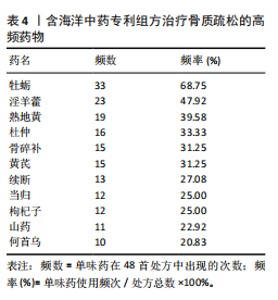
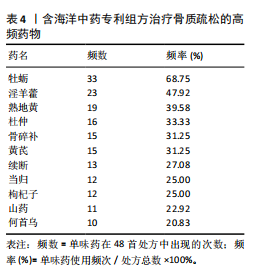
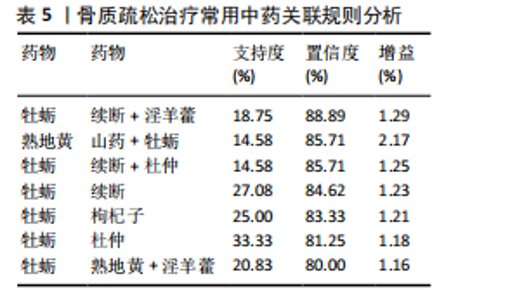
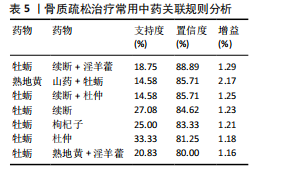
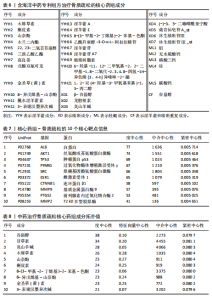
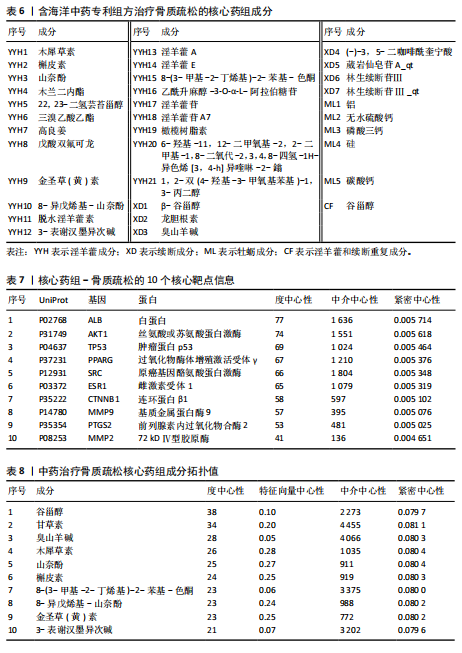
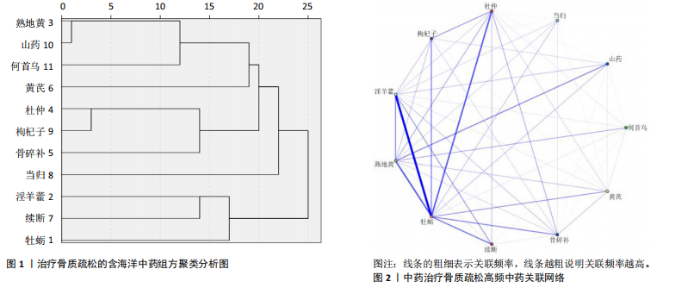
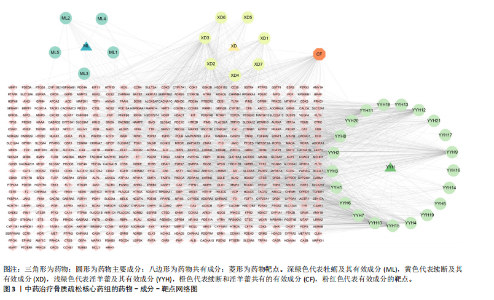
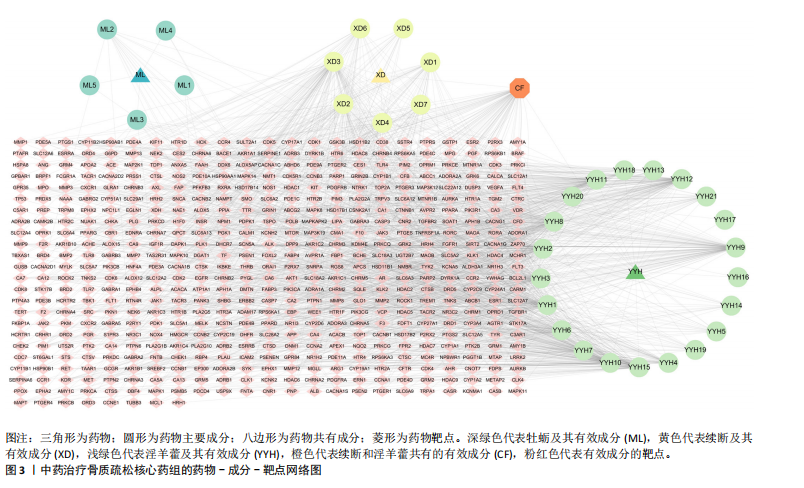
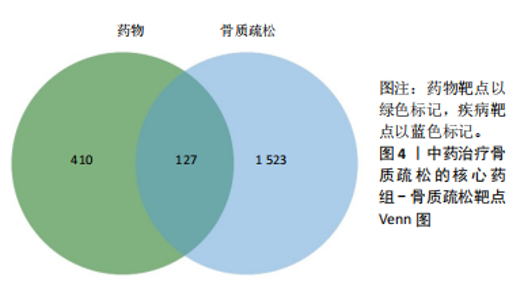
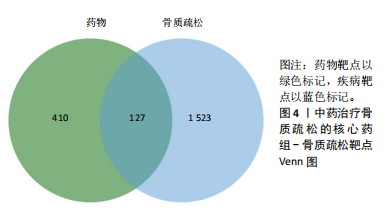
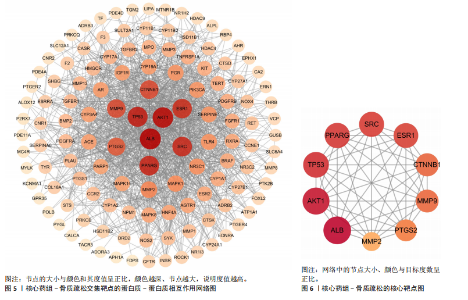
