Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (18): 3767-3774.doi: 10.12307/2025.636
Previous Articles Next Articles
RNA sequencing and quantitative proteomics analyses of molecular mechanism of medical ozone therapy for rabbit skeletal muscle injury
Ruan Zhen1, Kou Jiushe2
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Surgery, Xianyang Central Hospital, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Second Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-23Accepted:2024-07-22Online:2025-06-28Published:2024-11-27 -
Contact:Kou Jiushe, Chief physician, Second Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Ruan Zhen, MS, Physician, Department of Anesthesiology and Surgery, Xianyang Central Hospital, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Shaanxi Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project, No. 2019JM-483 (to KJS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ruan Zhen, Kou Jiushe. RNA sequencing and quantitative proteomics analyses of molecular mechanism of medical ozone therapy for rabbit skeletal muscle injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3767-3774.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
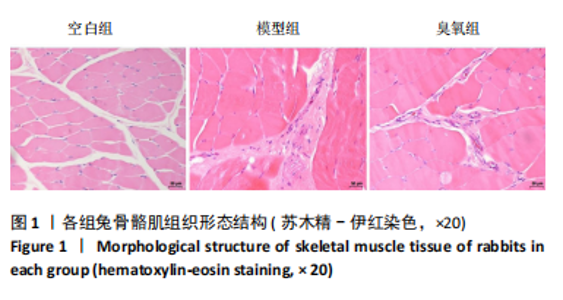
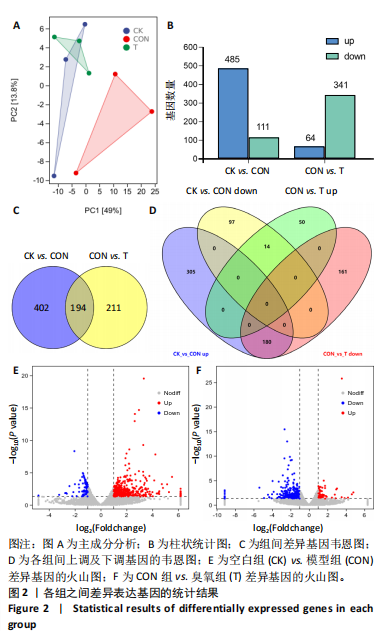
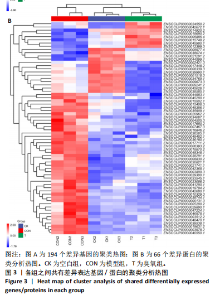
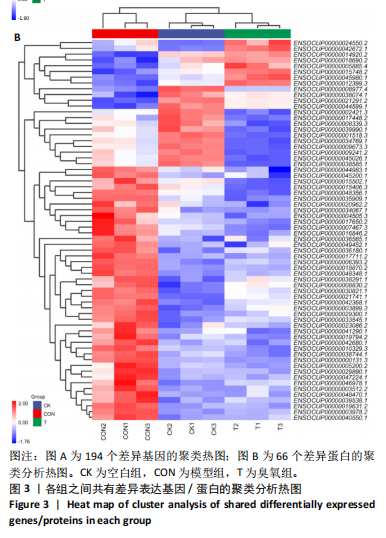
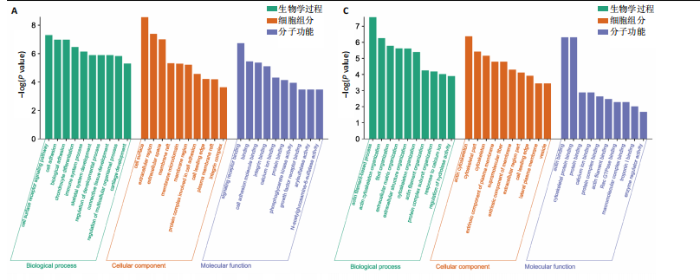
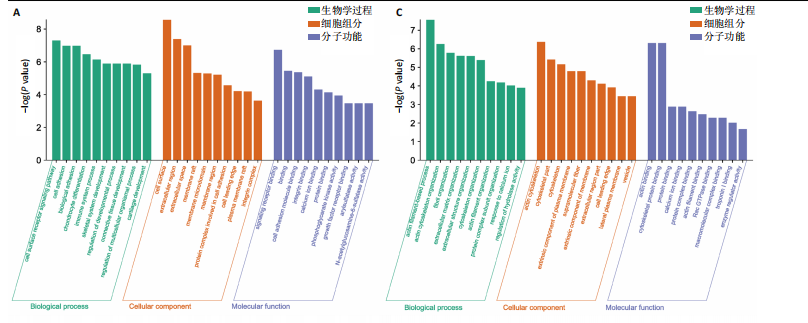
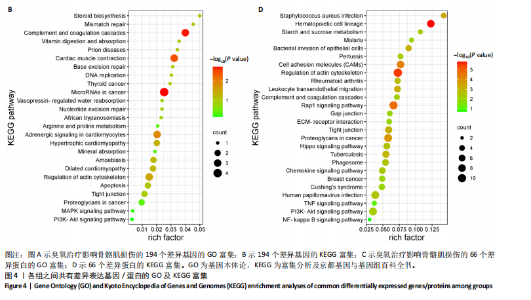
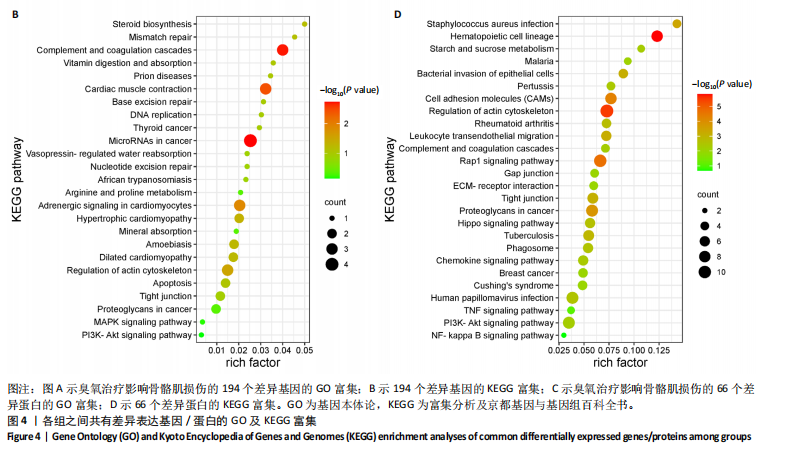
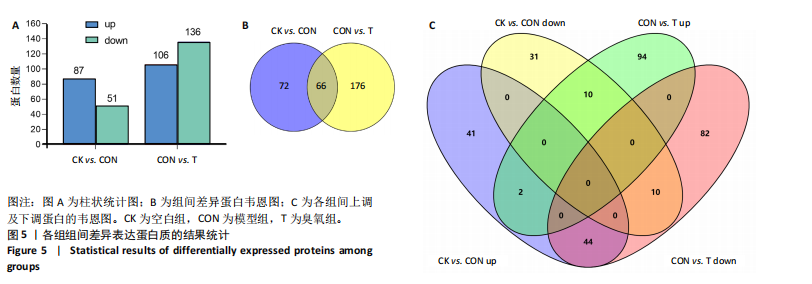
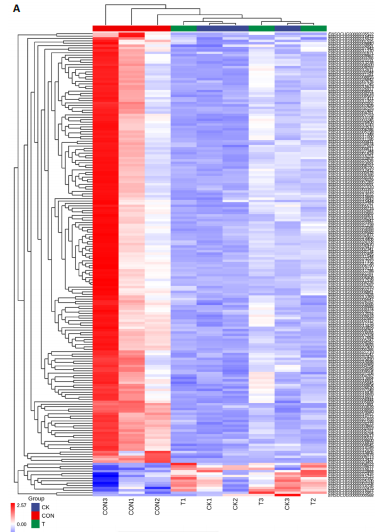
主成分分析结果显示,空白组和模型组之间的转录本差异较大,臭氧组和空白组之间的差异较小,见图2A。根据基因表达的相似性,主成分分析表明了两组之间不同的方向性,结果表明,臭氧治疗减少了肌肉挤压损伤引起的转录变化。对差异基因进行统计发现,模型组与空白组相比,共有596个差异基因,其中485个基因表达水平上调,111个基因下调;臭氧组与模型组相比,共有405个差异基因,其中64个基因表达水平上调,341个基因下调,见图2B。火山图结果更直接地显示了组间差异基因的分布,见图2E,F。韦恩图显示,模型组/空白组和臭氧组/模型组比较中,有194个共有差异表达的基因,其中180个基因在模型组/空白组中上调,而在臭氧组/模型组中下调,14个基因在模型组/空白组中下调,而在臭氧组/模型组中上调,见图2C,D,表明医用臭氧治疗影响了骨骼肌损伤中的194个基因的表达,这194个基因可能是臭氧治疗骨骼肌损伤的关键基因。对194个共有差异基因双向聚类分析显示:每组内的3个生物重复首先聚在一起,聚类成不同的区间;不同组的组内表达情况基本一致,表明组内相关性强,生物重复性好。相较于空白组和臭氧组,模型组有更多的基因上调;臭氧组和空白组的相似度较高,聚类分层接近,见图3A。 2.3.2 差异基因的富集分析 对模型组/空白组与臭氧组/模型组重叠的194个差异表达基因做GO 富集分析,分析结果见图4A,显示共有表达差异基因主要参与细胞表面受体信号通路、细胞黏附生物附着、免疫系统过程等生物学过程;主要富集于细胞表面、细胞外区域、细胞外间隙、膜筏、整合素复合物等细胞组分;参与信号受体结合、细胞黏附分子结合、整合素结合、钙离子结合、磷酸甘油酸酯激酶活性和生长因子受体结合等分子功能。