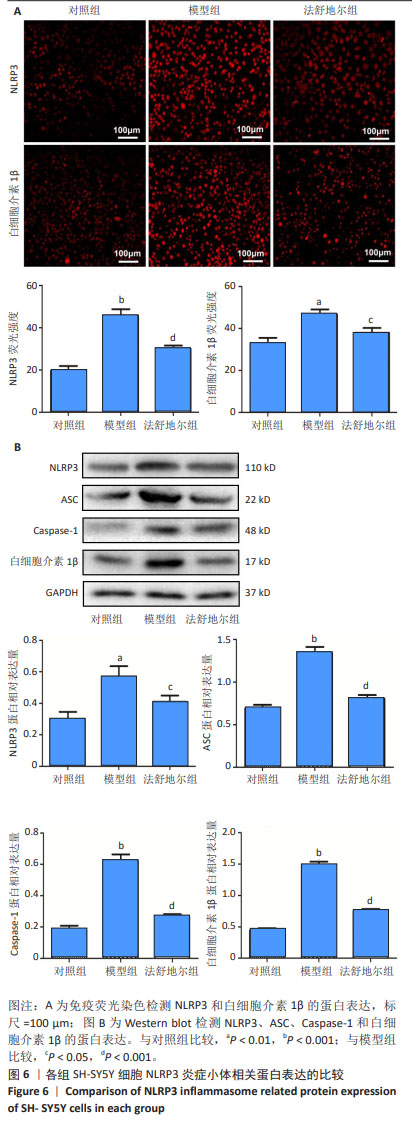
[1] KNOPMAN DS, AMIEVA H, PETERSEN RC, et al. Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1): 33.
[2] ZHOU B, FUKUSHIMA M. Clinical utility of the pathogenesis-related proteins in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22): 8661.
[3] JORFI M, MAASER-HECKER A, TANZI RE. The neuroimmune axis of Alzheimer’s disease. Genome Med. 2023;15(1):6.
[4] WANG C, ZONG S, CUI X, et al. The effects of microglia-associated neuroinflammation on Alzheimer’s disease. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1117172.
[5] HAN YH, LIU XD, JIN MH, et al. Role of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuronal pyroptosis and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Inflamm Res. 2023;72(9):1839-1859.
[6] YANG Z, LIU J, WEI S, et al. A novel strategy for bioactive natural products targeting NLRP3 inflammasome in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Pharmacol. 2023;13:1077222.
[7] XIA X, HE X, ZHAO T, et al. Inhibiting mtDNA-STING-NLRP3/IL-1β axis-mediated neutrophil infiltration protects neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Prolif. 2024;57(1):e13529.
[8] FANG EF, HOU Y, PALIKARAS K, et al. Mitophagy inhibits amyloid-β and tau pathology and reverses cognitive deficits in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22(3):401-412.
[9] QIU J, CHEN Y, ZHUO J, et al. Urolithin A promotes mitophagy and suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial cells and MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Neuropharmacology. 2022;207:108963.
[10] GUO MF, ZHANG HY, LI YH, et al. Fasudil inhibits the activation of microglia and astrocytes of transgenic Alzheimer’s disease mice via the downregulation of TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB pathway. J Neuroimmunol. 2020;346:577284.
[11] 魏文悦,王玉银,郭敏芳,等.法舒地尔抑制APP/PS1小鼠神经元凋亡的线粒体动力学作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(2): 232-238.
[12] GAO Y, YAN Y, FANG Q, et al. The Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil attenuates Aβ1-42-induced apoptosis via the ASK1/JNK signal pathway in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons. Metab Brain Dis. 2019;34(6): 1787-1801.
[13] BLENNOW K, DE LEON MJ, ZETTERBERG H. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 2006;368(9533):387-403.
[14] TAKAHASHI RH, NAGAO T, GOURAS GK. Plaque formation and the intraneuronal accumulation of β-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Pathol Int. 2017;67(4):185-193.
