Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (23): 4947-4955.doi: 10.12307/2025.096
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of aerobic exercise on mobilization and function of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with myocardial infarction
Zhao Peng1, Wang Congcong2, Wang Chenyu3
- 1Zhengzhou Shuqing Medical College, Zhengzhou 450064, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Health Service, Logistics University of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, Tianjin 300309, China; 3Zhengzhou University of Aeronautics, Zhengzhou 450015, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-06Accepted:2024-05-21Online:2025-08-18Published:2024-09-29 -
Contact:Wang Chenyu, MD, Professor, Zhengzhou University of Aeronautics, Zhengzhou 450015, Henan Province, China -
About author:Zhao Peng, Master, Lecturer, Zhengzhou Shuqing Medical College, Zhengzhou 450064, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province, No. 232102321125 (to WCY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Peng, Wang Congcong, Wang Chenyu. Effect of aerobic exercise on mobilization and function of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4947-4955.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
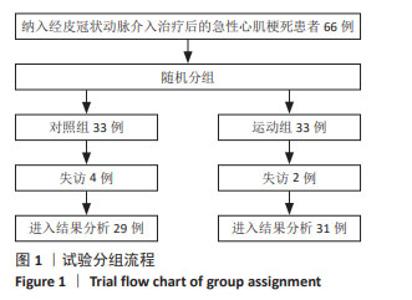
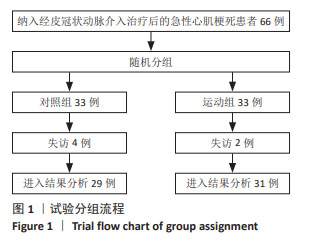
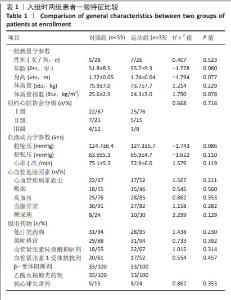
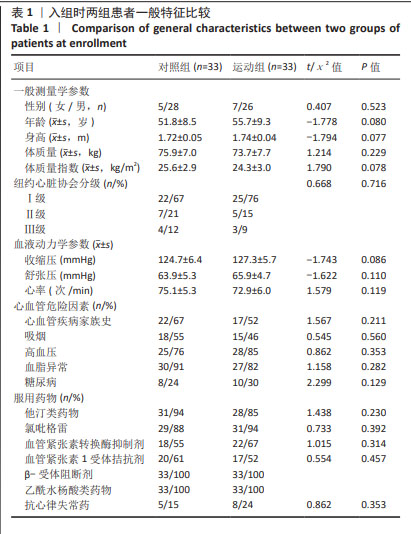
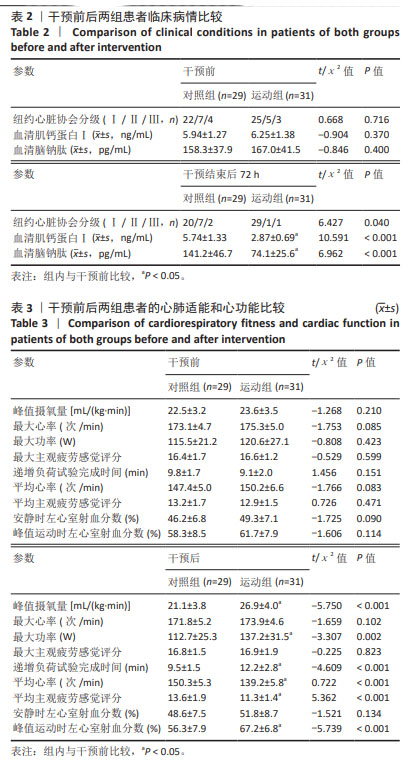
2.4 患者运动依从性和安全性评价 共60例患者完成全部试验,失访6例,其中对照组4例(12%)、运动组2例(6%),失访原因包括日程冲突(n=1)、自行车座椅问题(n=1)、既往医疗问题(n=2)、个人原因(n=1)以及无故失联(n=1),均与康复训练无关。12周运动干预过程中,运动组训练计划次数为1 395次,完成率为93.7%。 运动组患者运动中及运动后仅出现肌肉酸痛、气喘、咳嗽等症状,所有不良症状均较轻微,可继续进行运动或在停止运动经休息后完全缓解,无严重不良反应事件或心血管相关事件发生。 2.5 干预前后两组患者临床病情比较 见表2。干预前,两组患者的纽约心脏协会分级、血清肌钙蛋白Ⅰ和血清脑钠肽水平比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);干预结束后72 h,运动组患者纽约心脏协会分级、血清肌钙蛋白Ⅰ和血清脑钠肽水平低于干预前(P < 0.05),对照组各指标检测值与干预前比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),运动组患者纽约心脏协会分级、血清肌钙蛋白Ⅰ和血清脑钠肽水平均低于对照组(P < 0.05)。 2.6 干预前后两组患者心肺适能和心功能比较 见表3。 干预前,两组患者的心肺适能和心功能各指标比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。干预后结束后72 h,运动组患者的峰值摄氧量、最大功率、递增负荷试验完成时间、峰值运动时左心室射血分数均高于干预前(P < 0.05),平均心率和平均主观疲劳感觉评分均低于干预前(P < 0.05),对照组各指标检测值与干预前比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),运动组患者的峰值摄氧量、最大功率、递增负荷试验完成时间、峰值运动时左心室射血分数均高于对照组(P < 0.05),平均心率和平均主观疲劳感觉评分均低于对照组(P < 0.05)。 "
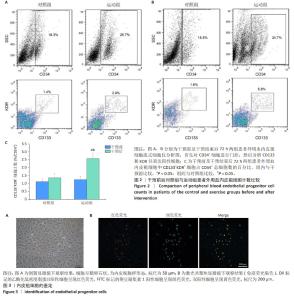
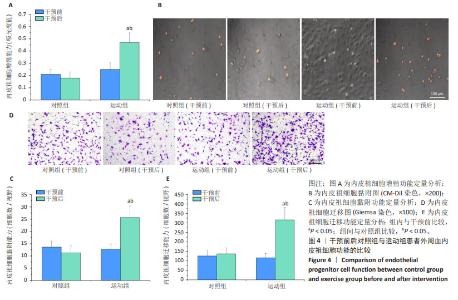
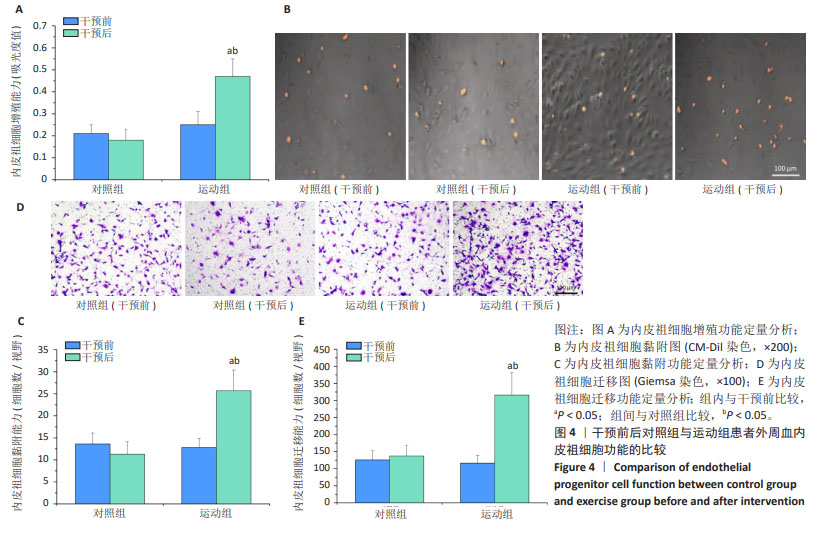
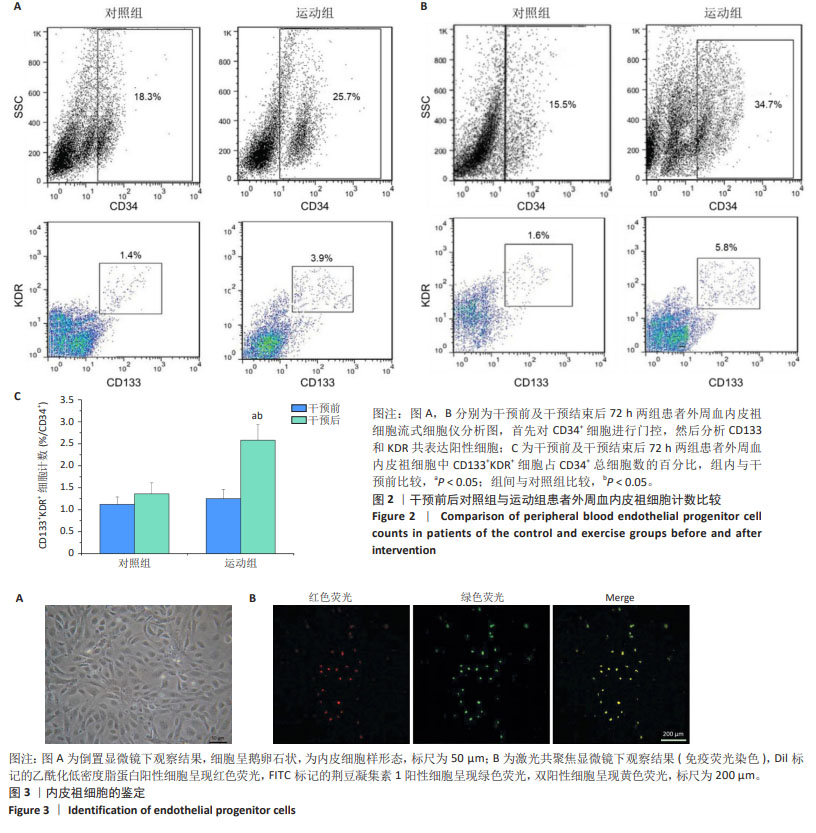
2.7 干预前后两组患者外周血内皮祖细胞计数比较 干预前,两组患者外周血内皮祖细胞计数比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。干预结束后72 h,运动组患者外周血内皮祖细胞计数高于干预前(P < 0.05),对照组患者外周血内皮祖细胞计数与干预前比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),运动组患者外周血内皮祖细胞计数高于对照组(P < 0.05),见图2。 2.8 内皮祖细胞鉴定 倒置显微镜观察显示,培养第7天的细胞呈鹅卵石状,为内皮细胞样形态,见图3A。用Dil标记的乙酰化低密度脂蛋白与FITC标记的荆豆凝集素1对细胞染色后,通过激光共聚焦显微镜鉴定发现,Dil标记的乙酰化低密度脂蛋白阳性细胞呈现红色荧光,FITC标记的荆豆凝集素1阳性细胞呈现绿色荧光,双阳性细胞呈现黄色荧光,即正在分化的内皮祖细胞,见图3B。"