KEGG pathway富集结果见图4B,显示这些差异基因主要富集于肌动蛋白细胞骨架调节、Rap1信号通路、细胞黏附分子、白细胞的跨内皮迁移、趋化因子信号通路、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B(phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B,PI3K-Akt)信号通路、核因子κB信号通路等。 2.4 蛋白质组学结果分析 2.4.1 差异蛋白的分析 模型组与空白组相比,共有 138 个差异表达蛋白质,其中上调的蛋白有 87 个,下调的蛋白有 51 个;臭氧组与模型组相比,共有 242 个差异表达蛋白,其中上调的蛋白有106 个,下调的蛋白有 136 个。蛋白质定量结果统计见图5A。韦恩图显示4组间共有66个差异表达蛋白,44个蛋白在模型组/空白组中上调,而在臭氧组/模型组中下调,10个蛋白在模型组/空白组中下调,而在臭氧组/模型组中上调(图5B,C)。对组间的66个共有差异蛋白进行双向聚类分析显示,组内聚类较好,组内各样本间相关性较好,3组间呈现明显差异,"

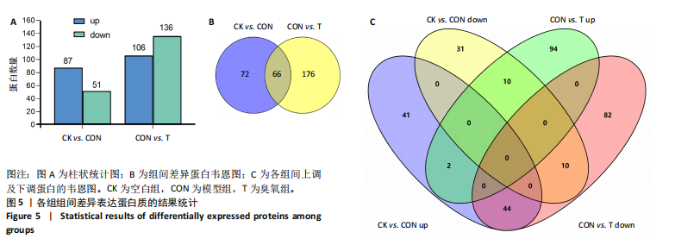
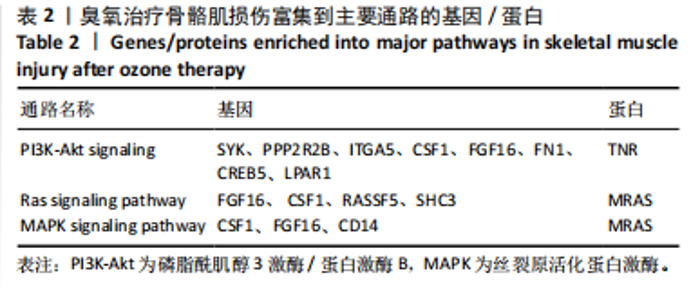
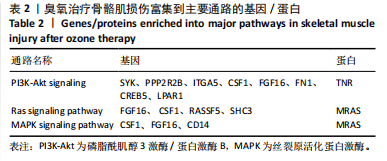
与转录组结果相一致,见图3B。 2.4.2 差异蛋白富集分析 66个共有差异表达蛋白质主要参与到基于肌动蛋白丝的过程、肌动蛋白细胞骨架组织、原纤维组织等生物学过程;富集到肌动蛋白细胞骨架、细胞骨架部分、细胞骨架等细胞组分,及肌动蛋白结合、细胞骨架蛋白结合、蛋白质结合等分子功能,见图4C。KEGG富集结果显示共富集到了63条信号通路,包含补体和凝血级联、心肌收缩、心肌细胞中的肾上腺素能信号传导、肌动蛋白细胞骨架的调节、PI3K-Akt 信号通路等,见图4D。 2.5 差异表达基因和差异表达蛋白共同富集的KEGG通路分析 对模型组/空白组与臭氧组/模型组的差异基因/蛋白取交集得到的194个差异基因和66个差异蛋白,分别对其进行KEGG通路的富集分析。其共同富集到的通路共有36条,主要通路有PI3K-Akt信号通路、Ras信号通路、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)信号通路,见表1,2。"

| [1] SOUZA J, GOTTFRIED C. Muscle injury: review of experimental models. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2013;23(6):1253-1260. [2] EDOUARD P, REURINK G, MACKEY AL, et al. Traumatic muscle injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2023;9(1):56. [3] YANG X, BROBST D, CHAN WS, et al. Muscle-generated BDNF is a sexually dimorphic myokine that controls metabolic flexibility. Sci Signal. 2019;12(594):eaau1468. [4] MANOTO SL, MAEPA MJ, MOTAUNG SK. Medical ozone therapy as a potential treatment modality for regeneration of damaged articular cartilage in osteoarthritis. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018;25(4):672-679. [5] HIDALGO-TALLóN FJ, TORRES-MORERA LM, BAEZA-NOCI J, et al. Updated Review on Ozone Therapy in Pain Medicine. Front Physiol. 2022;13:840623. [6] FITZPATRICK E, HOLLAND OJ, VANDERLELIE JJ. Ozone therapy for the treatment of chronic wounds: A systematic review. Int Wound J. 2018;15(4):633-644. [7] ALMAZ ME, SONMEZ IS. Ozone therapy in the management and prevention of caries. J Formos Med Assoc. 