Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (21): 4499-4505.doi: 10.12307/2025.163
Previous Articles Next Articles
Debridement, antibiotics, and implant retention combined with replacement of assembled components in treatment of acute prosthetic joint infection after total hip arthroplasty
Pan Xian1, 2, Zhang Yuanjin1, Zhang Guofu1, Li Jun1, Liu Bingxia3, Zhou Dingkang4, Sun Farui1, 2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, 3Department of Ultrasound Imaging, 4Department of Surgical Anesthesiology, Huangshi Central Hospital (Affiliated Hospital of Hubei Polytechnic University), Huangshi 435000, Hubei Province, China; 2Hubei Key Laboratory of Kidney Disease Pathogenesis and Intervention, Huangshi 435000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2024-02-21Accepted:2024-04-13Online:2025-07-28Published:2024-12-06 -
Contact:Sun Farui, PhD candidate, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Huangshi Central Hospital (Affiliated Hospital of Hubei Polytechnic University), Huangshi 435000, Hubei Province, China; Hubei Key Laboratory of Kidney Disease Pathogenesis and Intervention, Huangshi 435000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Pan Xian, MS, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Huangshi Central Hospital (Affiliated Hospital of Hubei Polytechnic University), Huangshi 435000, Hubei Province, China; Hubei Key Laboratory of Kidney Disease Pathogenesis and Intervention, Huangshi 435000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, No. 2023AFB1071 (to PXA); Scientific Research Project of Hubei Polytechnic University, No. 22xjz06W (to PXA)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Pan Xian, Zhang Yuanjin, Zhang Guofu, Li Jun, Liu Bingxia, Zhou Dingkang, Sun Farui. Debridement, antibiotics, and implant retention combined with replacement of assembled components in treatment of acute prosthetic joint infection after total hip arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4499-4505.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
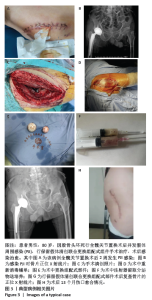
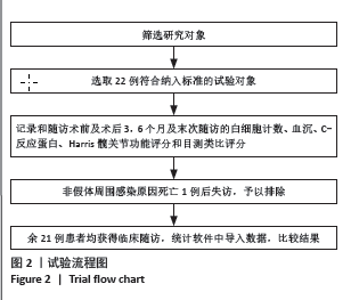
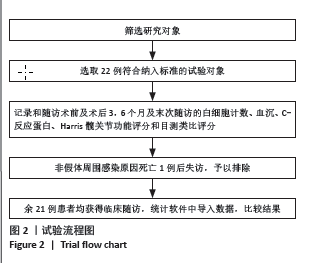
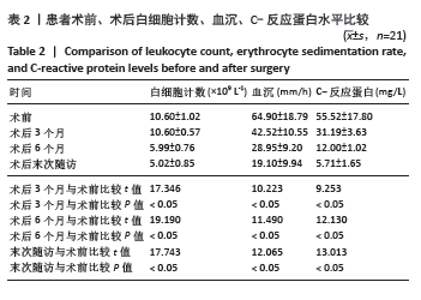
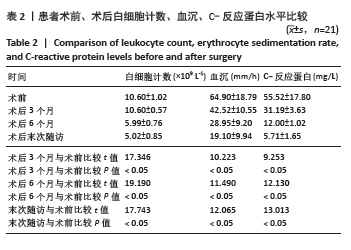
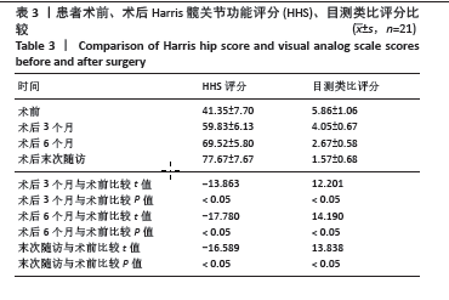
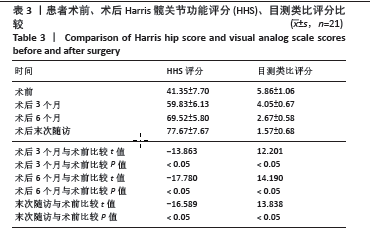
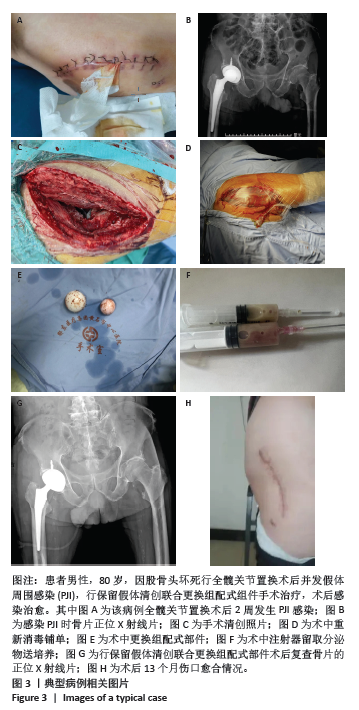
2.4 不良事件 此次研究中手术治疗失败1例,患者髋部合并皮肤银屑病,长期外用类固醇类激素治疗,术前因股骨头无菌性坏死行初次全髋关节置换,术后9 d发生PJI,明确PJI感染1 d后行保留假体清创联合更换组配式组件手术治疗,术后2 d患者髋关节伤口处渗血渗液,留取渗液的分泌物作培养结果提为金黄色葡萄糖球菌,考虑术后感染复发,后期行髋关节感染翻修治疗,随访至今达12个月,未出现感染征象。 2.5 典型病例 见图3。 2.6 植入物与宿主的生物相容性 此次研究所置入全髋关节假体中所有股骨柄的制造材料均为钛合金,且全部采用羟基磷灰石涂层,髋臼侧组件采用超高分子聚乙烯材料制造,具有良好的人体组织生物相容性,患者未出现植入物周围感染、过敏反应、免疫反应及排斥反应。 "
| [1] HUMPHREYS H, HOFFMAN P. The conundrum of ultraclean air, deep infections, and artificial joint replacement. J Hosp Infect. 2020;104: 123-124. [2] MATHEIS C, STÖGGL T. Strength and mobilization training within the first week following total hip arthroplasty. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2018; 22(2):519-527. [3] SHI H, XIAO L, WANG Z. Curative effect of artificial femoral head replacement and its effect on hip joint function and complications of senile patients with femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(2):623-628. [4] GUNDTOFT PH, PEDERSEN AB, VARNUM C, et al. Increased Mortality After Prosthetic Joint Infection in Primary THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(11):2623-2631. [5] MCPHERSON EJ, WOODSON C, HOLTOM P, et al. Periprosthetic total hip infection: outcomes using a staging system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(403):8-15. [6] TSUKAYAMA DT, ESTRADA R, GUSTILO RB. Infection after total hip arthroplasty. A study of the treatment of one hundred and six infections. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(4):512-523. [7] TRIANTAFYLLOPOULOS GK, SORANOGLOU V, MEMTSOUDIS SG, et al. Implant retention after acute and hematogenous periprosthetic hip and knee infections: Whom, when and how? World J Orthop. 