| [1] DAUERMAN HL, IBANEZ B. The edge of time in acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(15):1871-1874. [2] FRANTZ S, HUNDERTMARK MJ, SCHULZ-MENGER J, et al. Left ventricular remodelling post-myocardial infarction: pathophysiology, imaging, and novel therapies. Eur Heart J. 2022;43(27):2549-2561. [3] CUDDY TF, RAMOS JS, DALLECK LC. Reduced Exertion High-Intensity Interval Training is More Effective at Improving Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Cardiometabolic Health than Traditional Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(3):e483. [4] OIKONOMOU E, SIASOS G, TSIGKOU V, et al. Coronary artery disease and endothelial dysfunction: novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(7):1052-1080. [5] HUGHES CW, COHEN A. The repair of injured blood vessels. Surg Clin North Am. 1958;38(6):1529-1543. [6] DIPIETRO LA. Angiogenesis and wound repair: when enough is enough. J Leukoc Biol. 2016;100(5):979-984. [7] YANG JX, PAN YY, WANG XX, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells in age-related vascular remodeling. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(5):786-795. [8] AICHER A, ZEIHER AM, DIMMELER S. Mobilizing endothelial progenitor cells. Hypertension. 2005;45(3):321-325. [9] CHEN L, TANG S, ZHANG FF, et al. Cyp4a/20-HETE regulates ischemia-induced neovascularization via its actions on endothelial progenitor and preexisting endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019;316(6):H1468-H1479. [10] SHINTANI S, MUROHARA T, IKEDA H, et al. Mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2001;103(23):2776-2779. [11] VASA M, FICHTLSCHERER S, AICHER A, et al. Number and migratory activity of circulating endothelial progenitor cells inversely correlate with risk factors for coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 2001;89(1):E1-7. [12] CUADRADO-GODIA E, REGUEIRO A, NÚÑEZ J, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells predict cardiovascular events after atherothrombotic stroke and acute myocardial infarction. A PROCELL substudy. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0132415. [13] DIBBEN GO, FAULKNER J, OLDRIDGE N, et al. Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation for coronary heart disease: a meta-analysis. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(6):452-469. [14] ZHANG YM, LU Y, TANG Y, et al. The effects of different initiation time of exercise training on left ventricular remodeling and cardiopulmonary rehabilitation in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Disabil Rehabil. 2016;38(3):268-276. [15] MORAES-SILVA IC, RODRIGUES B, COELHO-JUNIOR HJ, et al. Myocardial infarction and exercise training: evidence from basic science. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;999:139-153. [16] VAN CRAENENBROECK EM, BRUYNDONCKX L, VAN BERCKELAER C, et al. The effect of acute exercise on endothelial progenitor cells is attenuated in chronic heart failure. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111(9): 2375-2379. [17] 中华医学会心血管病学分会预防学组,中国康复医学会心血管病专业委员会.冠心病患者运动治疗中国专家共识[J].中华心血管病杂志,2015,43(7):575-588. [18] 中华医学会心血管病学分会介入心脏病学组,中国医师协会心血管内科医师分会血栓防治专业委员会,中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会.中国经皮冠状动脉介入治疗指南(2016)[J].中华心血管病杂志,2016,44(5):382-400. [19] 郅季炘,高永成,马刚.改良高强度间歇运动在冠状动脉疾病患者心脏康复中的应用研究[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2023,45(1): 42-47. [20] 王玉燕,铁虎光,金丽山,等.冠心病病人外周血单个核细胞aim2表达水平及其与炎性因子的相关性[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2022,20(14):2585-2588. [21] 吴鸿涛,马艳,毕晓娟,等.人外周血与脐血内皮祖细胞生物学特性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(45):7911-7917. [22] 陈菊明,左琦,宋艳玲,等.氯沙坦对慢性心力衰竭患者外周血内皮祖细胞的影响研究[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2017,25(8):41-44. [23] 刘一炫,赵雅红,谢富兰,等.冠心病患者与健康人群外周血中内皮祖细胞微小rna表达[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(21):4792-4794. [24] GIANNUZZI P, TEMPORELLI PL, CORRÀ U, et al. Attenuation of unfavorable remodeling by exercise training in postinfarction patients with left ventricular dysfunction: results of the exercise in left ventricular dysfunction (elvd) trial. Circulation. 1997;96(6):1790-1797. [25] ADDOH O, EDWARDS MK, LOPRINZI PD. Considerations for the inclusion of cardiorespiratory fitness as a vital sign in the clinical setting. Prev Med. 2017;96:85-86. [26] KHAN H, KUNUTSOR SK, RAURAMAA R, et al. Long-Term Change in Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Relation to Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure (from the Kuopio Ischemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study). Am J Cardiol. 2018;121(8):956-960. [27] DAVIDSON T, VAINSHELBOIM B, KOKKINOS P, et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness versus physical activity as predictors of all-cause mortality in men. Am Heart J. 2018;196:156-162. [28] ROSS R, BLAIR SN, ARENA R, et al. Importance of assessing cardiorespiratory fitness in clinical practice: A case for fitness as a clinical vital sign: A scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation. 2016;134(24):e653-699. [29] LAUFS U, WERNER N, LINK A, et al. Physical training increases endothelial progenitor cells, inhibits neointima formation, and enhances angiogenesis. Circulation. 2004;109(2):220-226. [30] VASA M, FICHTLSCHERER S, ADLER K, et al. Increase in circulating endothelial progenitor cells by statin therapy in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2001;103(24):2885-2890. [31] KALKA C, TEHRANI H, LAUDENBERG B, et al. VEGF gene transfer mobilizes endothelial progenitor cells in patients with inoperable coronary disease. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000;70(3):829-834. [32] HARB IA, ASHOUR H, SABRY D, et al. Nicorandil prevents the nephrotoxic effect of cyclosporine-A in albino rats through modulation of hif-1α/vegf/eNOS signaling. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021;99(4): 411-417. [33] ZUO K, ZHI K, ZHANG X, et al. A dysregulated microrna-26a/epha2 axis impairs endothelial progenitor cell function via the p38 mapk/VEGF pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(2):477-488. [34] JING J, JIANG H, ZHANG L. Endothelial progenitor cells promote neural stem cell proliferation in hypoxic conditions through VEGF via the pi3k/AKT pathway. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2022;42(5):479-485. [35] ZHOU J, LI H, XUN L, et al. Hyperlipidemia attenuates the mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells induced by acute myocardial ischemia via vegf/enos/no/mmp-9 pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(19): 7877-7889. [36] STANISIC J, KORICANAC G, KOSTIC M, et al. Low-intensity exercise in the prevention of cardiac insulin resistance-related inflammation and disturbances in NOS and mmp-9 regulation in fructose-fed ovariectomized rats. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2019;44(11):1219-1229. [37] SUN X, HUANG LY, PAN HX, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and exercise restore motor function following spinal cord injury by activating pi3k/akt/mTOR pathway. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(5): 1067-1075. [38] WANG Y, CHEN L, ZHANG M, et al. Exercise-induced endothelial mecp2 lactylation suppresses atherosclerosis via the ereg/MAPK signalling pathway. Atherosclerosis. 2023;375:45-58. [39] SCHUH A, KROH A, KONSCHALLA S, et al. Myocardial regeneration by transplantation of modified endothelial progenitor cells expressing SDF-1 in a rat model. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16(10):2311-2320. [40] YAMAGUCHI J, KUSANO KF, MASUO O, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 effects on ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cell recruitment for ischemic neovascularization. Circulation. 2003;107(9):1322-1328. [41] ASKARI AT, UNZEK S, POPOVIC ZB, et al. Effect of stromal-cell-derived factor 1 on stem-cell homing and tissue regeneration in ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Lancet. 2003;362(9385):697-703. [42] URBICH C, DIMMELER S. Endothelial progenitor cells: characterization and role in vascular biology. Circ Res. 2004;95(4):343-353. [43] CHANG E, PATERNO J, DUSCHER D, et al. Exercise induces stromal cell-derived factor-1α-mediated release of endothelial progenitor cells with increased vasculogenic function. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;135(2): e340-e350. [44] PALMEFORS H, DUTTAROY S, RUNDQVIST B, et al. The effect of physical activity or exercise on key biomarkers in atherosclerosis--a systematic review. Atherosclerosis. 2014;235(1):150-161. |