2015;114(1):3-11. [8] OLIVIERO A, GIORDANO L, MAFFULLI N. The temporal effect of intra-articular ozone injections on pain in knee osteoarthritis. Br Med Bull. 2019;132(1):33-44. [9] BOCCI V, ZANARDIA I, VALACCHI G, et al. Validity of Oxygen-Ozone Therapy as Integrated Medication Form in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2015;15(2):127-138. [10] BOCCI V, ZANARDI I, TRAVAGLI V. Ozone: ANew Therapeutic Agent in Vascular Diseases. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2011;11(2):73-82. [11] BRAIDY N, IZADI M, SUREDA A, et al. Therapeutic relevance of ozone therapy in degenerative diseases: Focus on diabetes and spinal pain. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(4):2705-2714. [12] 寇久社, 吴涛, 张润宁, 等. 不同质量浓度臭氧对家兔骨骼肌损伤修复过程TNF-α的影响[J]. 西北药学杂志,2017,32(4):468-471. [13] 寇久社, 吴涛, 张润宁, 等. 不同质量浓度医用臭氧对兔骨骼肌损伤组织学与IL-6的影响[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2017,16(24):2415-2419. [14] 王建飞, 周艳, 刘吉宏, 等. 实验动物饲养管理和使用指南[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社,2012. [15] 寇久社, 张保平, 吴涛, 等. 一种家兔骨骼肌损伤模型构建新方法[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志,2016,22(12):892-895. [16] GULTEKIN FA, CAKMAK GK, TURKCU UO, et al. Effects of ozone oxidative preconditioning on liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats. J Invest Surg. 2013;26(5):242-252. [17] SUN H, HENG H, LIU X, et al. Evaluation of the healing potential of short-term ozone therapy for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1304034. [18] BOSCO MC. Macrophage polarization: Reaching across the aisle? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;143(4):1348-1350. [19] 乐海浪. 创伤后早期炎症因子TNF-α、IL-1、IL-6的研究进展[J]. 现代诊断与治疗,2014,25(4):763-765. [20] WYNN TA, CHAWLA A, POLLARD JW. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature. 2013;496(7446):445-455. [21] GONZALEZ ML, BUSSE NI, WAITS CM, et al. Satellite cells and their regulation in livestock. J Anim Sci. 2020;98(5):skaa081. [22] LI S, ZHANG Y, LU R, et al. Peroxiredoxin 1 aggravates acute kidney injury by promoting inflammation through Mincle/Syk/NF-κB signaling. Kidney Int. 2023;104(2):305-323. [23] WEINBLATT ME, KAVANAUGH A, GENOVESE MC, et al. An oral spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(14):1303-1312. [24] REED JR, STONE MD, BEADNELL TC, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 activation in mammary tumor cells promotes macrophage recruitment in a CX3CL1-dependent manner. