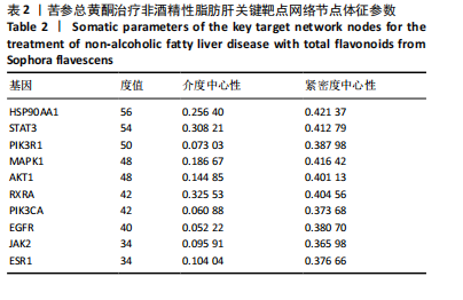
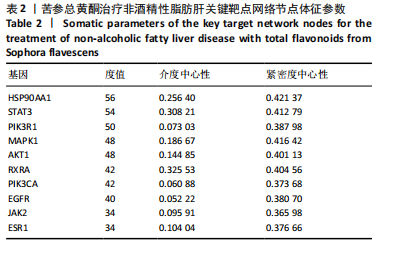
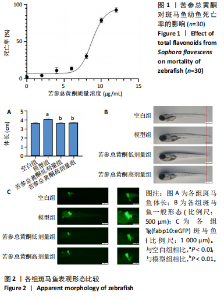
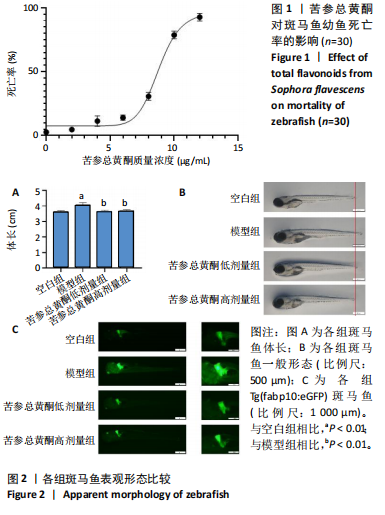
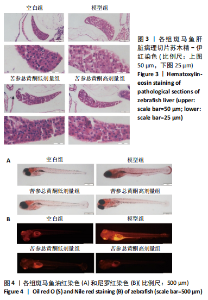
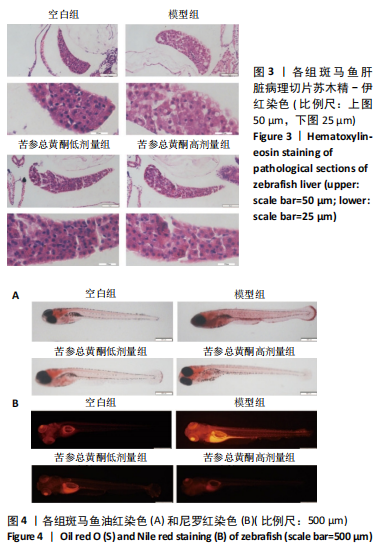
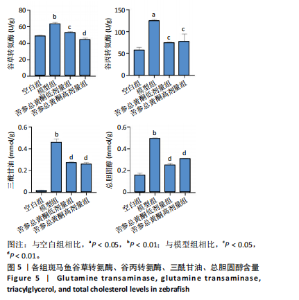
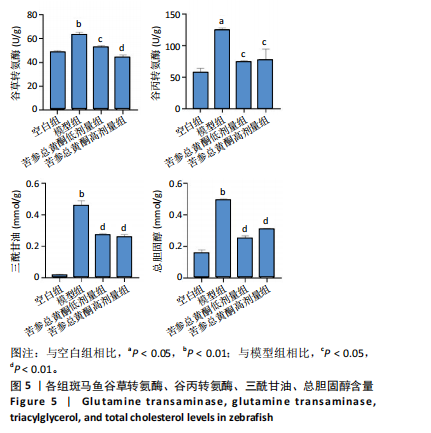
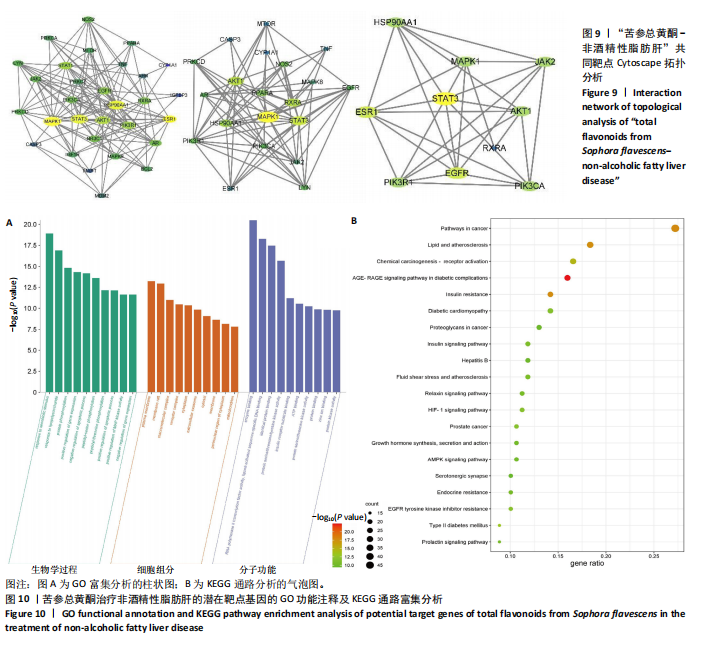
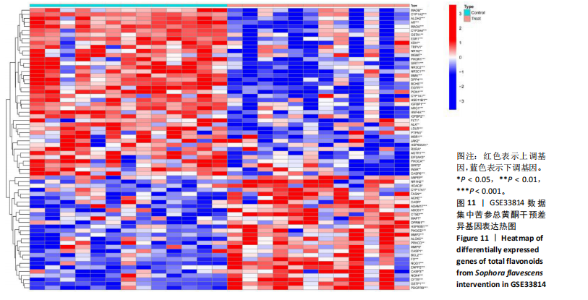
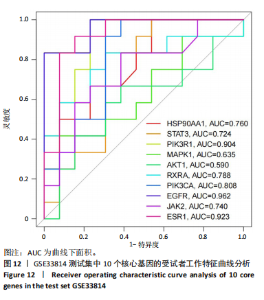
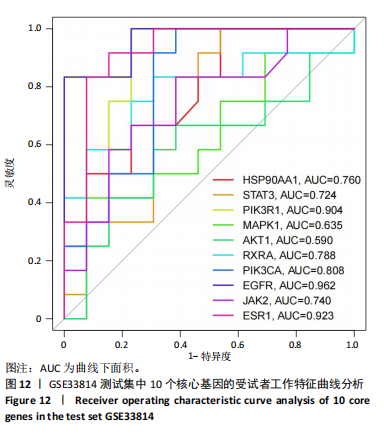
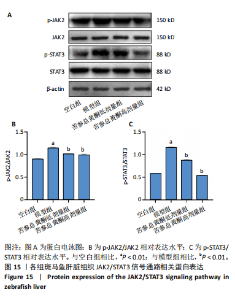
[1] SHAH PA, PATIL R, HARRISON SA. NAFLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma: The growing challenge. Hepatology. 2023;77(1):323-338.
[2] POUWELS S, SAKRAN N, GRAHAM Y, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022;22(1):63.
[3] RIAZI K, AZHARI H, CHARETTE JH, et al. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7(9):851-861.
[4] ALLEN AM, LAZARUS JV, YOUNOSSI ZM. Healthcare and socioeconomic costs of NAFLD: A global framework to navigate the uncertainties. J Hepatol. 2023;79(1):209-217.
[5] XANTHAKOS S. Rising tide of NAFLD in youth: A warning bell and call to action. Hepatology. 2023;78(4):1017-1019.
[6] LI Z, LIN M, LI Y, et al. Total flavonoids of Sophora flavescens and kurarinone ameliorated ulcerative colitis by regulating Th17/Treg cell homeostasis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;297:115500.
[7] LIU D, CHAN BC, CHENG L, et al. Sophora flavescens protects against mycobacterial Trehalose Dimycolate-induced lung granuloma by inhibiting inflammation and infiltration of macrophages. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):3903.
[8] HE X, FANG J, HUANG L, et al. Sophora flavescens Ait.: Traditional usage, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;172:10-29.