[15] BARAGE SH, SONAWANE KD. Amyloid cascade hypothesis: pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropeptides. 2015;52:1-18.
[16] SENGUPTA U, NILSON AN, KAYED R. The role of amyloid-beta oligomers in toxicity, propagation, and immunotherapy. EBioMedicine. 2016;6: 42-49.
[17] WANG Q, SONG LJ, DING ZB, et al. Advantages of Rho-associated kinases and their inhibitor fasudil for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(12):2623-2631.
[18] SELLERS KJ, ELLIOOTT C, JACKSON J, et al. Amyloid β synaptotoxicity is Wnt-PCP dependent and blocked by fasudil. Alzheimers Dement. 2018;14(3):306-317.
[19] XICOY H, WIERRINGA B, MARTENS GJ. The SH-SY5Y cell line in Parkinson’s disease research: a systematic review. Mol Neurodegener. 2017;12(1):10.
[20] KUMARI S, DHAPOLA R, REDDY DH. Apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease: insight into the signaling pathways and therapeutic avenues. Apoptosis. 2023;28(7-8):943-957.
[21] VARDIYAN R, EZATI D, ANVARI M, et al. Effect of L-carnitine on the expression of the apoptotic genes Bcl-2 and Bax. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2020;47(3):155-160.
[22] AKHTER R, SALEEM S, SAHA A, et al. The pro-apoptotic protein Bmf co-operates with Bim and Puma in neuron death induced by β-amyloid or NGF deprivation. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018;88:249-257.
[23] VAN ZELLER M, DIAS D, SEBASTIAO AM, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome: a starring role in amyloid-β- and tau-driven pathological events in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;83(3):939-961.
[24] ELLIOTT EI, SUTTERWALA FS. Initiation and perpetuation of NLRP3 in inflammation activation and assembly. Immunol Rev. 2015;265(1): 35-52.
[25] JIANG Q, GENG X, WARREN J, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) mediates NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent-pyroptotic and apoptotic cell death following ischemic stroke. Neuroscience. 2020;448:126-139.
[26] ZHOU QM, ZHAO HY, MA C, et al. Pocahemiketone A, a sesquiterpenoid possessing a spirocyclic skeleton with a hemiketal endoperoxide unit, alleviates Aβ25-35-induced pyroptosis and oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y Cells. Org Lett. 2022;24(26):4734-4738.
[27] BORRAJO A, RODRIGUEZ-PEREZ AI, VILLAR-CHEDA B, et al. Inhibition of the microglial response is essential for the neuroprotective effects of Rho-kinase inhibitors on MPTP-induced dopaminergic cell death. Neuropharmacology. 2014;85:1-8.
[28] FAN W, CHEN S, WU X, et al. Resveratrol relieves gouty arthritis by promoting mitophagy to inhibit activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:3523-3536.
[29] LI J, YANG D, LI Z, et al. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;84:101817.
[30] 林祎嘉,程丽珍,苗雅.线粒体自噬异常在阿尔茨海默病中的作用及机制研究综述[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2022,42(3): 387-392.
[31] KUMAR AV, MILLS J, LAPIERRE LR. Selective autophagy receptor p62/SQSTM1, a pivotal player in stress and aging. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:793328.
[32] YANG K, YAN Y, YU A, et al. Mitophagy in neurodegenerative disease pathogenesis. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(5):998-1005.
[33] KERR JS, ADRIAANSE BA, GREIG NH, et al. Mitophagy and Alzheimer’s disease: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Trends Neurosci. 2017; 40(3):151-166.
[34] REDDY PH, YIN X, MANCZAK M, et al. Mutant APP and amyloid beta-induced defective autophagy, mitophagy, mitochondrial structural and functional changes and synaptic damage in hippocampal neurons from Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27(14):2502-2516.
[35] QUADIR H, HAKOBYAN K, GADDAM M, et al. Role of Rho-associated protein kinase inhibition as therapeutic strategy for Parkinson’s disease: dopaminergic survival and enhanced mitophagy. Cureus. 2021;13(8): e16973. |