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45877. [25] CHONG ZZ, MAIESE K. The Src homology 2 domain tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2: diversified control of cell growth, inflammation, and injury. Histol Histopathol. 2007;22(11):1251-1267. [26] SALEH R, LEE MC, KHIEW SH, et al. CSF-1 in Inflammatory and Arthritic Pain Development. J Immunol. 2018;201(7):2042-2053. [27] VERGADI E, IERONYMAKI E, LYRONI K, et al. Akt Signaling Pathway in Macrophage Activation and M1/M2 Polarization. J Immunol. 2017; 198(3):1006-1014. [28] JACKMAN RW, CORNWELL EW, WU CL, et al. Nuclear factor-κB signalling and transcriptional regulation in skeletal muscle atrophy. Exp Physiol. 2013;98(1):19-24. [29] JU L, HU P, CHEN P, et al. Huoxuezhitong capsule ameliorates MIA-induced osteoarthritis of rats through suppressing PI3K/ Akt/ NF-κB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110471. [30] ZHANG C, SHAO Z, HU X, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling by Aloin for ameliorating the progression of osteoarthritis: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;89(Pt B):107079. [31] 李琪琪, 王雪娇, 初英杰, 等. 中国被毛孢醇提物通过MAPK/NF-κB通路双向调控巨噬细胞的免疫功能研究[J].中草药,2023,54(11): 3559-3567. [32] MITIN N, KUDLA AJ, KONIECZNY SF, et al. Differential effects of Ras signaling through NFkappaB on skeletal myogenesis. Oncogene. 2001; 20(11):1276-1286. |
| [1] | Zhang Yixuan, Li Dongna, Liu Chunyan. Pathological processes, inflammatory responses, and related biomarkers of periodontitis: a multi-omics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7601-7610. |
| [2] | Kang Linzhi, Liu Zhenshuai, Wei Jiaxu, Chang Na, Zhu Dacheng. Inhibitory effects of sinomenine hydrochloride in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia CEM cells and transcriptomic analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6674-6680. |
| [3] | Liu Zhaofeng, Yang Xuejun. Targeted biomarkers of single-cell RNA sequencing in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4351-4360. |
| [4] | Zhao Dun, Qi Lingchen, Xu Jinfan, Shao Min. Visual analysis of hotspots and frontiers in knee osteoarthritis pain field [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3280-3289. |
| [5] | Zhang Xinrui, Han Yue, Lei Lei, Liu Jianyu, Geng Chengkui. Comparative proteomic analysis of rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2683-2689. |
