜志锋.中医药治疗骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].老年医学研究,2021, 2(2):53-56. [12] 南京中医药大学.中药大辞典[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2006:14-3832. [13] 国家中医药管理局.中华本草[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2005:200-700. [14] 肖语雅,张华东,乌仁图雅,等.张华东教授治疗骨质疏松症临证经验[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2020,18(20):67-69. [15] 史恒蔚,李红专,马同,等.基于“正虚致痹”理论探讨“久病入络”与骨质疏松症的相关性机理[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(9):1395-1398. [16] 徐玉德,李盛华,周明旺,等.基于通络法探讨骨质疏松症与微循环障碍的相关性[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(5):760-762. [17] 包秀广.我院2019年中医药治疗骨质疏松症处方分析[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2020,7(52):175+180. [18] 强胜林,于海洋,蒋宜伟,等.基于“肝与大肠相通”理论谈肝-肠道微生态-骨质疏松症的相关性[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(5):763-766. [19] KENKRE JS, BASSETTJ. The bone remodelling cycle. Ann Clin Biochem. 2018;55(3): 308-327. [20] SAAD FA. Novel insights into the complex architecture of osteoporosis molecular genetics. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020;1462(1):37-52. [21] 李奕玉,关雅心,吴斌.双膦酸盐治疗原发性骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].实用医学杂志,2021,37(5):569-573. [22] 刘彦芳,秦莉,张达,等.槲皮素的生物学活性研究进展[J].国际眼科杂志, 2009,9(5):941-943. [23] SUN J, PAN Y, Li X, et al.Quercetin Attenuates Osteoporosis in Orchiectomy Mice by Regulating Glucose and Lipid Metabolism via the GPRC6A/AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:849544. [24] VAKILI S, ZAL F, MOSTA FAVI-POUR Z, et al. Quercetin and vitamin E alleviate ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by modulating autophagy and apoptosis in rat bone cells. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(5):3495-3509. [25] ABDULLAH A, RAVANAN P. Kaempferol mitigates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induced Cell Death by targeting caspase 3/7. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2189. [26] GAN L, LENG Y, MIN J , et al. Kaempferol promotes the osteogenesis in rBMSCs via mediation of SOX2/miR-124-3p/PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022; 927:174954. [27] 王雪峰,杨松,曹立新,等.山奈酚对卵巢去势大鼠的促骨胶原生成和减少骨小梁丢失的保护作用研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2020,36(10):1302-1305. [28] SONG SH, WANG D, MO YY, et al. [Antiosteoporotic effects of naringenin on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rat. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015;50(2): 154-161. [29] GUO D, WANG J, WANG X, et al. Double directional adjusting estrogenic effect of naringin from Rhizoma drynariae (Gusuibu). J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;138(2):451-457. [30] VIOLETTE SM, GUAN W, BARTLETT C, et al. Bone-targeted Src SH2 inhibitors block Src cellular activity and osteoclast-mediated resorption. Bone. 2001;28(1):54-64. [31] ZHU H, CHEN H, DING D, et al. Overexpression of PIK3R1 Promotes Bone Formation by Regulating Osteoblast Differentiation and Osteoclast Formation. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021;2021:2909454. [32] 倪佳,徐莹莹,邓婉玲,等.人MAPK3基因克隆及其在肝细胞癌细胞中的作用[J].遵义医科大学报,2022,45(4):463-469. [33] XIAO P, CHEN Y, JIANG H, et al. In vivo genome-wide expression study on human circulating B cells suggests a novel ESR1 and MAPK3 network for postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(5):644-654. [34] LI J. JAK-STAT and bone metabolism. JAKSTAT. 2013;2(3):e23930. [35] GABER T, BRINKMAN ACK, PIENCZIKOWSKI J, et al. Impact of Janus Kinase Inhibition with Tofacitinib on Fundamental Processes of Bone Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):865. [36] DAMERAU A , GABER T, OHMDORF S, et al. JAK/STAT Activation: A General Mechanism for Bone Development, Homeostasis, and Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(23):9004. [37] LIU XD, CAI F, LIU L, et al. MicroRNA-210 is involved in the regulation of postmenopausal osteoporosis through promotion of VEGF expression and osteoblast differentiation. Biol Chem. 2015;396(4):339-347. [38] GRUNEWALD M, KUNAR S, SHARIFE S, et al. Counteracting age-related VEGF signaling insufficiency promotes healthy aging and extends life span. Science. 2021;373(6554):eabc8479. [39] SONG N, ZHAO Z, MA X, et al. Naringin promotes fracture healing through stimulation of angiogenesis by regulating the VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling pathway in osteoporotic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2017;261:11-17. [40] TIAN H , CHEN F, WANG Y, et al. Nur77 Prevents Osteoporosis by Inhibiting the NF-κB Signalling Pathway and Osteoclast Differentiation. J Cell Mol Med. 2022; 26(8):2163-2176. [41] LUO H, GU R, OUYANG H, et al. Cadmium exposure induces osteoporosis through cellular senescence, associated with activation of NF-κB pathway and mitochondrial dysfunction. Environ Pollut. 2021;290:118043. |