[9] LIN Y, CHEN XJ, LI JJ, et al. A novel type lavandulyl flavonoid from Sophora flavescens as potential anti-hepatic injury agent that inhibit TLR2/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;307:116163.
[10] 郑帅,张凯,高雨秋,等.苦参总黄酮调控Nrf2/HO-1通路对肝纤维化大鼠的机制研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2021,37(12):2197-2204.
[11] SHAO J, LIU Y, WANG H, et al. An Integrated Fecal Microbiome and Metabolomics in T2DM Rats Reveal Antidiabetes Effects from Host-Microbial Metabolic Axis of EtOAc Extract from Sophora flavescens. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:1805418.
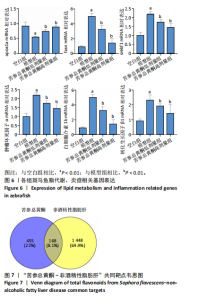
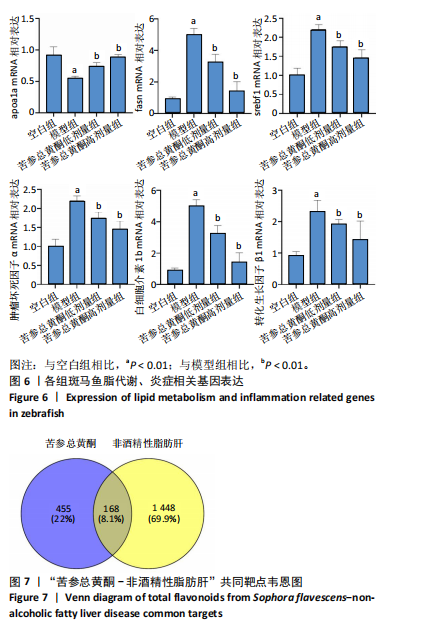
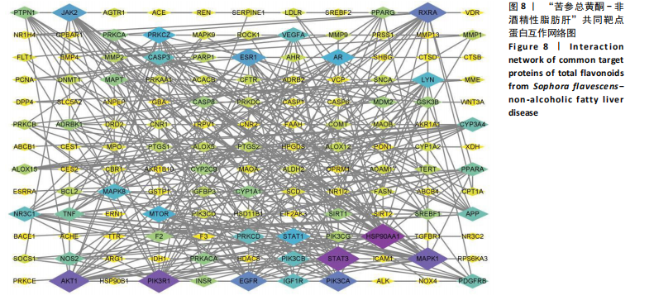
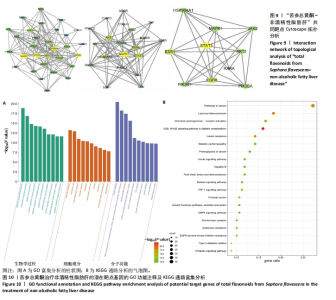
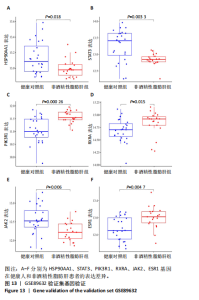
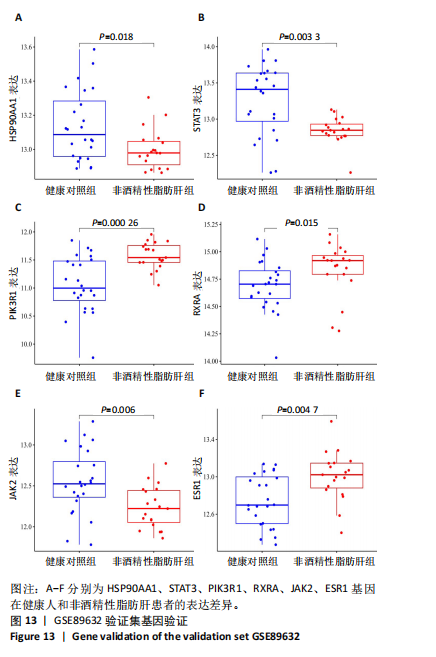
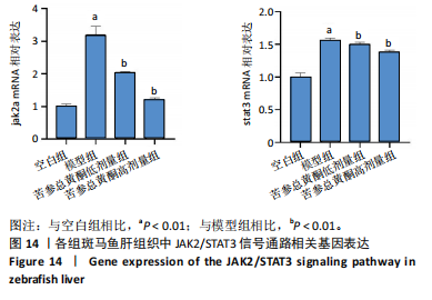
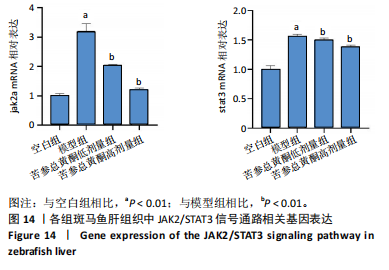
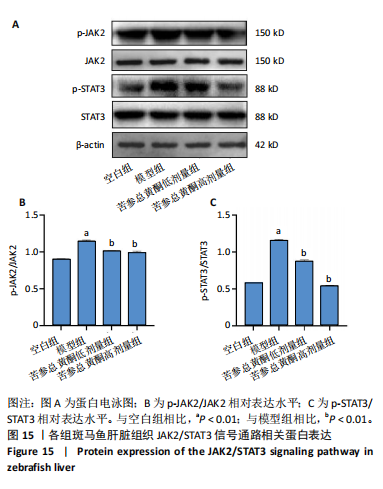
[12] 鲁思凡,朱晨,古玉凤,等.基于斑马鱼模型的疏肝降脂片改善非酒精性脂肪肝病的作用机制研究[J].中国医院药学杂志,2024, 44(16):1875-1881.
[13] FRIEDMAN SL, NEUSCHWANDER-TETRI BA, RINELLA M, et al. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. 2018;24(7):908-922.
[14] TARGHER G, BYRNE CD, TILG H. MASLD: a systemic metabolic disorder with cardiovascular and malignant complications. Gut. 2024;73(4): 691-702.
[15] CAO P, WANG Y, ZHANG C, et al. Quercetin ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) via the promotion of AMPK-mediated hepatic mitophagy. J Nutr Biochem. 2023;120:109414.
[16] LU Z, LIU L, ZHAO S, et al. Apigenin attenuates atherosclerosis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome in mice. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):7996.