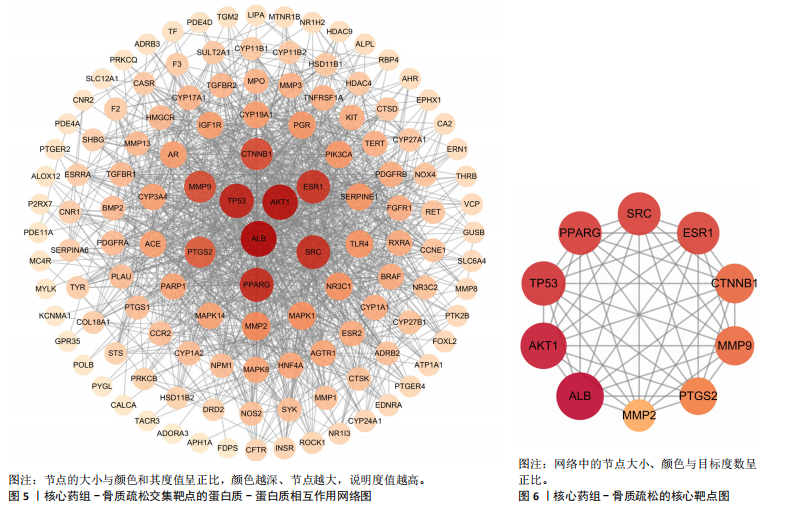
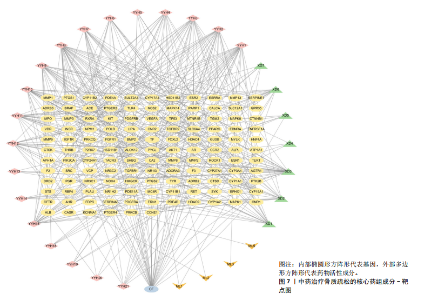
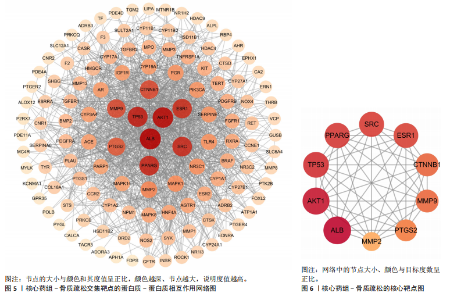
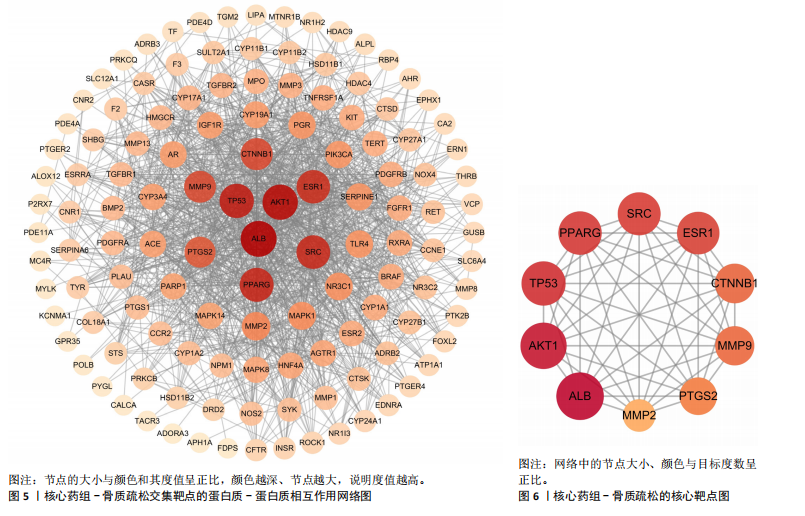
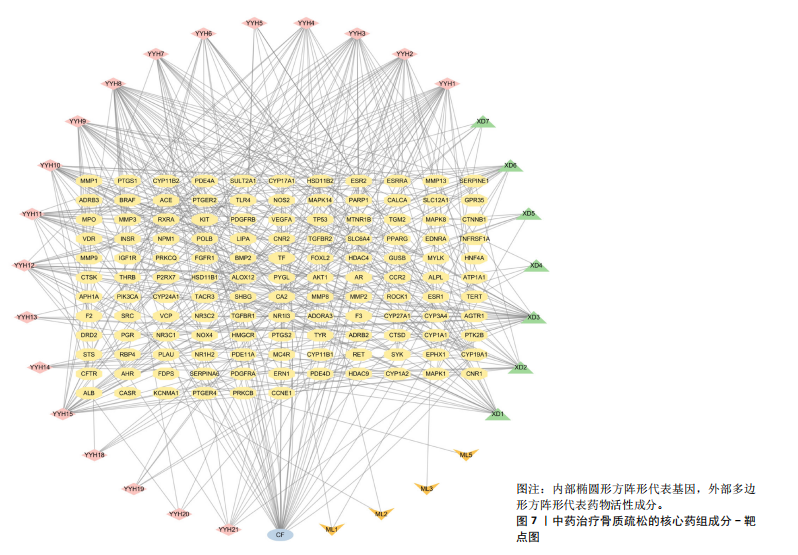
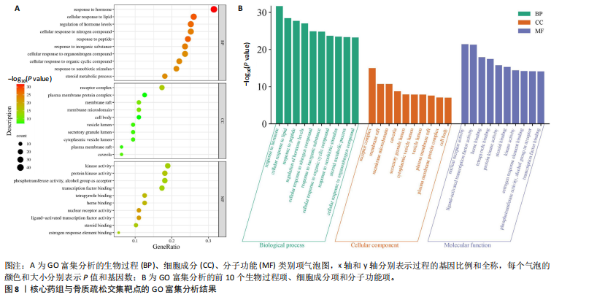
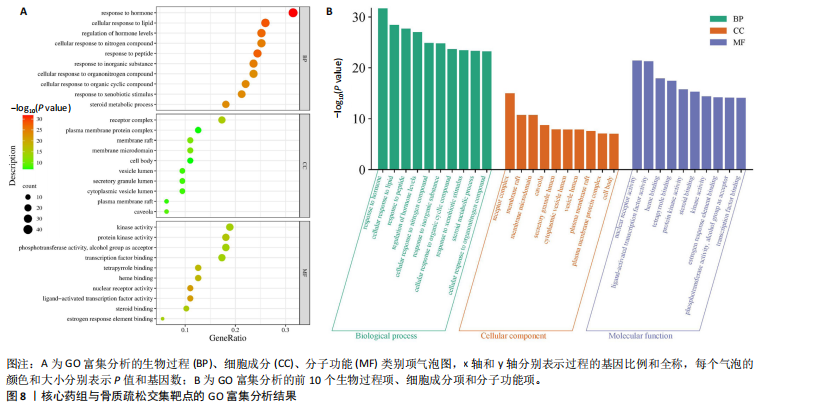
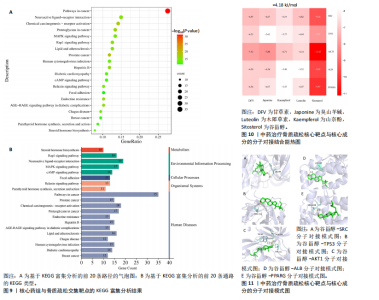
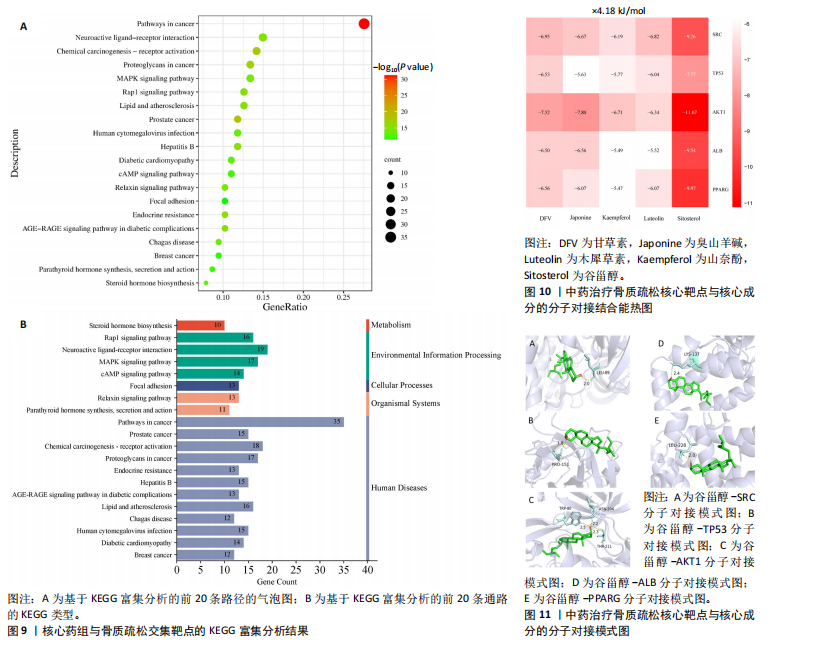
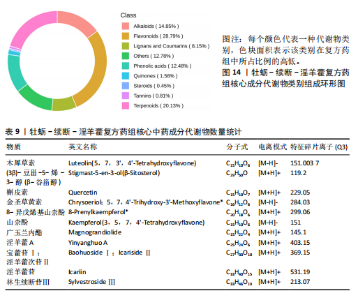