| [6] | Wang Peigeng, Ye Dongping. Application of single-cell RNA sequencing in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2822-2831. |
| [7] | Yan Ru, Wang Kairu, Zhang Feiyan, Jia Shaobin, Cong Guangzhi. Endothelial cell-specific bone morphogenetic protein 2 affects angiogenesis: bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 103-110. |
| [8] | Bu Xianzhong, Zhong Yuanming, Bu Baoxian, Li Jitian, Wang Lihe, Li Huiying, Yang Hanli, Xu Wei. Serum differential proteomic analysis of developmental cervical canal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5432-5439. |
| [9] | Lu Caixia, Zhang Simin, Nigeayi·Aihemaiti, Li Xueer, Chen Zeyuan, Maimaitituxun·Tuerdi. Medical ozone alleviates pain in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4300-4305. |
| [10] | Liu Jing, Liang Fangyuan, Li Jia, Wang Hua. Mechanisms of acupuncture in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea based on proteomics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4129-4136. |
| [11] | Huang Huimin, Xie Bingying, Huang Jingwen, Huang Xiaobin, Xie Lihua, Li Shengqiang, Ge Jirong. Protective mechanism of alendronate granule in a rat osteoporosis model based on TMT proteomic analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(16): 2505-2511. |
| [12] | Bu Xianzhong, Bu Baoxian, Xu Wei, Li Zhifei, Yang Hanli, Wang Weiwei, Zhou Jinyan, Zhong Yuanming. Serum differential proteomics between developmental cervical spinal stenosis and cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1704-1711. |
| [13] | Cheng Haotian, Zhao Xiaofeng, Lu Xiangdong, Zhao Yibo, Fan Zhifeng, Qi Detai, Wang Xiaonan, Zhou Runtian, Jin Xinjie, Zhao Bin. Single-cell RNA sequencing and the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 93-99. |
| [14] | Long Qingxi, Zhang Pingshu, Liu Qing, Ou Ya, Zhang Lili, Yuan Xiaodong. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the heterogeneity of astrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 139-146. |
| [15] | Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng. Proteomic study of Jintiange capsule in the treatment of retinoic acid-induced osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5634-5641. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||