| [1] | Li Zikai, Zhang Chengcheng, Xiong Jiaying, Yang Xirui, Yang Jing, Shi Haishan. Potential effects of ornidazole on intracanal vascularization in endodontic regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [3] | Gao Yang, Qin Hewei, Liu Dandan. ACSL4 mediates ferroptosis and its potential role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| [4] | Zhao Xiaoxuan, Liu Shuaiyi, Li Qi, Xing Zheng, Li Qingwen, Chu Xiaolei. Different exercise modalities promote functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1248-1256. |
| [5] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [6] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| [7] | Ji Long, Chen Ziyang, , Jin Pan, Kong Xiangkui, Pu Rui, . Lipophagy, exercise intervention and prevention and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7611-7619. |
| [8] | Fang Yuan, Qian Zhiyong, He Yuanhada, Wang Haiyan, Sha Lirong, Li Xiaohe, Liu Jing, He Yachao, Zhang Kai, Temribagen. Mechanism of Mongolian medicine Echinops sphaerocephalus L. in proliferation and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7519-7528. |
| [9] | Zhao Jianwei, Li Xunsheng, Lyu Jinpeng, Zhou Jue, Jiang Yidi, Yue Zhigang, Sun Hongmei. Deer antler stem cell exosome composite hydrogel promotes the repair of burned skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7344-7352. |
| [10] | Pan Chun, Fan Zhencheng, Hong Runyang, Shi Yujie, Chen Hao. Effect and mechanism of polystyrene microplastics on prostate in male mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7353-7361. |
| [11] | Wu Qingyun, Su Qiang. Antioxidant nanomedicine-mediated targeted therapy for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7431-7438. |
| [12] | Tian Yushi, Fu Qiang, Li Ji . Bioinformatics identification and validation of mitochondrial genes related to acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6697-6707. |
| [13] | Wang Jiaqian, , Jiang Changjun, Peng Yi, Ma Mi, Li Junhan. Study on the role of aerobic exercise in regulating the CNPY2-mediated AKT/GSK3β pathway for improving non-alcoholic fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6441-6448. |
| [14] | Zeng Yu, Xie Chengwei, Hong Yuanqi, Su Shenghui, Dong Xieping. In vitro angiogenesis and osteogenesis properties of copper-doped mesoporous bioactive glass [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(28): 5941-5949. |
| [15] | Li Zeming, Zhang Yuntao, Wang Maolin, Hou Yudong. Role and mechanism of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha regulating bone homeostasis in oral and maxillofacial diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5680-5687. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||