[1] AIBAR-ALMAZÁN A, VOLTES-MARTÍNEZ A, CASTELLOTE-CABALLERO Y, et al. Current Status of the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(16):9465.
[2] HARRIS K, ZAGAR CA, LAWRENCE KV. Osteoporosis: Common Questions and Answers. Am Fam Physician. 2023;107(3): 238-246.
[3] LORENC R, GŁUSZKO P, FRANEK E, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in Poland : Update 2017. Endokrynol Pol. 2017;68(5): 604-609.
[4] LANGDAHL BL. Overview of treatment approaches to osteoporosis. Br J Pharmacol. 2021;178(9):1891-1906.
[5] COSMAN F, LANGDAHL B, LEDER BZ. Treatment Sequence for Osteoporosis. Endocr Pract. 2024;30(5):490-496.
[6] REID IR, BILLINGTON EO. Drug therapy for osteoporosis in older adults. Lancet. 2022;399(10329):1080-1092.
[7] 郑熙,朱敏,甘露,等.60岁以上人群骨质疏松性骨折发病特点及转归分析[J].老年医学与保健,2017,23(6):499-501.
[8] 张云飞,安军伟,龚幼波,等.原发性骨质疏松症的中医药防治研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(4):554-558.
[9] 秦昆明,史大华,董自波,等.海洋中药资源综合开发利用现状与对策研究[J].中草药,2020,51(19):5093-5098.