| [1] | Liu Baofang, Xu Bin, Chen Lei. Pueraria decoction in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 193-199. |
| [2] | Ran Lei, Han Haihui, Xu Bo, Wang Jianye, Shen Jun, Xiao Lianbo, Shi Qi. Molecular docking analysis of the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Cibotium barometz and Epimedium for rheumatoid arthritis: animal experiment validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 208-215. |
| [3] | Zuo Jun, Ma Shaolin. Mechanism of beta-sitosterol on hypertrophic scar fibroblasts: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 216-223. |
| [4] | Chai Shuang, Ma Jiangtao, Yang Yanbing, Su Xiaochuan, Xie Yan, Teng Junyan, Qin Na. The role and mechanism of estrogen receptor in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis by Gushukang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2574-2578. |
| [5] | Xiong Wei, Yuan Lingmei, Qian Guowen, Huang Jinyang, Pan Bin, Guo Ling, Zeng Zhikui. Application of Chinese medicines of tonifying kidney and strengthening bones in the repair of segmental bone defects using bone tissue engineering scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3438-3444. |
| [6] | He Zike, Wang Shangzeng. Eucommia ulmoides Oliver aqueous extract promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation through upregulating Nur77 protein expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2371-2378. |
| [7] | Wu Jingjing, Lin Haixiong, Sun Weipeng, Li Zige, Jiang Ziwei. Mechanism by which naringin regulates osteogenic differentiation in osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1722-1727. |
| [8] | Zhao Yuwei, Gao Yuting, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin . Mechanism of Ermiao San in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 742-748. |
| [9] | Wen Xiaoyu, Sun Yuhao, Li Zhuoxian, Xu Lijing, Xia Meng. Network pharmacology and proteomics analysis of Jiawei Xiaoyao San in the treatment of liver cancer complicated with depression in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5132-5142. |
| [10] | Zhao Dun, Fang Bin, Yi Chunzhi, He Mincong, Zheng Jiaqian, Li Yue. Effects of total flavonoids of Rhizoma drynariae on bone remodeling and expression of bone morphogenetic protein-2, vascular endothelial growth factor and CD31 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4638-4642. |
| [11] | Luo Zhen, Huang Yuxi, Chai Shengting, Li Feilong, Chen Qunqun. Bushen Jianpi Huoxue Recipe is closely related to the target of histone demethylase JMJD2B in promoting osteogenic differentiation in osteoporosis: an in vitro cell experimental verification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4643-4650. |
| [12] | Shen Zhen, Guo Ying, Jiang Ziwei, Zhang Yan, Li Zige, Chen Zehua, Ye Xiangling, Chen Guoqian. Comparison of the effects between two routes of total flavones of Rhizoma Drynariae administration on large segmental bone defects in rats based on bone tissue engineering technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(27): 4346-4352. |
| [13] | Deng Bowen, Li Xiaoye, Jiang Shengyuan, Liu Gan, Zhao Yi, Zhang Houjun, He Feng, Mu Xiaohong. Mechanisms of Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu Decoction in the treatment of cervical spondylosis and anxiety disorder based on the principle of “treating different diseases with the same method”: a network pharmacology analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3650-3656. |
| [14] | Li Anan, Jiang Tao, Zhan Min, Cai Yuning, Song Min, Li Congcong, Lin Wenzheng, Zhang Jiayuan, Liu Wengang. Pharmacological mechanism of Shenling Baizhu San in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 197-204. |
| [15] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Huanan, Chen Feng, Chai Yuan, Gan Bin, Li Song, Chen Dingpeng. Potential molecular mechanism of Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Decoction in the treatment of gouty arthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 245-252. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||