2016;7(9):546-552. [8] KUIPER JW, WILLINK RT, MOOJEN DJ, et al. Treatment of acute periprosthetic infections with prosthesis retention: Review of current concepts. World J Orthop. 2014;5(5):667-676. [9] PATEL R, ALIJANIPOUR P, PARVIZI J. Advancements in Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infections after Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. Open Orthop J. 2016;10:654-661. [10] PARVIZI J, TAN TL, GOSWAMI K, et al. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(5):1309-1314. [11] OTTO-LAMBERTZ C, YAGDIRAN A, WALLSCHEID F, et al. Periprosthetic Infection in Joint Replacement. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2017;114(20):347-353. [12] ROMANO CL, MANZI G, LOGOLUSO N, et al. Value of debridement and irrigation for the treatment of peri-prosthetic infections. A systematic review. Hip Int. 2012;22 Suppl 8:S19-S24. [13] COSTERTON JW, STEWART PS, GREENBERG EP. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999;284(5418): 1318-1322. [14] COSTERTON JW. Biofilm theory can guide the treatment of device-related orthopaedic infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(437):7-11. [15] OSMON DR, BERBARI EF, BERENDT AR, et al. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(1): e1-e25. [16] ACHERMANN Y, STASCH P, PREISS S, et al. Characteristics and treatment outcomes of 69 cases with early prosthetic joint infections of the hip and knee. Infection. 2014;42(3):511-519. [17] KUIPER JW, VOS SJ, SAOUTI R, et al. Prosthetic joint-associated infections treated with DAIR (debridement, antibiotics, irrigation, and retention): analysis of risk factors and local antibiotic carriers in 91 patients. Acta Orthopaedica. 2013;84(4):380-386. [18] LAUDERDALE KJ, MALONE CL, BOLES BR, et al. Biofilm dispersal of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on orthopedic implant material. J Orthop Res. 2010;28:55-61. [19] MA R, HU X, ZHANG X, et al. Strategies to prevent, curb and eliminate biofilm formation based on the characteristics of various periods in one biofilm life cycle. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12:1003033. [20] NEELIMA M, CHANDRASHEKAR BR, GOEL S, et al. “Is powered toothbrush better than manual toothbrush in removing dental plaque?” - A crossover randomized double-blind study among differently abled, India. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2017;21(2): 138-143. [21] CCAHUANA-VASQUEZ RA, ADAM R, CONDE E, et al. A 5-week randomized clinical evaluation of a novel electric toothbrush head with regular and tapered bristles versus a manual toothbrush for reduction of gingivitis and plaque. Int J Dent Hyg. 2019;17(2): 153-160. [22] SCHMALZ G, KIEHL K, SCHMICKLER J, et al. Correction to: No difference between manual and different power toothbrushes with and without specific instructions in young, oral healthy adults-results of a randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig. 2018;22(3):1609. [23] GRAMMATOPOULOS G, KENDRICK B, MCNALLY M, et al.Outcome Following Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention in Hip Periprosthetic Joint Infection-An 18-Year Experience. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(7):2248-2255. [24] LORA-TAMAYO J, SENNEVILLE É, RIBERA A, et al. The Not-So-Good Prognosis of Streptococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infection Managed by Implant Retention: The Results of a Large Multicenter Study. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(12):1742-1752. [25] TSANG SJ, TING SIMPSON AHRW, GASTON P. Outcomes following debridement, antibiotics and implant retention in the management of periprosthetic infections of the hip: a review of cohort studies. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(11):1458-1466. [26] QASIM SN, SWANN A, ASHFORD R. The DAIR (debridement, antibiotics and implant retention) procedure for infected total knee replacement - a literature review. SICOT J. 2017;3:2. [27] HIGUERA C. Another Option in the Armamentarium: Understanding the Role of Irrigation and Debridement to Treat Hip Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Commentary on an article by Andrew J. Bryan, MD, et al.: “Irrigation and Debridement with Component Retention for Acute Infection After Hip Arthroplasty. Improved Results with Contemporary Management”. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(23):e131. [28] SOCIÉTÉ DE PATHOLOGIE INFECTIEUSE DE LANGUE FRANÇAISE (SPILF), COLLÈGE DES UNIVERSITAIRES DE MALADIES INFECTIEUSES ET TROPICALES (CMIT), GROUPE DE PATHOLOGIE INFECTIEUSE PÉDIATRIQUE (GPIP), et al. [Recommendations for clinical practice. Osteo-articular infection therapy according to materials used (prosthesis, implants, osteosynthesis)]. Med Mal Infect. 2009;39(10): 745-774. [29] BENE N, LI X, NANDI S. Factors affecting failure of irrigation and debridement with liner exchange in total knee arthroplasty infection. Knee. 2018; 25(5): 932-938. [30] CHAUSSADE H, UCKAY I, VUAGNAT A, et al. Antibiotic therapy duration for prosthetic joint infections treated by Debridement and Implant Retention (DAIR): Similar long-term remission for 6 weeks as compared to 12 weeks. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;63:37-42. [31] SCHOLTEN R, KLEIN KP, GISOLF J, et al. Empiric antibiotic therapy in early periprosthetic joint infection: a retrospective cohort study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023;33(1):29-35. [32] TATARELLI P, ROMANI T, SANTORO V, et al. Debridement, antibiotics and implant retention (DAIR): An effective treatment option for early prosthetic joint infections. J Infect Chemother. 2021;27(8):1162-1168. [33] ZJMMERLI W, WIDMER AF, BLATTER M, et al. Role of rifampin for treatment of orthopedic implant-related staphylococcal infections: a randomized controlled trial. Foreign-Body Infection (FBI) Study Group. JAMA. 1998;279(19):1537-1541. [34] RODRiGUEZPARDO D, PlGRAU C, LORAl_AMAYO J, et al. Gram-negative prosthetic joint infection: outcome of a debridement, antibiotics and implant retention approach. A large multicentre study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20(11):O911-919. [35] ABOLTINSC, DOWSEY MM, PEEL T, et al. Early prosthetic hip joint infection treated with debridement, prosthesis retention and biofilm-active antibiotics: functional outcomes, quality of life and complications. Intern Med J. 2013;43(7):810-815. [36] SENDI P, ZJMMERLI W. Antimicrobial treatment concepts for orthopaedic device-related infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18(12): 1176-1184. [37] KARAU MJ, SCHMIDT-MALAN SM, ALBANO M, et al. Novel Use of Rifabutin and Rifapentine to Treat Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a Rat Model of Foreign Body Osteomyelitis. J Infect Dis. 2020;222(9):1498-1504. [38] GOETZ J, KEYSSNER V, HANSES F, et al. Animal experimental investigation on the efficacy of antibiotic therapy with linezolid, vancomycin, cotrimoxazole, and rifampin in treatment of periprosthetic knee joint infections by MRSA. Bone Joint Res. 2022; 11(3):143-151. [39] RESENDE VAC, NETO AC, NUNES C, et al. Higher age, female gender, osteoarthritis and blood transfusion protect against periprosthetic joint infection in total hip or knee arthroplasties: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(1):8-43. [40] LORA-TAMAYO J, MURILLO O, IRIBARREN JA, et al. REIPI Group for the Study of Prosthetic Infection. A large multicenter study of methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infections managed with implant retention. Clin Infect Dis. 2013; 56(2):182-194. [41] TRIANTAFYLLOPOULOS GK, POUL_TSIDES LA, ZHANG W, et al. Periprosthetic knee infections treated with irrigation and debridement: outcomes and preoperative predictive factors. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(4):649-657. [42] ALY R, MAIBACH HE, MANDEL A. Bacterial flora in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 1976;95(6):603-606. [43] DRANCOURT M, ARGENSON JN, TISSOT DUPONT H, et al. Psoriasis is a risk factor for hip-prosthesis infection. Eur J Epidemiol. 1997;13(2): 205-207. [44] LOFIN I, LEVINE B, BADLANI N, et al. Psoriatic arthritis and arthroplasty: a review of the literature. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2008;66(1):41-48. [45] BEYER CA, HANSSEN AD, LEWALLEN DG, et al. Primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with psoriasis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73(2): 258-259. [46] KUNUTSOR SK, WHITEHOUSE MR, BLOM AW, et al. Patient-Related Risk Factors for Periprosthetic Joint Infection after Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150866. |