[10] 侯小涛,刘婧曦,吴东阳,等.我国海洋生物废弃物药用研究现状与策略[J].广西科学,2021,28(6):577-587.
[11] 龚世禹,刘艺琳,李世明,等.海洋中药的研究进展[J].安徽农业科学,2020,48(8): 26-29.
[12] 范星华. 骨痿骨折的中医病机探讨 [J]. 中医正骨, 2022, 34(9): 67-68.
[13] 卞琴,沈自尹,王拥军.骨髓间充质干细胞在中医理论中的归属[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2011,17(7):794-797.
[14] 付先军, 王振国, 王长云, 等. 海洋中药的内涵与外延探讨 [J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2016,18(12):2034-2042.
[15] 陆洁航,李正言,杜国庆,等.骨松宝制剂治疗原发性骨质疏松症的系统评价与Meta分析[J].中国中药杂志,2023, 48(11):3086-3096.
[16] 姜耘宙,汪正明,王瑞,等.β-谷甾醇改善绝经后骨质疏松的实验研究[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2024,48(2):131-137,146.
[17] 邢如温,李双进.甘草素对乳腺癌内分泌治疗后继发性骨质疏松大鼠Wnt/β-catenin信号通路作用的研究[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2023,18(8):1566-1574.
[18] 许勇,谢贤斐,颜威,等.木犀草素调控PI3K/AKT通路改善绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠模型骨丢失的机制[J].热带医学杂志, 2022,22(5):639-643,688,封4.
[19] 杨启培,陈锋,崔伟,等.山奈酚活性单体治疗骨质疏松症的相关信号通路[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(26):4242-4249.
[20] YU T, YOU X, ZHOU H, et al. p53 plays a central role in the development of osteoporosis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020; 12(11):10473-10487.
[21] SUSVA M, MISSBACH M, GREEN J. Src inhibitors: drugs for the treatment of osteoporosis, cancer or both? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2000;21(12):489-495.
[22] JAISWAL N, GAVIN MG, QUINN WJ, et al. The role of skeletal muscle Akt in the regulation of muscle mass and glucose homeostasis. Mol Metab. 2019;28:1-13.
[23] KAWAMURA N, KUGIMIYA F, OSHIMA Y, et al. Akt1 in osteoblasts and osteoclasts controls bone remodeling. PLoS One. 2007;2(10):e1058.
[24] SUGATANI T, HRUSKA KA. Akt1/Akt2 and mammalian target of rapamycin/Bim play critical roles in osteoclast differentiation and survival, respectively, whereas Akt is dispensable for cell survival in isolated osteoclast precursors. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280(5):3583-3589.
[25] LEE SE, WOO KM, KIM SY, et al. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p38, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways are involved in osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 2002;30(1):71-77.
[26] MOON JB, KIM JH, KIM K, et al. Akt induces osteoclast differentiation through regulating the GSK3β/NFATc1 signaling cascade. J Immunol. 2012;188(1):163-169.
[27] SUZUKI E, OCHIAI-SHINO H, AOKI H, et al. Akt activation is required for TGF-β1-induced osteoblast differentiation of MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts. PLoS One. 2014; 9(12):e112566.
[28] CHEN LS, ZHANG M, CHEN P, et al. The m6A demethylase FTO promotes the osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells by downregulating PPARG. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43(5):1311-1323.
[29] 李哲立,严孙杰.糖尿病患者血清白蛋白、血红蛋白与骨质疏松的关系[C].中华医学会糖尿病学分会第二十次全国学术会议论文集,2016:573-574.
[30] 董紫怡,宋程威,崔亚宁,等.膜微区相关结构模型及甾醇成像技术的研究进展[J].电子显微学报,2019,38(5):542-549.
[31] 卢义钦,沈士弼.“膜筏”的国际规范定义[J].中国科技术语,2007,9(4):38.
[32] XIE Y, SHI X, SHENG K, et al. PI3K/Akt signaling transduction pathway, erythropoiesis and glycolysis in hypoxia (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(2):783-791.
[33] PAN BL, TONG ZW, LI SD, et al. Decreased microRNA-182-5p helps alendronate promote osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in osteoporosis via the Rap1/MAPK pathway. Biosci Rep. 2018; 38(6):BSR20180696. |