[17] AGHEMO A, ALEKSEEVA OP, ANGELICO F, et al. Role of silymarin as antioxidant in clinical management of chronic liver diseases: a narrative review. Ann Med. 2022;54(1):1548-1560.
[18] OATES AC, BROWNLIE A, PRATT SJ, et al. Gene duplication of zebrafish JAK2 homologs is accompanied by divergent embryonic expression patterns: only jak2a is expressed during erythropoiesis. Blood. 1999; 94(8):2622-2636.
[19] WU K, TAN XY, XU YH, et al. JAK and STAT members of yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and their roles in leptin affecting lipid metabolism. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2016;226:14-26.
[20] 马春松,程珂,郭勋,等. miR-194a介导饲料维生素D_3调节黄颡鱼JAK-STAT免疫通路的研究[J].水生生物学报,2023,47(1):11-24.
[21] LIU M, LI S, GUAN M, et al. Leptin pathway is a crucial target for anthocyanins to protect against metabolic syndrome. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024:1-16. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2323093.
[22] PARK J, ZHAO Y, ZHANG F, et al. IL-6/STAT3 axis dictates the PNPLA3-mediated susceptibility to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2023;78(1):45-56.
[23] SUN M, ZHAO X, LI X, et al. Aerobic Exercise Ameliorates Liver Injury in Db/Db Mice by Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis and Inflammation Through the Nrf2 and JAK2/STAT3 Signalling Pathways. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:4805-4819.
[24] BELLONI L, DI COCCO S, GUERRIERI F, et al. Targeting a phospho-STAT3-miRNAs pathway improves vesicular hepatic steatosis in an in vitro and in vivo model. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13638.
[25] SULTAN M, BEN-ARI Z, MASOUD R, et al. Interleukin-1α and Interleukin-1β play a central role in the pathogenesis of fulminant hepatic failure in mice. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0184084. |