| [1] | Li Yuanfeng, Ye Pufeng, Pan Guifeng, Mai Zhenjiang. Dose-effect relationship between dexmedetomidine and ropivacaine during pericapsular nerve group block in elderly patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4514-4520. |
| [2] | Zheng Zewei, Ye Kaijing, Zhang Kuo, Zhao Qinghua, Chen Xiutian, Jiang Yulai, Yi Yanzi, Zhang Qingwen. Hypoproteinemia after total hip arthroplasty: risk factors and nomogram prediction model establishment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(15): 3147-3152. |
| [3] | Min Meipeng, Wu Jin, URBA RAFI, Zhang Wenjie, Gao Jia, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Fan Lei. Role and significance of artificial intelligence preoperative planning in total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1372-1377. |
| [4] | Lu Lin, Chen Haicheng, Chen Chujie, Zhou Chi, Chen Zhenqiu. Factor analysis of pelvic tilt outcome after primary unilateral total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5817-5822. |
| [5] | Ge Jin, Huang Dong, Yan Jinlian, Xu Zhengquan, Wang Yehua. Relationship between low back pain and spinal-pelvic sagittal parameter changes in patients with hip-spine syndrome after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5823-5827. |
| [6] | Li Zhengyuan, Hao Lin, Chen Shenghong, Peng Kai, Wang Jun, Yin Zongsheng. Topical application of vancomycin in prevention of early incision infection in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(33): 5346-5350. |
| [7] | Li Zhipeng, Huan Dawei, Yuan Zhaofeng, Ding Kai, Qiu Yue, Xia Tianwei, Shen Jirong. Mid- and long-term state after total hip arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in the elderly: evaluation using propensity score matching method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3839-3844. |
| [8] | Zhang Liying, Ding Yuwu, Yu Xiaoming, Liao Wangsheng, Wang Jiening. Body weight support Tai Chi footwork improves balance function after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2840-2845. |
| [9] | Pan Yunchun, Wei Hongjun, Ren Guoqing, Zhang Qiliang. Comparison of gait and hip ambulation ability after total hip arthroplasty through different approaches [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2846-2851. |
| [10] | Zhang Kai, Guo Zhuotao, Ma Qiaoqiao, Zha Guochun, Guo Kaijin. Accuracy and influencing factor of artificial intelligence planning system in patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1863-1868. |
| [11] | Ke Yuqi, Chen Changjian, Wu Hao, Zheng Lianjie. Comparison of 12-month follow-up results of primary total hip arthroplasty between modified direct anterior approach and direct anterior approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [12] | Yan Ruizhong, Li Jiahui, Lin Shuzhong, Wu Xiaogang, Guo Zhijian, Liu Wenqi, Liu Qiang. Effect of pelvic tilt on the stress at the acetabular side in standing position after total hip arthroplasty: finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5795-5800. |
| [13] | Guo Zhuotao, Zhang Kai, Zha Guochun, Guo Kaijin. A matched controlled trial of lumbar fusion effect on mid-term outcomes after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5801-5805. |
| [14] | Li Qizhe, Kong Yao, Fan Jiannan, Wu Yeting, Yang Hua, Xiao Yinlong, Sun Hong. Measurement and clinical significance of acetabular parameters in the Guizhou population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(36): 5856-5863. |
| [15] | You Aijia, Li Wenjie, Zhou Junli, Li Chun. Systematic evaluation of six dressings on wound safety following total hip and knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 486-492. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||